The factors for selecting a crucible include the crucible’s material composition, size, shape, capacity, and service life.
Selecting the right crucible is a critical decision in a variety of industrial processes, especially in metallurgy and glassmaking where high temperatures are required to melt materials.
A crucible is a container that can withstand extreme temperatures, and its selection can significantly affect the efficiency and safety of the process.
This article will explore the basic factors that must be considered when selecting a crucible to ensure optimal performance and safety.
Material compatibility for selecting a crucible
The material composition of a crucible is a key factor when selecting a crucible. Different materials have different heat resistance and chemical properties, which can affect the melting process. For example, ceramic crucibles are suitable for non-ferrous metals because of their resistance to thermal shock, while graphite crucibles are favored for their resistance to high temperatures and ability to withstand chemical reactions with the molten metal. The material selection must match the specific requirements of the melting process to prevent contamination or structural failure.

Thermal Shock Resistance
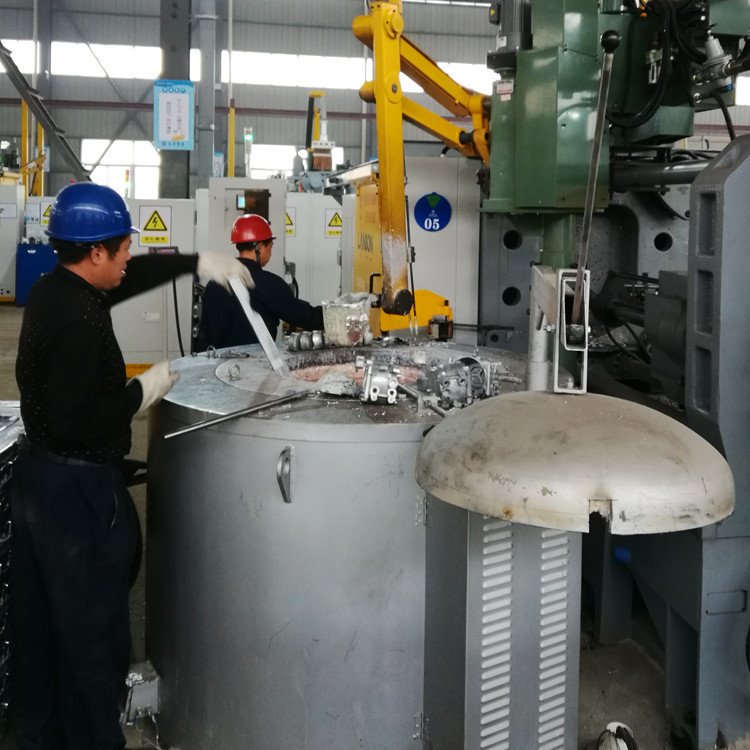

Thermal shock resistance is another key factor to consider when selecting a crucible. This property refers to the ability of the crucible to withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking or breaking. Crucibles used in processes with frequent heating and cooling cycles must have high thermal shock resistance to maintain their integrity.
The material and construction of the crucible play an important role in determining its thermal shock resistance.
This making it a key factor in the selection process.
Size and capacity for selecting a crucible
The size and shape of the crucible are also important factors when selecting a crucible. The crucible must be large enough to accommodate the material being melted and provide enough space for the molten material to flow and mix. The shape of a crucible can affect even heat distribution and ease of material handling.
For example, a wide-mouthed crucible may be easier to load and unload.
While a deeper crucible may be better suited for certain types of melting processes.
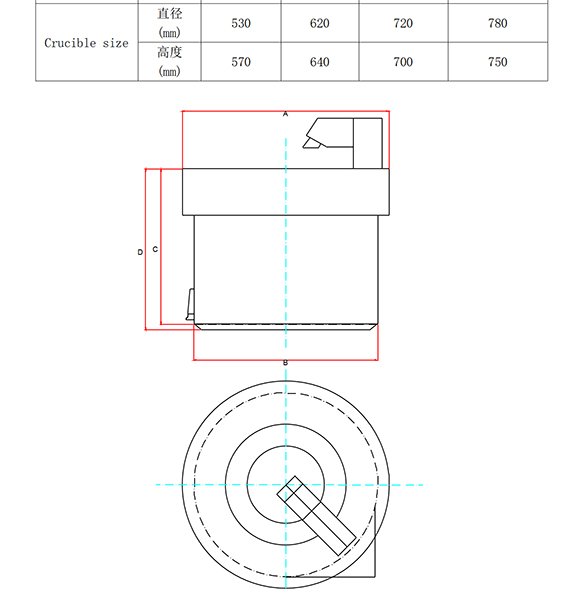
Crucible Capacity and Efficiency
The capacity of a crucible is directly related to the efficiency of the melting process. A crucible that is too small may require multiple melting cycles, increasing the time and energy required for the process. On the other hand, a crucible that is too large may waste energy and resources. Therefore, selecting a crucible with the appropriate capacity is critical to optimizing the efficiency of the melting process.
Crucible Life and Durability
The life and durability of a crucible are key factors when selecting a crucible. Crucibles that wear quickly or fail during use can result in costly downtime and safety hazards. The material, construction, and maintenance of a crucible all contribute to its life. Selecting a crucible with long life and high durability can reduce maintenance costs and increase the safety of the melting process.
Design for a crucible
The crucible design should be easy to operate, such as easy pouring of molten metal, and compatible with the pouring system of the die casting machine. Some crucibles may have specially designed pouring spouts to reduce metal splashing and oxidation.
Die casting machine compatibility

The crucible should be compatible with the design and operation of the die casting machine to ensure that the metal can be transferred from the crucible to the mold smoothly and efficiently. The interface design of the crucible should match the gating system of the die casting machine.
By the end
Selecting the right crucible is crucial to the success of the die casting industry.In summary, selecting a crucible is a multifaceted decision that requires careful consideration of multiple factors, including material composition, thermal shock resistance, size and shape, capacity, and life.
By understanding these factors and their impact on the melting process, informed decisions can be made when selecting crucibles to ensure the efficiency, safety, and success of high temperature industrial processes.
Haichen is dedicated to providing high-quality die-casting machines and components.
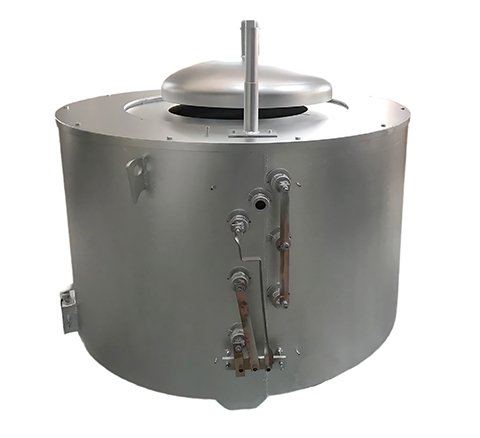

Which including a comprehensive range of crucibles to meet diverse production requirements.
Haichen die-casting machines are designed to accommodate various sizes and types of crucibles, offering flexibility and ease of use to fulfil different production needs.
Our experienced team will assist you in selecting crucibles suited to your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and reliability.
By choosing Haichen, you gain access to industry-leading equipment and professional technical support to enhance your die-casting operations.



