Types of ladles for die casting machine:
- Automated Ladles
- Manual Ladles
- Gearbox Rotation Ladles
- Bottom Pour Ladles
- Lip Pour Ladles
- Teapot Spout Ladles
- Closed Ladles
- Cast Iron
- Steel/Stainless Steel
- Ceramic/Refractory Materials
- Large Tonnage Ladles
- Transfer Ladles
- Specialty Ladles
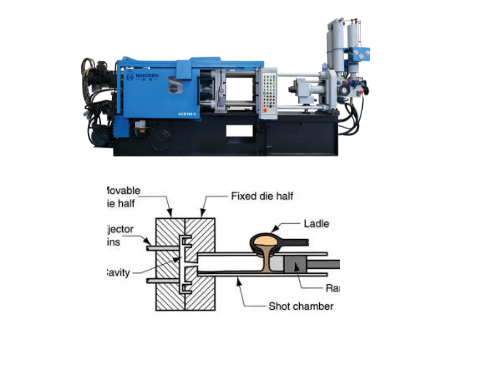
Ladles devices used to convey molten metal from the holding furnace and pour it into the press chamber of the die casting machine.
The automated system of die casting machine pouring bags achieves precise metal injection control through various technical means to ensure casting quality and production efficiency.
In die casting production units, automatic pouring systems usually work in tandem with automatic spraying systems, extraction robots, cooling control units, etc., to form a complete automated production process to achieve efficient and precise production.
The automation system of die casting machine pouring bags achieves precise control over the metal injection process through the integration of advanced control technology, sensors, robots, and automation equipment, thereby improving casting quality and production efficiency.
Types of ladles
- Automated Ladles: Therefore, these devices enable high-volume automated operations, thereby ensuring consistent and precise pouring. Examples include articulating ladlers and electric/automated ladles.
- Manual Ladles: For smaller-scale operations, manual ladles like hand ladles, bull ladles, and bucket ladles are used.
- Gearbox Rotation Ladles: These can be manual or motorized and are designed to minimize physical exertion for tilting.
- Bottom Pour Ladles: These ladles pour molten metal from the bottom, which helps to prevent surface dross and contaminants from entering the mold, leading to a cleaner casting.
- Lip Pour Ladles: In this classic design, molten metal is poured over the rim of the ladle.
Teapot Spout Ladles: This design is a variation of the lip pour that uses a spout to provide more control over the pour.
Closed Ladles: These are ideal for casting reactive or contamination-sensitive metals, as they keep the molten metal enclosed during transport and pouring. - Cast Iron: A common and cost-effective material for ladle cups, often heat-treated for durability.
- Steel/Stainless Steel: Used for a variety of casting applications, particularly in automated systems.
- Ceramic/Refractory Materials: Used for their superior insulation, chemical inertness, and non-wetting properties, especially for high-purity or high-temperature alloys.
- Large Tonnage Ladles: Designed for very large die casting machines and high volumes of molten metal.
- Transfer Ladles: Used to transport molten metal from a holding furnace to the die casting machine.
- Specialty Ladles: Designed for specific applications, such as ductile iron treatment or long-distance transfer.

How the ladles for die casting machine works
The working principle of the ladles of the die casting machine mainly involves the precise feeding of molten metal from the furnace into the injection chamber of the die casting machine for the subsequent die casting process.
The workflow typically consists of the following steps:
- Soup
- Moving and pouring the soup
- Drip & Reset
- Automatic control
Soup
The ladle inserts a soup spoon into the furnace through a robotic arm or linkage mechanism to suck up the molten metal.
The tilt angle of the spoon can be adjusted to control the amount of soup to be taken.
Moving and pouring the soup
After filling the molten metal, the soup spoon will move over the barrel of the die casting machine
And pour the soup at an angle, pouring the molten metal into the injection chamber of the die casting machine.
This process can be achieved by a straight or cross-beam feeder.
Where the cross-beam feeder uses a rocker mechanism to drive the spoon to swing closer to or away from the die-casting machine.
Drip & Reset
When the soup is poured, the spoon returns to a level state and then moves back to the standby position.
In some designs, a drip function is also available to eliminate oxides on the surface of the molten aluminum, further improving product quality.

Automatic control
Modern soup feeders are usually controlled by PLC and frequency converter to ensure the accuracy and stability of the action.
There are two modes of operation: manual and automatic, and you can choose the corresponding mode to operate according to your needs.
In short, the soup feeder of the die-casting machine realizes the automatic conversion from the furnace to the die-casting machine by accurately controlling the actions of taking the soup, moving, pouring the soup and resetting, and improves the production efficiency and product quality.

Furnace and ladles
Furnace is a device that melts metal during the die casting process.
Different types of furnaces are selected according to the type of metal and process requirements.
For example, an IF induction furnace is mentioned for melting metals, while an electric stove is mentioned as an alternative to a traditional stove.
It is noted that furnace is used to melt metal and keep it in its liquid state, providing molten metal for die casting.
The furnace needs to keep the metal above the melting point while reducing heat loss through insulation.
In cold chamber die casting, the furnace is independent of the die casting machine, the metal is transferred to the die casting machine and, and the hot chamber die casting integrates the furnace with the die casting machine.

The composition of the ladles for die casting machine
- Soup spoon
- Main bracket
- Moving mechanism
- Rocker Arm Mechanism
- Soup feeding mechanism
- Load-bearing beams
- Drive mechanism
- Control system
- Safety and auxiliary devices
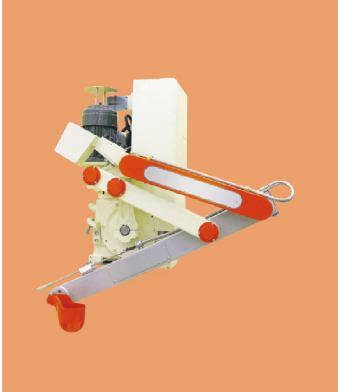
Soup spoon
This is the core component of the soup feeder, which is used to scoop and pour out molten metal.
In some designs, the spoon is rotated by a linkage mechanism or servo motor drive to achieve the action of scooping and pouring soup.
Ladles Ceramic soup
lads have a high melting point (1860°C±10°C) and a low coefficient of thermal expansion.
Which makes them excellent in high temperature environments.
which can effectively block oxide scale from entering the aluminum soup, thereby improving the defect rate of die castings.
In addition, ceramic spoons are maintenance-free, do not require overcoating, and have a long service life, generally 6-12 months.
However, ceramic soup spoons have a lower heat transfer efficiency and are 1/15 of those of cast iron.
Cast iron soup ladles , although they conduct heat well, require regular maintenance to prevent rust.
The service life of cast iron soup spoons is usually more than 3 months, and it is cost-effective.
However, cast iron spoons are not as resistant to thermal shock and corrosion as ceramic spoons in high-temperature environments.
Therefore, ceramic soup spoons perform best in high-temperature environments, with good thermal insulation effect and long life.
Cast iron soup spoons have good thermal conductivity, but care needs maintenance.
Main bracket
As the basic structure of the entire soup feeder, the main bracket supports other components such as the moving mechanism, the rocker arm mechanism and the soup feeding mechanism.
Moving mechanism
Arranged on the main support, it is responsible for driving the movement of the soup spoon in the horizontal and vertical directions.
Servo motor or linkage mechanism to ensure precise positioning and operation.
Rocker Arm Mechanism
Located on the moving mechanism, it is used to drive the swing of the soup spoon.
So that the soup spoon can be close to or away from the die casting machine.
The rocker mechanism is usually with a connecting rod to improve the stability and accuracy of the operation.
Soup feeding mechanism
It is connected with the rocker arm mechanism and is used to drive the rotation of the soup spoon to complete the action of scooping and pouring soup.
The mechanism is likewise with connecting rods to ensure smooth and accurate operation.
Load-bearing beams
In some designs, load-bearing beams serve as the basis for moving parts and support the entire operation of the feeder.
It usually straddles the die casting machine and the furnace and moves by means of a sliding connection.
Drive mechanism
Including servo motor, reducer, gear, etc., which is used to provide power and control the movement of each component.
These drive mechanisms can be linear mobile drives or complex linkage drive systems.
Control system
PLC (programmable logic controller) is usually used for control to achieve automatic operation and precise control.
The system may also include a touchscreen interface for operators to set parameters and monitor equipment status.
Safety and auxiliary devices
Such as thermal insulation pads, safety guardrails, etc., to protect operators and equipment from hot melts.
Together, these components enable the feeder to transfer and pour the metal liquid efficiently and safely during the die casting process.
Different designs may be adapted to specific application needs, such as a five-link construction to improve soup dispensing accuracy or servo control to improve operational stability.
The drip function of the soup feeder
- Function design
- Drip function
Function design
Realize the drip function design of the die-casting machine soup feeder, through the cooperation of the mechanical arm.
And the material spoon to ensure that the metal liquid is accurately and stably transferred from the furnace to the inlet of the press chamber of the die casting machine.
Specifically, the soup feeder comprises a soup feeding bracket that is provided with a transverse moving track on the bracket.
Drip function
The sliding base can slide along the track, because it is with a robotic arm.
The end of the mechanical arm with a material spoon.
And the metal liquid is scooped out of the furnace and transferred to the vacuum box for processing by the mechanical arm.
So that it becomes a semi-solid metal slurry, and then the semi-solid metal slurry is scooped up to the inlet of the press chamber of the die-casting machine by the mechanical arm.
Design Advantages
Temperature control
By converting high-temperature metal liquid into a relatively low-temperature semi-solid metal paste
It can extend the service life of die casting moulds, and improve the metallographic structure of the product , and reduce the sand and pores.
Thereby improving the mechanical properties of the product.
Automation and precision
The design of the robotic arm and spoon can achieve more accurate and stable transfer of metal liquids, avoiding errors and instability in traditional manual operations.
For example, traditional soup feeders use the position of the soup spoon to control the amount of soup to be fed.
which is prone to errors due to wear and tear of parts, while the modern die-casting process requires accurate dosing to achieve the desired effect.
Safety and efficiency
Automated equipment reduces the labor intensity of workers and the harshness of the working environment, and at the same time reduces the risk of safety accidents caused by improper operation.
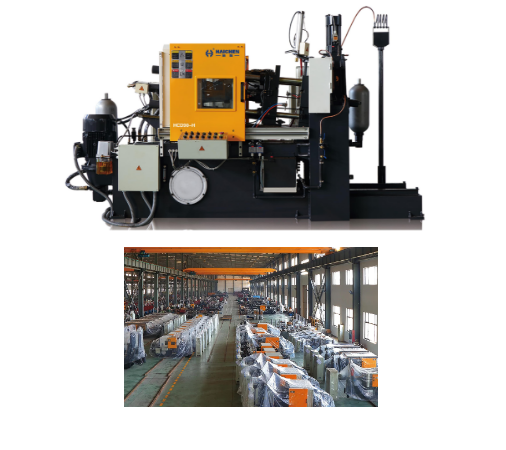

Haichen ladle case
Haichen equips the die-casting machine with high-level automatic auxiliary equipment such as automatic coating spraying device, automatic quantitative pouring device, automatic pick-up manipulator and automatic cooling water adjustment device for casting mould.
These equipment can realize the automatic control of the main processes such as uniform spraying of parting agent in the mould cavity, quantitative pouring, blank cooling and engraving, mould cooling,
And pick-up in production, ensuring the production of high-quality die castings for customers.




