Components of vacuum machine including:
- vacuum pumps
- vacuum tanks
- Vacuum Pipe
- vacuum valves
Which work together to achieve the desired vacuum level.
Thereby reducing porosity and defects in castings, and improving the mechanical properties and surface quality of castings.
Vacuum die casting is a method for manufacturing high volumes of identical precision parts, usually with complex geometries.
Also,vacuum die casting is similar to traditional die casting; however, it employs a vacuum system to evacuate air and gases from the die before injecting the molten metal.
This improves product quality overall and, in particular, reduces porosity. Lower porosity leads to more consistent mechanical behavior.
Vacuum machine
The vacuum machine in the vacuum die casting machine is a core auxiliary system whose main function is to quickly extract the air in the cavity of the die casting mold in a very short time, thereby significantly improving the quality of the casting.

What Is Vacuum Die Casting?
Vacuum die casting is a variation of traditional die casting. Like most such methods, molten metal is injected into a metal die cavity under pressure. However, the key difference with vacuum die casting is that a vacuum system is used to remove all the air and other gasses from the die cavity before the molten metal is injected. For this reason, vacuum die casting is also referred to as gas-free die casting.
Variations of this technique, such as high vacuum die casting (HVDC) or even ultra-high vacuum die casting (UHVDC), are named for the internal vacuum’s intensity. Higher vacuum means less gas in the die, and therefore better quality casting from a material porosity perspective.
Vacuum die casting works by evacuating most of the air and other gasses from the die prior to injection. This means that there is very little gas present in the die when the molten metal is injected. The resulting parts are far less likely to have the porosity defects that plague die-cast items. The vacuum in the mold also helps draw the molten metal into every channel. An evacuated die therefore provides numerous benefits over traditional die casting.
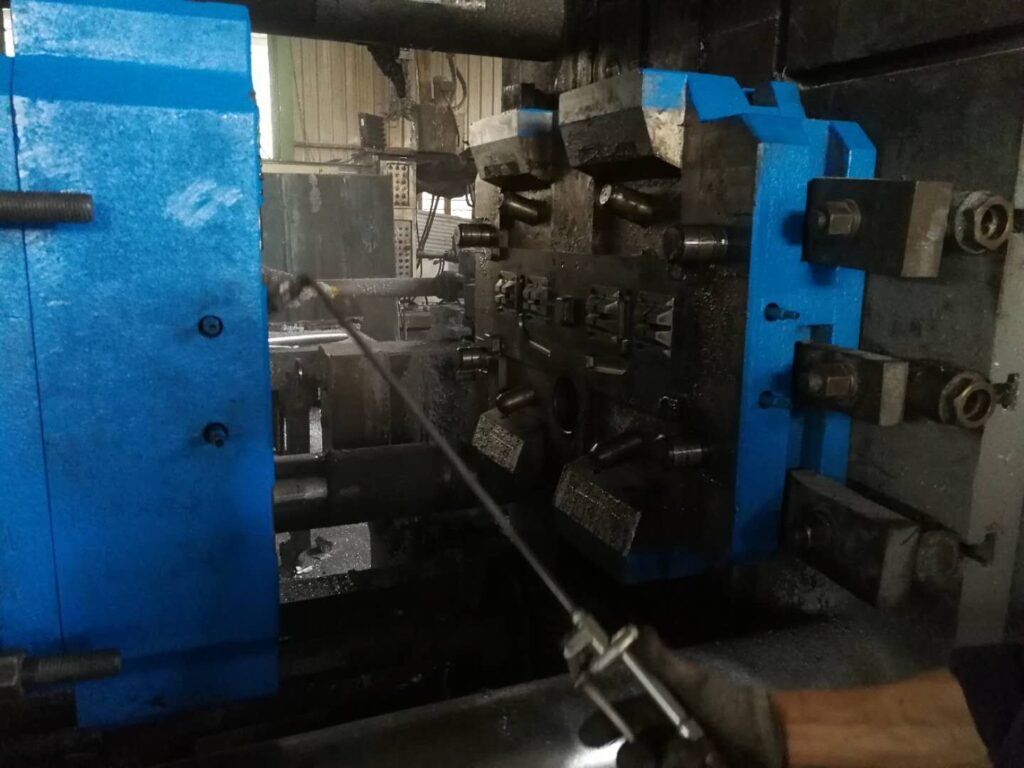

Vacuum pump
- Rotary vane pump
- Spool valve pump
- Roots pump
- Diffusion pumps
- Molecular Pump
- Lon pump
The vacuum pump is the core equipment of the vacuum system,which is used to pump out the air in the mold cavity to form a vacuum state.
Typically, an electric motor drives a vacuum pump that is capable of creating a high vacuum to ensure that the molten metal does not create porosity when filling the mold cavity at high pressure.
Rotary vane pump
Suitable for medium and low vacuum requirements, simple structure, easy maintenance, but the ultimate vacuum degree is relatively low.
Spool valve pump
It is also a type of mechanical vacuum pump and has similar performance characteristics.
Roots pump
Suitable for high vacuum or ultra-high vacuum die casting, high vacuum, strong exhaust capacity and stability.
Diffusion pumps
Suitable for high vacuum requirements, high pumping rates, but long start-up times and heating.
Molecular Pump
Suitable for ultra-high vacuum requirements, stable pumping rate, no need for heating, but higher price.
Lon pump
Suitable for very high vacuum and long-term stable operation, but with a small pumping rate.

Vacuum Tank
- Core role
- Pressure regulation function
- Accessibility
Vacuum tanks play a key role in die casting machines and related applications, primarily used to quickly evacuate air from mold cavities to stabilize system pressure and reduce pressure fluctuations.
Thereby improving casting quality.
Core role
In the die casting process, due to the extremely short metal injection time, the vacuum pump can not quickly remove the cavity air by directly relying on the vacuum pump.
As a buffer storage device, the vacuum tank is pumped to a high vacuum level by the vacuum pump in advance, and the valve is opened through the control system at the moment of die-casting,
So that the cavity gas is quickly sucked into the tank to achieve a rapid vacuum environment.
This helps reduce air bubbles and oxidation in the molten metal, improving casting density and surface quality.

Pressure regulation function
The vacuum tank can stabilize the pressure of the vacuum system, buffer the fluctuations caused by pump start-stop or operation, and ensure a smooth die-casting process.
If the volume is too small, the pressure stabilization effect is poor,If the volume is too large, the system will start up for a longer period of time, consuming more power and space.
Generally, the design needs to maintain a stable vacuum within half a minute to avoid problems such as sand collapse.
Accessibility
In some applications, vacuum tanks are also used to separate moisture or dust from gases, ensuring a clean vacuum environment.
And are integrated with control systems for functions such as blowing, measurement, and data logging.
Vacuum Pipe
- Quickly establish vacuum
- Ensure sealed transmission
- Optimize the exhaust path
In vacuum die casting systems, vacuum pipes are the key components that connect the vacuum source with the mold cavity.
And its core role is to efficiently extract the air in the cavity in a very short time to create the required vacuum environment.
Quickly establish vacuum
The vacuum pipeline works together with the vacuum valve and vacuum tank, opens at the moment of injection, and uses the pre-stored vacuum negative pressure to quickly suck the cavity gas to make up for the defect of insufficient direct pumping speed of the vacuum pump.
Ensure sealed transmission
Pipes need to be highly sealed to prevent air or water vapor from seeping in, which can disrupt the vacuum and cause porosity in the casting. Usually a special vacuum hose or metal tube is used, and a seal is equipped to ensure the airtightness of the connection.
Optimize the exhaust path
The pipe should be connected to the mold exhaust channel to ensure that the gas in the cavity is efficiently discharged.

Vacuum valve
- Pure mechanical vacuum valve
- Rotary Vacuum Valve
- Pre-Pumping Valve
- Three-dimensional quenching exhaust valve
- Location of the vacuum valve
Vacuum valves are mechanical and hydraulic, and the mechanical vacuum valve has a long pumping time, high vacuum degree and stable performance.
Pure mechanical vacuum valve
Suitable for cold chamber die-casting, using alloy molten kinetic energy to close, simple structure, low cost, but poor mobility and matching.
Rotary Vacuum Valve
Creates a closed exhaust channel when closing the mold, and is suitable for applications that require precise control of the exhaust time.
Pre-Pumping Valve
Drains the gas from the hose before the injection starts, especially effective for cold chamber die casting.
Three-dimensional quenching exhaust valve
By increasing the cross-sectional area of the exhaust channel, the pumping speed is increased.
Which is suitable for occasions that require high-efficiency exhaust.
Location of the vacuum valve
A vacuum valve is set at the point where the alloy melt is last filled in order to pump out as much gas as possible.
In the design process, consider the reasonable setting of exhaust channels and exhaust points on the mold to increase the flexibility of exhaust and the simplicity of exhaust channels.
Haichen‘s vacuum machine
Haichen can adjust the design of the vacuum machine according to different die casting needs, and can customize a variety of configurations according to customer needs.
Such as vacuum from 8 groups to 16 sets of molds, single injection barrel to double injection barrel evacuation and thimble chamber vacuuming to flexibly respond to die casting needs of different sizes and complexities.

Applications of Vacuum Die Casting
The biggest application of vacuum die casting is the mass production of automotive parts. Metal cast with the aid of a vacuum is far less porous than other cast metals, so welds and heat treatments are far less likely to cause blistering or other defects.
The automotive industry uses vacuum die casting more than any other in the world. This is for a number of reasons, such as the high volume of identical parts produced, the high strength-to-weight ratio it lends thin-walled components, and the parts’ dimensional accuracy.
The alloys used for automotive manufacture — especially aluminum and magnesium alloys — are well suited to vacuum die casting.
The aerospace industry also uses vacuum die casting products, as even complex shapes can be made this way. Plus, parts can be designed with thin walls that give them good strength-to-weight ratios.
Vacuum die casting machines are also used in many industries with large assembly lines that produce thousands of identical components.
These include the manufacture of electrical machinery, appliances, and power tools.



