Two heat treatment processes are quenching and tempering.These two common heat treatment processes are helpful to improve the mechanical properties of metal die casting products.
Different materials serve distinct purposes in engineering applications, necessitating performance treatments to meet essential requirements. Engineers employ various techniques during the manufacturing process to achieve the desired properties.
Quenching and tempering are two key processes in the heat treatment of metals and each serves a different purpose,let’s check them out.
Qnching
The purpose is to improve the mechanical properties of metal die casting products.
such as hardness and wear resistance, while improving the material properties or chemical properties of the die casting.
Quenching makes the material harder, but also increases brittleness and internal stresses.
Tempering
The function is to eliminate the internal stresses generated during the quenching process and to reduce brittleness.
This in turn improves the toughness and stability of the die cast metal product.
Tempering also promotes the transformation of unstable unbalanced organisation into stable balanced organisation.
Thus improving the mechanical properties of the material.
The significance of heat treatment of die casting products

Heat treatment of die casting products is of great importance and is an essential operation in the industry.
Mainly have the following five aspects of die casting industry significance:
- Improve mechanical properties
- Improve the microstructure
- Extend the life of the mould
- Eliminate stress and improve processing performance
- Improve corrosion and wear resistance
Improve mechanical properties
Through heat treatment, such as solid solution treatment and aging treatment, the strength and hardness of die casting aluminium alloy can be significantly improved.
For example, 2024 deformed aluminium alloy in 495 ℃ solid solution treatment, by 190 ℃ aging treatment for 8 hours, the alloy strength significantly improved.
A356 aluminium alloy after T6 heat treatment, its tensile strength and hardness has also been improved.
Improve the microstructure
Itcan optimise the microstructure of die casting materials, making them more uniform and dense.
For example, AZ91D magnesium alloy after 300 ℃ isothermal treatment, the β-phase occurs coarsening and granularity, so as to improve the tensile strength of the material.
Extend mould life

This can improve the hardness, toughness and dimensional stability of die casting moulds, thus extending the service life of moulds.
For example, 3Cr2W8V steel die casting mould after vacuum treatment, hardness and toughness will improve.
Eliminate stress and improve processing performance
Heat treatment can eliminate the residual stress produced in the die casting process, improve the cutting and machining performance of the material.
For example, H13 steel die casting mould after surface heating treatment, its mechanical properties and metallographic organisation will also optimize.
Improve corrosion resistance and wear resistance
Certain treatment process can also improve the corrosion resistance and wear resistance of die casting mould.

For example, magnesium alloy die casting mould after quenching graded cooling and ion nitriding treatment, its abrasion resistance and high temperature corrosion resistance significantly improved.
Heat treatment of die casting products can not only enhance the mechanical properties and microstructure of the material.
Can also extend the mould life and improve the processing performance, is an indispensable and important part of die casting production.
Heat treatment steps for die-cast products
Heat treatment steps for die casting products usually include solution, quenching, tempering stage and aging treatment.
We exhaustively introduce the role of each heat treatment step.
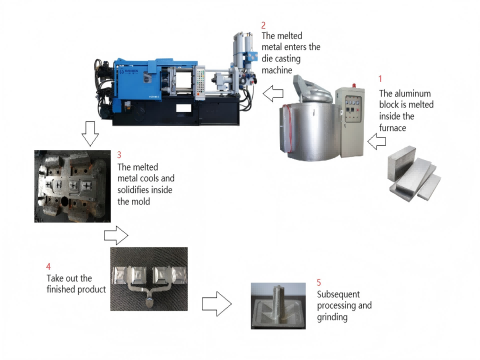
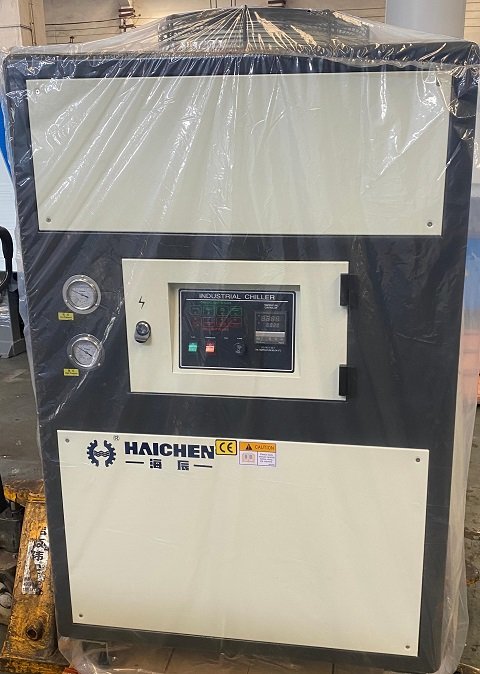
For the production of 100×100×20 mm aluminium road studs, we strongly recommend employing a 300-tonne horizontal cold-chamber die-casting machine. For instance, the Haichen HCD-C die-casting machine possesses sufficient clamping force (3000 kN), mould dimensions (900×900 mm), and adjustable injection parameters, making it an ideal choice for this application.
Should you wish to learn more about Haichen die-casting machines or bespoke solutions, please do not hesitate to enquire.
- Solid solution treatment
- Quenching
- Tempering
- Ageing treatment
Solid solution treatment

Die castings are heated to a certain temperature so that the solute elements in the alloy are fully solidified into the matrix.
For example, the solid solution treatment temperature of aluminium alloy die castings is usually between 495℃ and 540℃, and the holding time is about 2 hours.
Quenching
After solid solution treatment, the die casting is rapidly cooling to fix its microstructure.
In addition some aluminium alloy die castings will be quenched after completing the solid solution treatment.
Tempering
After quenching, the die casting is heated to a lower temperature and held for a period of time.
So as to eliminate internal stress and improve toughness.
For example, certain die casting moulds are quenched at 1070°C and then tempered at 650°C to 700°C.
Ageing treatment
By controlling the aging temperature and time to further improve the mechanical properties of die castings.
The treatment process used for high strength aluminium-silicon alloy gearbox intermediate plate is 495°C x 2 hours + 180°C x 3.5 hours.
These steps can be adjusted and optimised according to specific material and product requirements to achieve the best performance and service life.
Benefits of Heat Treatment of Die Casting Products
The advantages of heat treatment of die-cast products are extremely obvious, and it has increasingly become a necessary production step to enhance product quality and competitiveness.
We have an experience to share with you.

- Enhance mechanical properties
- Improve the microstructure
- Improvement of thermal conductivity
- Enhancement of dimensional stability
Enhance mechanical properties
Heat treatment can significantly improve the strength, ductility and toughness of die castings. Toughness is equal to the service life of the product, which is the part that customers value most.
For example, AZ91D magnesium alloy die casting after heat treatment, tensile strength (σb) from 232 MPa to 243 MPa, elongation (δ5) from 3.1% to 4.6%, impact toughness (Ak) from 5.1 J greatly increased to 19 J. Aluminium alloy die casting after optimization of heat treatment, yield strength of up to 360 MPa, tensile strength up to 430 MPa .
Improve the microstructure

Heat treatment can refine the grain, spherical eutectic silicon phase and reduce defects.
For example, solid solution treatment can make the silicon phase broken and spheroidised, dissolve intermetallic compounds, so as to optimise the organisational structure. Combined with hot isostatic pressing (HIP), it also reduces porosity and further improves densification.
Improvement of thermal conductivity

Through solution treatment and aging (e.g. T7 process), the concentration of matrix solutes can be reduced to promote eutectic spheroidisation, which significantly improves the thermal conductivity of aluminium alloy die castings. This is particularly important for heat dissipating components such as automotive motors, heaters and street light backplates.
Enhancement of dimensional stability
Heat treatment reduces internal residual stresses and reduces the risk of distortion. All metal parts are more or less subject to strength requirements.
Then the temperature of the dimensions is the most ideal working condition, right?



