The basic die casting process step has the main links from the preparation of metal raw materials to the injection until the post-processing of the die casting products.
Formal Die Casting Production Process The basic steps in die casting are: mould preparation and lubrication, mould closure and pressurisation, metal injection, cooling and curing, demoulding and removal, scrap handling, and surface treatment and post-treatment.
Together, these steps ensure that the castings are of high quality and precision, making them suitable for a variety of industrial applications.
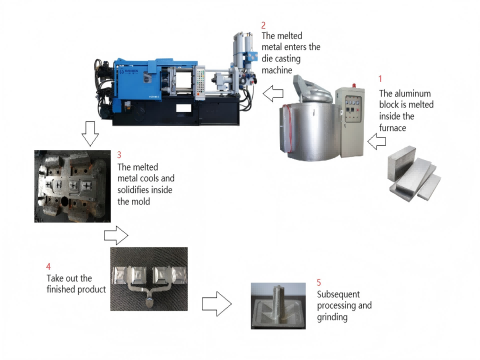
The die casting process is the technical means for the complete production of alloy workpieces of various strengths in applications.
Formal die-casting production process
The die casting process steps are as follows:
- Preparation of raw materials
- Mould preparation
- Melting the metal
- Injecting the metal
- Cooling and solidification
- Opening the mould and removing the casting
- Post-treatment
Preparation of raw materials
The raw materials used in the die casting process are mainly metal ingots, such as aluminium alloys and zinc alloys.
These metal ingots need to be melted and treated to ensure that their quality meets the requirements.
Mould preparation
The mould is a very important part of the die-casting process, which determines the shape and size of the final product.
The moulds are usually made of hardened tool steel and need to lubricat and maintained before each use.
Melting the metal
An ingot of metal put in a casting furnace and heating to a liquid state.
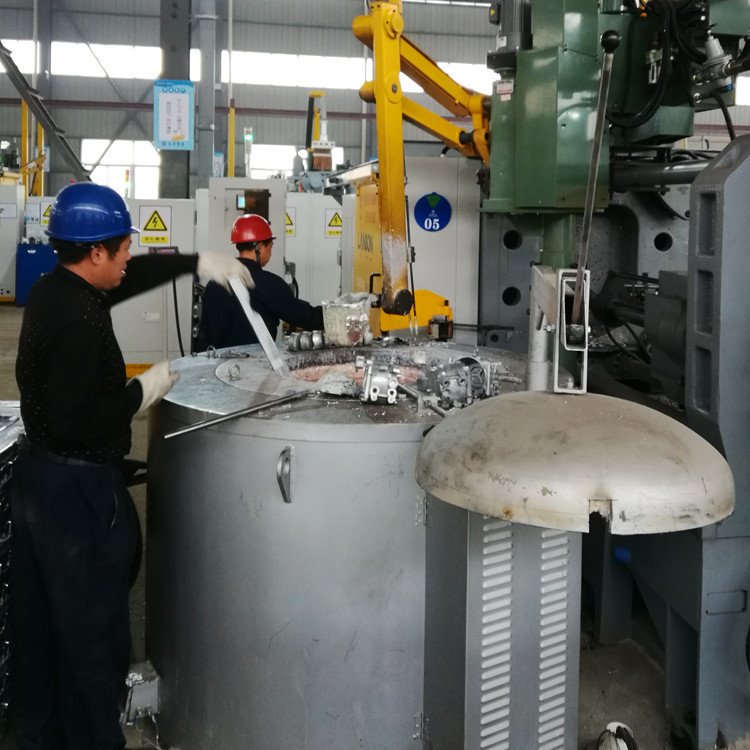

This step requires precise control of temperature and time to ensure that the metal is melted evenly and impurities are removed.
Injecting the metal
The molten metal is injecting into the mould cavity through a gate.
This process is usually carring out under high pressure to ensure that the metal can quickly fill the mould cavity and form the desired shape.
Cooling and solidification
The metal injected into the mould is rapidly cooled and solidified under high pressure.
This process requires a controlled cooling rate to avoid defects such as porosity and shrinkage.
Opening the mould and removing the casting
After the metal has completely solidified, the mould is opened and the casting is removed from the mould.
After removal, cleaning and subsequent processing, such as deburring and heat treatment.

Post-treatment
In order to improve the surface quality and performance of the castings, will need some post-treatment operations.
Such as machining, surface coating, etc.
These steps together constitute the basic flow of the die casting process step.
Each step needs to strictly control to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.
Design process of die casting machine mould
The design process of die casting moulds is a complex and multi-step process in die casting process step.
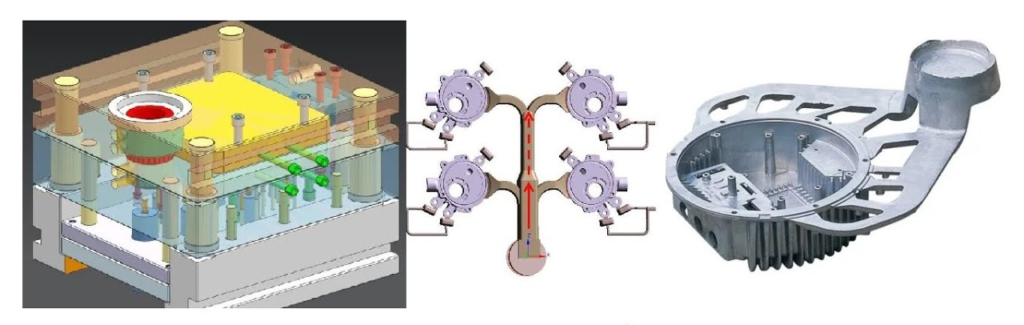
Involving multiple considerations and technical means, the following detailed design process:
- Determine the design objectives and requirements
- 3D modelling and preliminary design steps
- Steps of die casting mould structure design
- Cooling system design steps
- Process parameter optimisation step
- Die casting mould manufacturing and trial mould
- Die casting mould maintenance and improvement
Determine the design objectives and requirements
According to the product’s structural characteristics and process requirements, determine the design of the mould’s parting surface and casting system.
For example, when designing the die-casting mould of motorbike engine shell, the largest cross-section is selecting as the parting surface.
And use simulation software to simulate the filling process.
3D modelling and preliminary design steps

Use 3D modelling software (such as UG or AutoCAD) to carry out the preliminary design of the mould.
Including the casting system, cooling system and core extraction mechanism.
Numerical simulation using computer-aided engineering (CAE) software.
to optimise the layout and parameters of the pouring system to ensure smooth filling, good exhaust, and reduce the occurrence of defects.
Steps of die casting mould structure design
Design the specific structure of the mould, including the slider, ejector bar, cooling channels, etc.
For example, for castings with inclined holes or inclined cavities,need to design an angled core extraction mechanism.
For moulds that require rotary de-threading,so we can design a rotary automatic de-threading device with a rack and pinion mechanism.
Cooling system design steps
The design of the cooling system has an important influence on the filling time of the mould and the quality of the castings.
The traditional cooling channels are usually straight drilling holes.
And the conformal cooling technology introduced in recent years optimises the design of the cooling channels through finite element analysis and heat transfer analysis.
Improve surface finish and reduce the need for spray cooling.
Process parameter optimisation step
Numerical simulation software (e.g. Magmasoft, Anycasting, etc.) is using in the simulation of the filling and solidification process.
to determine the optimum process parameters such as pouring temperature, injection speed and mould temperature.
The simulation results are verified through experiments to further optimise the process parameters and improve casting quality and productivity.
Die casting mould manufacturing and trial mould

Moulds are usually usd hardened tool steel and need to precision machine to ensure high precision and durability.
In the die-casting mould manufacturing is finish the trial mould to test the effectiveness of the design, and according to the actual situation for adjustment and optimisation.
Die casting mould maintenance and improvement
Moulds need to maintaine and inspect regularly in the course of use in order to prolong the service life and maintain good production performance.
With the accumulation of production experience and technological progress, continuously improve the die-casting mould design, improve production efficiency and product quality.
The design of die-casting mould is a process of comprehensive consideration of product demand, process conditions and mould performance.
Through reasonable three-dimensional modelling, numerical simulation, process parameter optimization, as well as mould manufacturing and trial mould and other steps, can effectively improve the success rate of mould design and casting quality.
Different processes of metal melting in die casting machine

The different types of die casting metal melting processes fall into two main categories: hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting.
It’s the first step in die casting process step production.
Each of these two methods has its own characteristics in the process of melting the metal, injecting it into the mould and cooling and solidifying it.

Suitable for different materials and application scenarios.
- Hot chamber die casting
- Cold chamber die casting
- Vacuum die casting
- Semi-solid die casting
- Low-pressure die casting
Hot chamber die casting
Characteristics: In the hot chamber die casting process, the cylindrical chamber of the injection system is completely submerging in the molten metal bath.
This reduces the distance the metal has to travel in each cycle, thus shortening the cycle time.
Applicable materials: This method is typically using for low melting point metals such as zinc, copper, lead and magnesium alloys.
Advantages: High productivity, suitable for high volume production and capable of rapid prototyping.
Disadvantages: As the injection system is immersing in molten metal for a long time, it is easy to lead to corrosion of the equipment and affect the life of the mould.
Cold chamber die casting
Characteristics: cold chamber die casting process, liquid metal is poured into the injection sleeve before each injection, and pushed into the mould cavity by high pressure.
This method avoids direct contact between the metal injection system and the molten metal, thus reducing corrosion problems in the equipment.
Suitable materials: For high melting point metals such as aluminium and its alloys, magnesium alloys and copper alloys.
Advantages: Suitable for high melting point metals, reducing equipment corrosion and extending mould life.
Disadvantages: relatively low production efficiency, need higher initial investment for equipment and mould manufacturing.
In addition to this, there are some special variants of the die casting process:
Vacuum die casting
By applying a vacuum in the mould to reduce porosity and improve the denseness and mechanical properties of the casting.
Semi-solid die casting
The alloy is heating to a semi-solid state (about 50% solid) and then injecting into the mould.
This method can improve the density and mechanical properties of castings.
Low-pressure die casting
Suitable for rotary axis symmetry is not good aluminium parts, by reducing the pressure to reduce defects.
Taken together, hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting are two of the most common types of die casting processes, and they are selected according to the melting point and fluidity of the metal to meet the manufacturing needs of different materials and products.
Die casting machine automation pickup process steps

Automation pick up process is a key link in die casting production.
Its main purpose is to complete the casting of the work of taking out through automation equipment efficiently and accurately.
Thus improve production efficiency and product quality.
The following is the seven steps of die casting machine automation process:
- Mould state detection
- Casting removal
- Placement of castings
- Integrity check
- Subsequent processing
- Safety and efficiency guarantee
- Flexible production
Mould state detection
After the die-casting is completed, the first by the robot or robot on the state of the mould to detect, confirm that the mould has been opened in place, and ready to take out the castings.
Casting removal
Robots or robots according to the detection results, quickly take out the casting from the mould.
This process typically requires high-precision sensors and servo control systems to ensure accuracy and stability of movement.
The system adopts a six-axis robot with high flexibility and accuracy, which can quickly and accurately complete the pick-up operation.
Placement of castings

The removed castings are placed in a designated location, such as on a conveyor belt or other handling equipment.
This process ensures that the castings are not damaged and can proceed to subsequent processes.
Integrity check
After placing the casting, the system performs an integrity check to ensure that the casting is free of defects.
This can be achieved by visual inspection, photoelectric sensing, camera inspection and other techniques.
Subsequent processing
Qualified castings will go to the subsequent processing, such as removing the sprue set slag packages, cooling, trimming, grinding, and so on.
Unqualified castings are marked and returned to the furnace to be re-melted for the next pouring.
Safety and efficiency guarantee
The whole pick-up process is managed by PLC control system to ensure the synchronisation and safety of the action.
At the same time, the application of servo motor drive and high-precision encoder makes the movement of the robot more stable and reliable.
Flexible production
Modern automated pick-up system also has high flexibility, can adjust the working mode and parameters according to different moulds and production demand, so as to adapt to the production of many kinds of products.
Through the above steps, die casting machine automation pickup process to achieve high efficiency, precision and safety production goals, significantly improve the overall efficiency of die casting production and product quality.
By the end
Haichen, as a die-casting machine manufacturer, has been a pioneer in introducing high-pressure die-casting machines to overseas markets since 2005. Our die-casting machines support multiple operating languages, such as English, Spanish, Russian, and Chinese… making us the most reliable and trustworthy partner for your die-casting machinery needs. The three key performance requirements for our die-casting machines are: ease of operation, high cycle speed, and high casting quality for thin-walled and structural parts. This allows us to provide high-quality, precise control for your die-casting process step.



