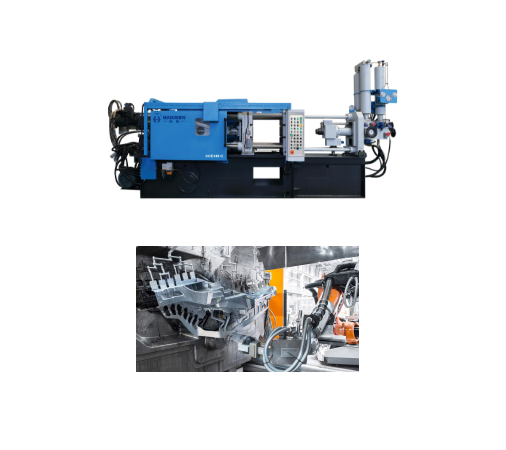
Zinc is a brittle, bluish-white, malleable and malleable metal, aluminum alloy is an alloy composed of aluminum and other alloying elements, such as copper, magnesium, zinc, silicon, etc.
Zinc metal is a versatile metal element with clear physical and chemical properties, with good electrical and thermal conductivity.

But low hardness and brittleness, but it can become malleable within a specific temperature range such as 100-150°C, so it is widely used in industry, construction, medical and other fields.
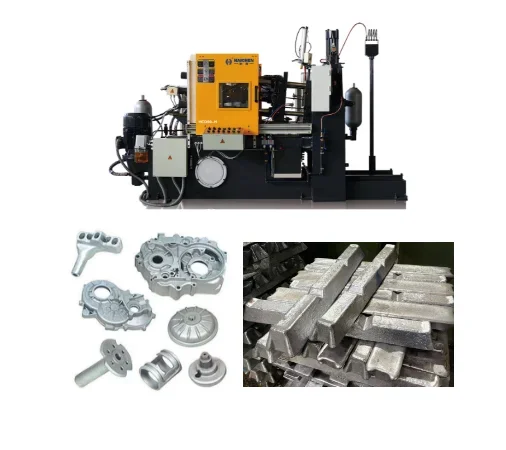
Aluminum alloys are high-performance materials formed by alloying aluminum with other elements, which are widely used in the industrial field, and their properties and applications are optimized through alloying element ratios and process control.
What is Aluminum alloy?
Aluminum is a metal that can be combined with other elements in specific proportions, altering its mechanical and physical properties, making it suitable for different applications.
This combination makes it an “alloy”. For example, mixing aluminum with magnesium results in a strong and lightweight alloy that is ideal for use in the aerospace and automotive industries.
It offers advantages such as low density, corrosion resistance, and good thermal conductivity.
Many different products, including metal casings, automobiles, and aircraft components, are made of aluminum alloys.
Aluminum alloy is suitable for cold chamber die casting machines, such as Haichen‘s HCD-C series die casting machine can die-cast a variety of aluminum alloy products.
For more information about this versatile metal, you can contact us.

What is Zinc?
Zinc refers to a metal alloy composed primarily of zinc, along with other metallic elements.
The common elements used in zinc alloy include aluminum, magnesium, copper, cadmium, lead, titanium, and other low-temperature zinc alloys.
Zinc alloys are prepared by melting the constituents and processing them through die-casting or other pressure-shaping methods to obtain the desired material form.

Features of zinc alloy
It has excellent casting performance, enabling the production of intricate and thin-walled precision parts with a smooth surface finish.
Enables surface treatment options such as electroplating, spraying, painting, polishing, and grinding.
During the melting and die-casting processes, it doesn’t absorb iron, resists pressure corrosion, and does not adhere to molds.
Possesses favorable mechanical properties and offers wear resistance at ambient temperatures.
Boasts a low melting point of 385℃, facilitating easy die casting.

What Are the Characteristics of Aluminum Alloy?
Aluminum alloys are characterized by several things.
Perhaps their most famous attribute is their low weight that makes them ideal for use in areas where reduced weight is important.
A natural oxide layer forms on the aluminum alloy’s surface, making it corrosion resistant and keeping it protected in all different environments.
In spite of their low density, they are strong and durable, factors that make them useful in projects where strength and weight have to be carefully balanced.
They can also be easily shaped and formed, making them a versatile material for those in manufacturing to work with.

The Difference Between Aluminium and Zinc Alloys
- Material
- Property
- Die casting process
- Weight
Material
Zinc alloy material has a significant specific gravity and exhibits excellent casting performance.
It boasts high density and strength, comparable to or even surpassing that of high-quality steel.
As a result, zinc alloy die casting parts typically weigh more than aluminum alloy die casting parts.
Property
The zinc alloy material exhibits a low melting point, favorable mechanical properties, and wear resistance. It is also suitable for surface treatment applications.
On the other hand, aluminum alloy demonstrates excellent electrical conductivity, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance.
Die casting process
The melting points of zinc and aluminum alloys vary. Zinc alloys have a lower melting point compared to aluminum alloys.
This discrepancy in melting points necessitates using special processing equipment and parameters when die casting.
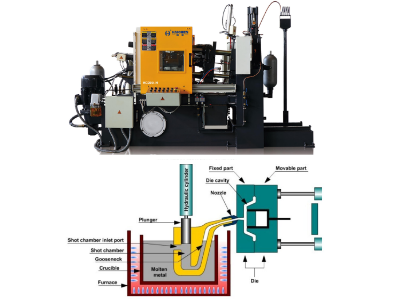
Zinc alloy die casting commonly employs a hot chamber die casting machine. The zinc alloy is melted within this machine, enabling faster cycle times.
In contrast, aluminum alloy die casting utilizes a cold chamber die casting machine. The aluminum alloy is melted outside the machine and then poured into the injection machine. This process takes longer compared to hot chamber die casting.
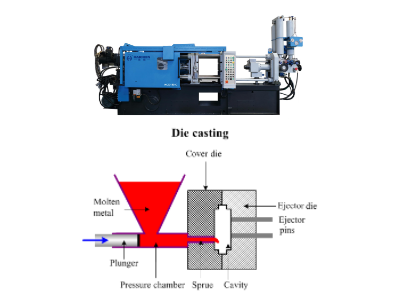
The utilization of different processing equipment and parameters for zinc alloy die casting and aluminum alloy die casting leads to divergent properties in the finished products.
Zinc alloy die castings tend to be more durable and corrosion-resistant than their aluminum counterparts. Conversely, aluminum alloy die castings are typically lighter and possess better thermal conductivity.
Weight
In terms of weight, zinc alloy is generally denser and heavier than aluminum.Pure zinc has a specific density of 5g/cm3, while aluminum has a lower density of 2.7g/cm3.
This higher density contributes to zinc alloys’ superior impact resistance compared to aluminum parts, making them a preferred material for manufacturing castings intended for structural applications.
When and Why You Should Choose Haichen Zinc Die Casting
- Parts with Thin Walls
- Harsh Environmental Conditions
- Lesser Residual Stress
- Die cast mold
- Faster Production
- Parts with Thin Walls
Parts with Thin Walls
Zinc die casting is well-suited for producing parts with thin walls due to its strength compared to other materials. The dense nature of zinc ensures structural integrity and stability, reducing material usage and die-casting costs.
Harsh Environmental Conditions
Zinc die casting excels in harsh environmental conditions, particularly those prone to corrosion. Its exceptional corrosion resistance forms a protective layer on the parts when exposed to such conditions.
Lesser Residual Stress
Die casting involves applying pressure to inject molten metal into the die. High-pressure die casting can lead to residual stress on parts, but zinc die casting, which utilizes low-pressure die casting, minimizes residual stress.
Die cast mold
Choosing zinc die casting is advantageous if you are working with delicate die casting molds. Zinc die casting molds can last approximately ten times longer than aluminum die-casting molds.
Haichen has a professional mold design and production team, if you need to contact us through this link.
Faster Production
Zinc alloys have a low melting point, enabling a hot chamber die-casting process with high-pressure injection. This results in a higher cycle rate compared to other materials.
Unlike in aluminum die casting where the operator melts the aluminum outside the machine before pouring it into the injection machine, in zinc die casting, the zinc is melted within the machine
By considering these factors, zinc die casting can be a preferred choice in various scenarios.

Why and When Choose Haichen Aluminum Die Casting
- Strength-to-weight ratio
- High operating temperatures
- Electrical conductivity
Strength-to-weight ratio
If you’re seeking lightweight and high tensile strength properties, it’s advisable to consider aluminum die casted parts. These parts are well-known for their ability to offer both characteristics.
Notably, the aerospace industry widely utilizes die cast parts made from aluminum due to their lightweight nature.
High operating temperatures
Due to their high melting point and ability to withstand high temperatures, aluminum die castings are the favored option for applications that involve elevated operating temperatures, such as in metallurgical processes.
This characteristic ensures that the structural and physical properties of the castings remain intact even when exposed to extreme heat.
Haichen provides exceptional zinc alloy die casting services to its customers, whether you need complex structures or compact zinc components, we can meet your needs.
Electrical conductivity
Due to their excellent electrical conductivity, aluminum die castings are the preferred choice for various electronic components in die casting.
This is particularly important in applications such as EMI shielding, where parts must be protected from electromagnetic signals.




