Casting defects refer to unwanted irregularities that occur during the casting process. These can affect the quality, functionality, and performance of the final product. According to different standards, casting defects can divide into various types: including surface defects, internal defects, chemical defects, and metallurgical defects
Identifying casting defects requires multi-technology collaboration: visual and penetrant testing for surface screening. At the same time with deep analysis of internal structure using radiation and ultrasound. Both two combine with the technology to improve efficiency.
There are many methods for identifying casting defects. It can mainly divided into traditional methods and modern technical methods.

Types and characteristics of casting defects
The identification of casting defects firstly require us a clear understanding of their physical characteristics and causes of formation. The following 4 points are the classification and characteristics of common defects:
- Crack type defects
- Hole type defects
- Casting defects
Crack type defects
Cold crack: It is in the form of a long strip, with an unoxidized surface and a metallic luster. The crack runs through the entire section and is often caused by unreasonable casting design (such as large differences in wall thickness) or poor sand mold yielding, resulting in stress concentration.
Hot cracking: The cross-section is oxidized and lacks luster, with tortuous cracks caused by improper pouring system leading to uneven cooling or hindered material shrinkage.
Hole type defects
- Pores: Smooth holes on the inner wall, distributed on the surface or inside. The causes include moisture in the furnace charge, excessive moisture content in the molding sand, failure to dry the casting tools, or excessive casting speed.
- Shrinkage: Appearing in patches, with uneven hole walls, caused by uneven metal solidification shrinkage or unreasonable riser design.
- Inclusions: The inner wall of the hole is rough, containing oxides or sand particles, due to impurities in melting or foreign objects mixed in during the pouring process.
Casting defects
- Cold insulation: Metal flow is not completely fused to form joints, visible cracks on the surface, often due to low pouring temperature or poor mold exhaust.
- Misruns: Incomplete casting caused by incomplete filling of the mold, often due to slow pouring speed or improper mold design.

Identify casting defects with traditional methods
Traditional methods typically rely on manual experience for defect recognition, such as through visual observation. Select appropriate detection methods based on the defect location (surface or interior) and type:
Visual inspection
Observe the casting surface with the naked eye or a magnifying glass to identify obvious defects such as cracks, pores, slag inclusions, etc. This method is simple and intuitive. But it easily affectes by the operator’s experience and cannot detect tiny defects.
Non-destructive testing technology
including ultrasonic testing, eddy current testing, radiographic testing, etc. These methods can detect internal defects such as pores, shrinkage cavities, inclusions, etc. without destroying the material. For example, ultrasonic testing widely uses in the detection of cracks in welded joints and semi-enclosed workpieces.

Identify casting defects with modern technical methods
With the advancement of technology, more and more advanced detection techniques are being applied here.
- Computer vision and deep learning
- X-ray detection
- Waveform transformation technology
Computer vision and deep learning
using deep learning models (such as convolutional neural networks CNN, Xception models, etc.) combined with image processing technology. It can automatically identify and classify casting defects automatically. For example, a system based on the Mask R-CNN architecture can simultaneously detect and segment defects, improving detection efficiency and accuracy.
X-ray detection
X-ray imaging technology is an important means of detecting casting defects. It can use to identify internal defects such as pores, slag inclusions, cracks, etc. In recent years, digital radiography (DR) technology has further improved detection sensitivity and speed.
Waveform transformation technology
Using 2D wavelet transform to process X-ray images can effectively detect typical defects in casting, such as pores, external inclusions, and shrinkage holes.
Machine learning and data mining: Through methods such as principal component analysis (PCA) and self-organizing maps (SOM), casting.
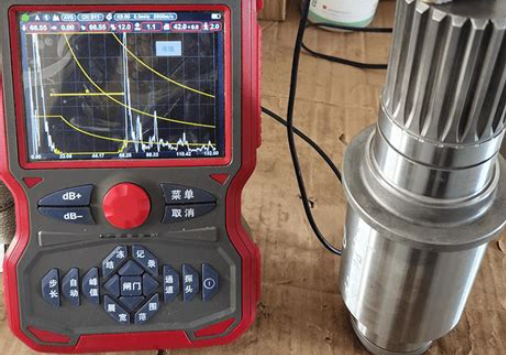
Above all, the identification methods of casting defects range from traditional manual visual inspection to modern automated detection technology. With the development of technology, especially the application of deep learning and computer vision, the detection of casting defects has become more efficient and accurate.



