To accurately estimate die casting part cost, it is essential to consider various cost components. These include material costs, tooling costs, die-casting machine costs, labor costs, overhead expenses, and any secondary operations required.
The process of die-casting parts can be analyzed through cost estimation formulas and examples.
Incorporating factors like material waste and scrap rates further enhances the accuracy of cost calculations.
And consider design factors like wall thickness and draft angles to optimize efficiency.
For costing, material and manufacturing costs are summed, with factors like the metal’s density and current market price influencing the raw material cost.
Die-cast parts can be optimized in their mold design through computer simulation to reduce defects.
This mainly relies on computer-aided design (CAD) and computer-aided engineering (CAE) technologies, especially the application of casting simulation software.

Material selection
Choose the right metal material according to the performance requirements of the die casting parts, such as aluminum alloy, zinc alloy, magnesium alloy, etc.
Consider factors such as the material’s flowability, shrinkage, strength, and corrosion resistance.

Mold Design
Molds are specialized products with high technological content. Instead, it should be high-quality at a better price, and the quality, precision, and life of the mold should be the first priority.
Design the gating system of the mold to ensure that the molten metal can fill the cavity evenly and smoothly.
Consider exhaust design to avoid porosity and other defects.
Determine the cooling system of the mold to control the solidification process and reduce thermal stress.
Haichen has designed overpressure casting molds, such as aluminum casting for road studs, aluminum casting for radiators, and aluminum pots, etc.
Size calculation
According to the drawing size of the die casting part, considering the shrinkage of the material, calculate the size of the mold cavity.
Consider machining allowances and tolerances to ensure the dimensional accuracy of the parts.

Production Cost Estimate
Calculate the cost of raw materials, including metal materials and auxiliary materials.
Estimate mold manufacturing cost and service life.
Consider energy consumption, labor costs, and equipment depreciation in the production process.
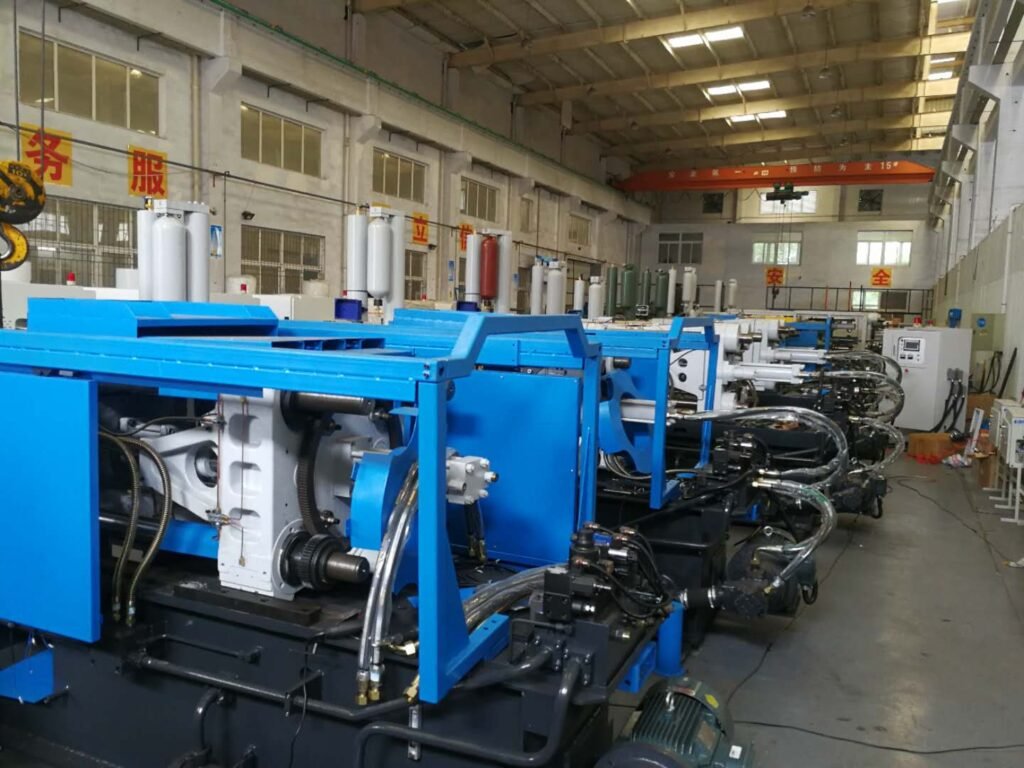

Quality Control
Develop inspection standards and methods to ensure that the quality of die castings meets the requirements.
Regularly check the condition of the mold and repair or replace the damaged parts in time.
Process parameter optimization
Determine the optimal process parameters such as pouring temperature, injection speed, pressure and holding time through experiments.
Perform hydrodynamic analysis using simulation software to optimize the design of gating and cooling systems.
Determine part geometry and material type
Identify the shape and size of the desired die casting, as well as the type of material used (e.g., aluminum, zinc, magnesium, or brass).
The choice of material affects the shrinkage and the dimensional accuracy of the final product.
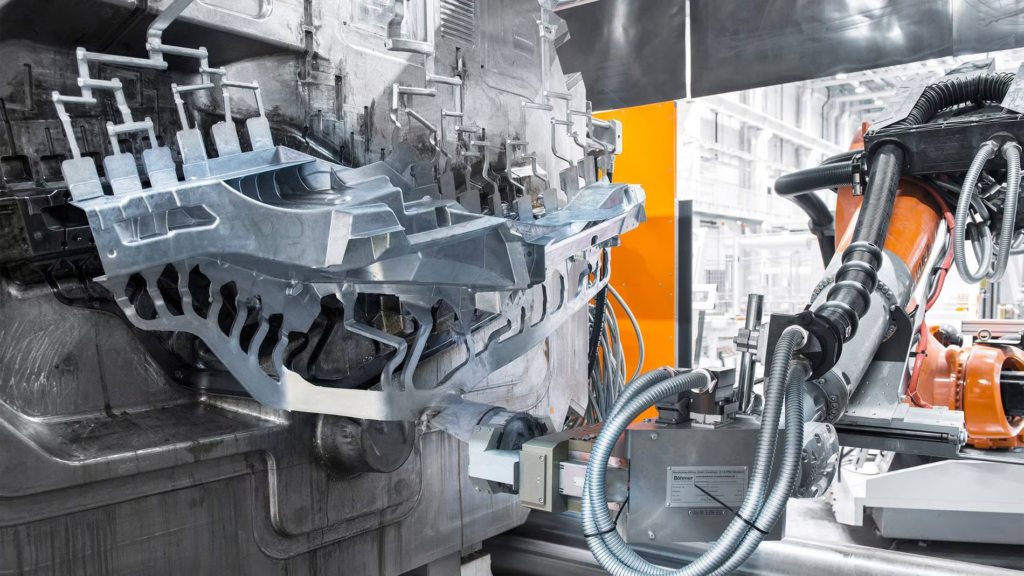

Calculate the pressure of the die casting machine
According to the size and shape of the die casting, choose the right die casting machine.
The pressure of the machine is usually expressed in tonnage, for example from 200 tons to 5000 tons.
Other than that,the pressure of the die casting machine must be greater than the force required for the mold separation during the die casting process.
Calculate metal velocity
Metal velocity is one of the important factors affecting the quality of die castings. The metal velocity can be calculated by the following formula:
V is the metal velocity (unit: m/s); Q is the metal flow rate (unit: m³/s); A is the gate area (unit: m²).
Calculate Gate Area
The formula for calculating gate area is: A=Q/V
Q is the metal flow rate (unit: m³/s); V is the metal velocity (unit: m/s); A is the gate area (unit: m²).
Determine the gate design
Select the appropriate gate design based on the geometry, wall thickness, and surface roughness requirements of the part. Common gate designs include sprues, runners, and sprue rings.
The design of the gate has a direct impact on product quality, such as preventing problems such as porosity, cratering, and flash.
Choosing Machine for Die Casting Part
Choosing the right die casting machine requires several factors to consider, including the complexity of the part, size, type of material, production batch.
And the technical parameters and performance of the die casting machine.
- Cold chamber die casting machine
- Hot chamber die-casting machine
- Determine the complexity and size of the part
Determine the complexity and size of the part
Simple-shaped parts are suitable for pressure casting or metal mold casting, while more complex molds are required for parts with complex shapes.
Cold chamber die casting machine
Suitable for casting high melting point alloys, such as aluminum, magnesium, copper, etc., with a closed injection chamber.
Which can achieve precise control of the flow and cooling of molten metal, suitable for the production of complex shapes of high-strength parts.

Hot chamber die-casting machine
Suitable for casting non-ferrous alloy parts with low melting point, such as zinc, aluminum, etc.
With an open injection chamber, simple operation, high degree of automation, suitable for mass production.

Haichen die casting solution
Understanding the die-casting cost is of vital importance for procurement and component design engineers, as they need to optimize to enhance the production efficiency of custom metal components.
Haichen can accurately calculate the cost of the die-casting production line by considering factors such as material selection, component complexity, production volume, and mold costs.

Haichen’s expertise in the complexity, cost analysis, and optimization methods of metal die-casting technology offers valuable insights to manufacturers seeking custom molds or services.
By understanding the factors influencing die-casting costs and implementing cost optimization strategies, manufacturers can achieve efficient and cost-effective production, thereby meeting the needs and expectations of customers.




