Die Casting vs Forging: Die casting uses high-pressure injection for precision, while forging applies compressive force for strength.
Die casting and forging are two widely used manufacturing processes for producing metal parts, each with its own unique advantages and applications. Understanding the differences between these processes can help manufacturers choose the most suitable method for their specific needs.
The Difference Between Die Casting vs Forging
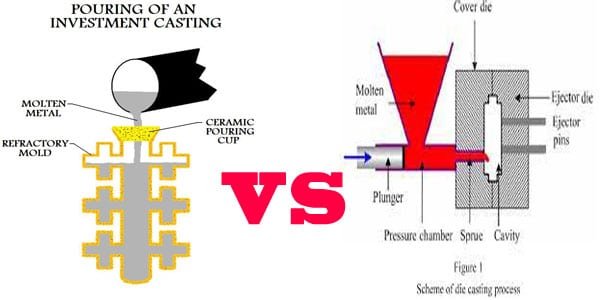
1. Process Overview
Die Casting:
Die casting is a process where molten metal is injected into a reusable mold (or die) under high pressure. The metal rapidly cools and solidifies within the mold, taking on the shape of the desired part. Die casting produces complex shapes with high precision and dimensional accuracy. It commonly creates thin-walled parts with intricate details, like automotive components, consumer electronics, and aerospace parts.
Forging:
Forging involves shaping metal by applying compressive forces using a hammer or press. Heat the metal to a plastic state and then deform it into the desired shape. Forging produces strong, durable parts with high structural integrity and is commonly used for large, heavy components like engine blocks, gears, and structural parts.
2. Material Considerations
Die Casting:
Die casting is typically used with non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, and copper alloys. These metals have lower melting points, making them suitable for injection into molds. The choice of material depends on the specific requirements of the part, such as strength, weight, and corrosion resistance.
Forging:
Forging commonly uses ferrous metals such as steel and iron, as well as some non-ferrous metals like aluminum and titanium. The choice of material depends on the desired mechanical properties and the application of the final part. Forging can produce parts with higher strength and toughness compared to die casting.

3. Precision and Complexity
Die Casting:
Die casting excels in producing parts with high precision and complex geometries. The use of high-pressure injection allows for the creation of intricate designs and thin walls, which are difficult to achieve with forging. Die casting is ideal for applications requiring detailed features and tight tolerances.
Forging:
While forging can produce parts with high strength and durability, it is generally less suitable for complex shapes and thin walls. Forging is more effective for producing large, solid components with uniform mechanical properties. The process is ideal for applications where strength and structural integrity are paramount.
4. Production Volume and Cost
Die Casting:
Die casting is highly efficient for high-volume production runs. The use of reusable molds allows for rapid production of identical parts, reducing per-unit costs. The initial tooling costs are high, but the process’s efficiency and consistency offset these costs.
Forging:
Forging is often more cost-effective for lower production volumes. The tooling costs are generally lower, and the process is more flexible in terms of part size and shape. However, the per-unit costs can be higher due to the labor-intensive nature of the process.
5. Surface Finish and Post-Processing
Die Casting:
Die casting produces parts with a smooth surface finish, often requiring minimal post-processing. The high-pressure injection process ensures that the metal fills the mold cavity uniformly, resulting in a consistent surface quality.
Forging:
Forging typically results in a rougher surface finish, which may require additional machining or finishing processes to achieve the desired surface quality. This can add to the overall production time and cost.
HAICHEN:Die Casting Technology
HAICHEN is a leading manufacturer of die casting machines, known for its advanced technology and high-quality products. HAICHEN’s machines are designed to deliver exceptional precision, efficiency, and reliability, making them ideal for a wide range of applications. Key features of HAICHEN’s machines include:
- Advanced Control Systems: HAICHEN machines are equipped with state-of-the-art control systems that ensure precise temperature and pressure regulation, crucial for producing high-quality parts.
- Energy Efficiency: HAICHEN’s machines incorporate energy-saving technologies, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
- Automation: Automated systems for mold handling, injection, and ejection enhance productivity and reduce labor costs.

Choosing between die casting VS forging depends on the specific requirements of the part, production volume, and cost considerations. Die casting produces complex, high-precision parts in high volumes efficiently, while forging creates large, durable components with high structural integrity.



