The repair function of die-cast shot sleeves restores critical dimensions and surface integrity, extending service life by 50–70% at 30–50% lower cost than replacement.
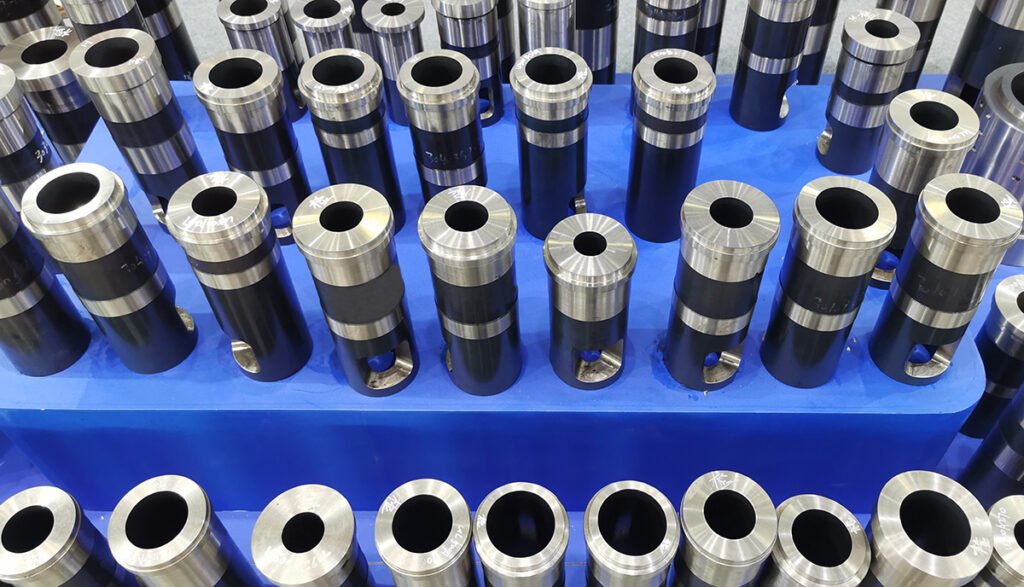
Shot sleeves in die casting are cylindrical components that hold molten metal before injection into the mold.
They are susceptible to wear and tear from the high temperatures and pressures of the process.
Repairing or reconditioning shot sleeves is a common practice to extend their lifespan and maintain optimal performance.
If you are looking for a manufacturer to repair such products, you can contact Haichen.
The manufacturer of Shot Sleeves repair
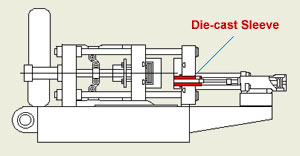
The injection sleeve, or cold chamber, is a key factor in the aluminum die-casting process.
Due to uneven expansion, different inner sleeve temperatures can cause deformation, ultimately leading to premature wear, inconsistent injection rates and longer downtime.
Haichen suggests adhering to appropriate steel and heat treatment specifications, as well as high-quality processing practices.
This can minimize deformation to the greatest extent and enhance the durability and wear resistance of the sleeve.
Coatings that can withstand the requirements of this hot zone, including nitrided coatings, are excellent solutions for lubrication and the correct mating surface micro-finish, which can increase the service life of the sleeve.
Haichen uses qualified materials, follows strict heat treatment procedures, and has many years of manufacturing experience to ensure that high tolerance parameters meet your requirements.
Combining our advanced plunger rods and tips, our sleeves will offer you the ultimate advantage to enhance your die-casting operations.
For a cold chamber that operates for a long time, proper lubrication of the plunger tip in the injection sleeve is indispensable.

Die-cast shot sleeves core repair functions & methods
- Dimensional Restoration
- Surface Re-Engineering
- Structural Integrity Repair
Dimensional Restoration
- Honing/Polishing:
- Removes oxidation, erosion, and microcracks from the inner diameter (ID).
- Achieves ID tolerance ±0.025 mm and surface roughness Ra ≤0.4 μm.
- Straightening:
- Corrects bending via hydraulic presses or thermal stress relief.
- Ensures ≤0.05 mm/m straightness for smooth plunger movement.
Surface Re-Engineering
- Hardfacing (Welding):
- Rebuilds worn ID with cobalt alloys (e.g., Stellite 6, HRC 55-60).
- Restores original dimensions after 0.3–0.8 mm wear.
- Plasma Nitriding:
- Reapplies diffusion layer (0.2–0.3 mm depth, ≥1,000 HV hardness).
- Enhances abrasion/erosion resistance for aluminum/brass alloys.
Structural Integrity Repair
- Crack Sealing:
- TIG welding fills cracks <1 mm deep.
- Post-weld heat treatment (PWHT) relieves stress.
- Ultrasonic Testing:
- Verifies wall thickness uniformity (≥95% of original).
- Detects sub-surface defects missed by visual inspection.
Best Practices for die-cast shot sleeves maximizing repair success
- Pre-Repair Inspection
- Post-Repair Treatment
- Preventive Maintenance
Pre-Repair Inspection:
Measure ID wear at 3+ cross-sections.
Dye penetrant testing for microcracks.
Post-Repair Treatment:
Apply boron nitride coating to reduce aluminum adhesion.
Slow preheating (<150°C) to prevent thermal shock.
Preventive Maintenance:
Rotate sleeves every 50k shots to distribute wear.
Use ceramic plunger tips to reduce sleeve abrasion.
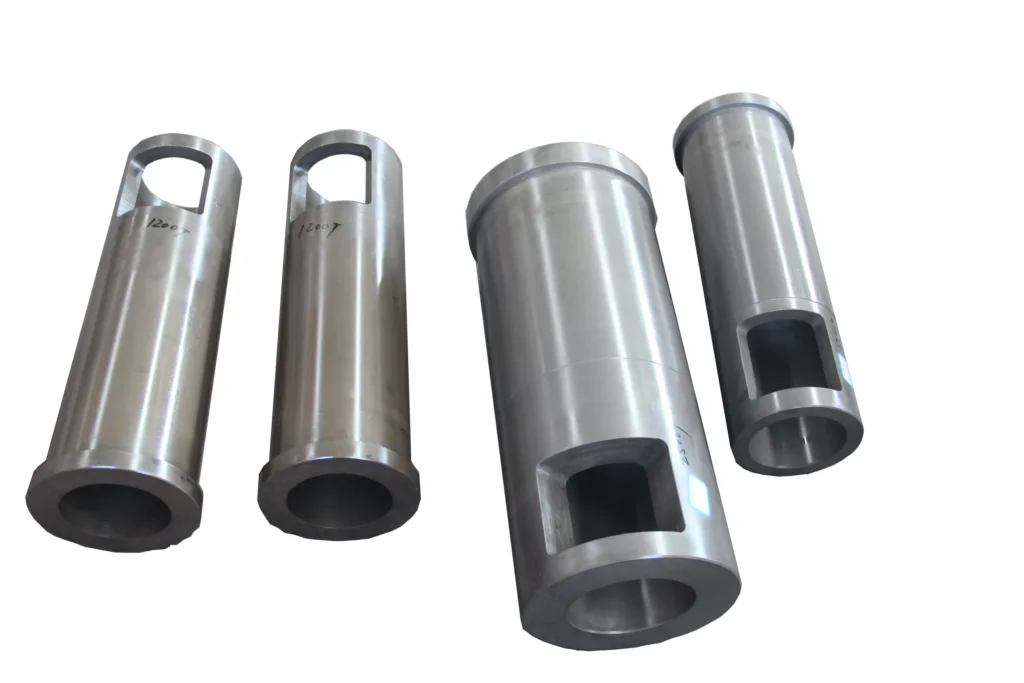

Die-cast shot sleeves common types of faults
- Inner wall wear and erosion
- Deformation and cracking
- Abnormal fitting clearance
- Thermal fatigue damage
Inner wall wear and erosion
The high-speed flow of molten metal leads to wear on the surface of the feed port and inner hole, which affects the tightness (such as flying material).
Deformation and cracking
Bending or cracking of the sleeve caused by excessive ejection force or insufficient stiffness of the sleeve (e.g., spraying).
Abnormal fitting clearance
The injection head is not the same shaft as the sleeve, and insufficient cooling leads to jamming or strain.
Thermal fatigue damage
Repeated thermal stresses lead to degradation of material properties, resulting in localized spalling or microcracks.

Repair process methods and technical difficulties
- Mounting restoration
- Plating repair technology
- Welding sleeve repair
- Composite repair process
Mounting restoration
- Applicable scenarios: inner wall wear or ovality out of tolerance.
- Process steps
- After reaming, Haichen will have the workers embed a new sleeve (semi-finished product).
- They fix it with an inorganic adhesive (such as copper oxide-phosphate glue) to restore the inner hole’s accuracy.
- Difficulty
- The adhesive surface of the old and new sleeves needs to be highly clean.
- And the wall thickness and strength need to be guaranteed after reaming.
Plating repair technology
- Plating process
- Iron plating, chrome plating or hard chrome plating is used to repair the wear of the inner wall and improve the wear resistance.
- Flame spraying
- Suitable for local damage, but it is necessary to choose a high-temperature resistant coating.
- Such as tungsten carbide and control the spray thickness.
- Difficulty
- The bonding strength and uniformity of the coating are required to be high, and the coating needs to be avoided.
Welding sleeve repair
- A-type sleeve
- Used for small defect repair, reinforced by welding of two semi-circular guard plates, simple operation but limited pressure capacity.
- Type B sleeve
- Suitable for high-pressure or annular defects, workers must weld the annular seam and longitudinal seam, and then verify the weld quality through non-destructive testing (UT, MT) after repair.
- Difficulty
- Hydrogen-induced cracking
- The hydrogen source (e.g., pre-cleaning, low-hydrogen electrode) and cooling rate need to be controlled during welding.
- Burn-through risk
- In-service pipe welding needs to balance the heat input to prevent pipe wall rupture caused by excessive penetration.
Composite repair process
- Carbon fiber or glass fiber reinforced epoxy resin is used to wrap or wrap the defective parts, and form a high-strength reinforcing layer after curing.
- Advantages
- Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, suitable for complex geometries.
- Difficulty
- Engineers must ensure strong bonding between the fiber and matrix material, and precisely control the construction process (such as vacuum infusion).

Repair Material Selection
- Criteria Wear resistance
- High temperature resistance
- Corrosion resistance
- Plating technology
- Oxidation treatment
Criteria Wear resistance
Die steel (e.g. H13), stainless steel or ductile iron (tensile strength≥ 550 MPa) is preferred.
High temperature resistance
The working temperature needs to withstand more than 600°C to avoid thermal softening.
Corrosion resistance
Resistant to chemical attack by molten metals (e.g. aluminium alloys), chrome plating or oxidation can provide added protection.
Plating technology
Chrome plating to improve surface hardness (HV≥800), nickel plating to enhance corrosion resistance.
Oxidation treatment
Blackening or oxidative dyeing to form a protective film to reduce the coefficient of friction.
Haichen die-cast shot sleeves
Quality repairs and maintenance of cold chamber shot sleeves plays an important role in achieving the maximum life cycle of your shot end die cast tooling.
Diversified Tooling Innovations offers full service reconditioning or repair of cold chamber shot sleeves.
In the long term, cold chamber shot sleeve reconditioning will always be found to be the most economic solution to increase the life cycle of your shot end die cast tooling.
Please contact Haichen sales department to determine your cold chamber shot sleeve reconditioning or repair options.




