Plunger rings (also known as plunger tips or plunger heads) are critical components in die casting machines, responsible for sealing the shot sleeve and ensuring precise injection of molten metal into the mold. Their material must withstand extreme temperatures, high pressure, and abrasive wear.
The plunger ring is a key component in the die casting process. Their successful operation depends on a number of factors. One of the most important factors is the effective fit to a round, straight, thermally stable and dimensionally stable injection sleeve, which Haichen has specialised in for more than 20 years.
The material selection of our pressure rod ring should be comprehensively considered according to the specific die casting process, alloy type, operating temperature and cost. Stainless steel, copper alloy, high temperature alloy and ceramic materials have their own advantages and disadvantages and are suitable for different application scenarios.
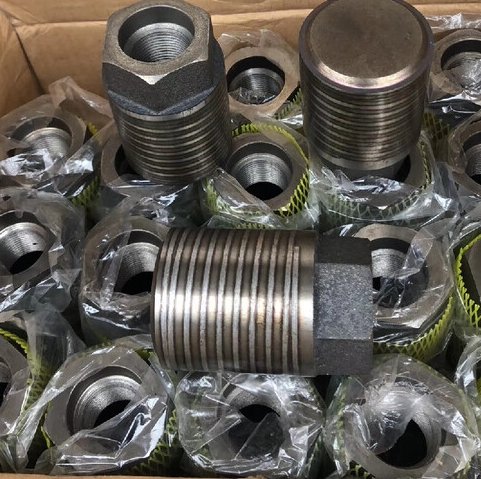

Mature die casting Plunger ring material
Below are the primary materials used for plunger rings, their properties, and applications:
- H13 Tool Steel
- Tungsten Carbide (WC)
- Ceramic-Coated Plunger Rings
- Bimetallic Plunger Rings die casting
- Graphite-Embedded Steel
- Selection Criteria
H13 Tool Steel

- Properties:
- High thermal fatigue resistance (up to 600°C).
- Good toughness and moderate wear resistance.
- Cost-effective for general-purpose use.
- Advantages:
- Balances durability and affordability.
- Suitable for aluminum, zinc, and magnesium alloys.
- Disadvantages:
- Requires frequent replacement in high-wear applications.
- Applications:
- Low to medium-volume production of automotive and consumer parts.
Tungsten Carbide (WC)
- Properties:
- Extreme hardness (1,500–2,200 HV) and wear resistance.
- High compressive strength but brittle.
- Advantages:
- Long lifespan in high-volume production.
- Ideal for abrasive alloys (e.g., aluminum with silica additives).
- Disadvantages:
- Prone to cracking under thermal shock.
- Higher cost compared to H13.
- Applications:
- High-pressure aluminum die casting (e.g., engine blocks).
Ceramic-Coated Plunger Rings

- Properties:
- Base material (e.g., H13 steel) with ceramic coatings (e.g., chromium nitride, TiAlN).
- Reduced friction and anti-sticking properties.
- Advantages:
- Minimizes soldering (metal adhesion) in aluminum casting.
- Extends service life by 30–50% vs. uncoated steel.
- Disadvantages:
- Coating delamination under extreme thermal cycling.
- Applications:
- Aluminum die casting with high melting temperatures.
Bimetallic Plunger Rings die casting
- Properties:
- Combines a steel core (e.g., H13) with a wear-resistant outer layer (e.g., nickel alloy or tungsten carbide).
- Advantages:
- Enhanced durability without full tungsten carbide costs.
- Better thermal shock resistance than pure carbide.
- Disadvantages:
- Complex manufacturing increases initial cost.
- Applications:
- Medium-volume production of zinc and magnesium parts.
Graphite-Embedded Steel
- Properties:
- Steel matrix with embedded graphite particles for self-lubrication.
- Reduces friction and heat generation.
- Advantages:
- Ideal for low-melting-point alloys (e.g., zinc, magnesium).
- Minimal maintenance due to inherent lubrication.
- Disadvantages:
- Lower strength compared to tungsten carbide.
- Applications:
- High-speed zinc die casting (e.g., connectors, hardware).
Selection Criteria

- Alloy Type:
- Aluminum: Tungsten carbide or ceramic-coated rings.
- Zinc/Magnesium: H13 steel or graphite-embedded rings.
- Production Volume:
- High-volume: Tungsten carbide or bimetallic rings.
- Low-volume: H13 steel (cost-effective).
- Operating Temperature:
- High temps (e.g., aluminum): Ceramic-coated or tungsten carbide.
- Low temps (e.g., zinc): H13 or graphite-embedded.
Maintenance Tips

- Lubrication: Use high-temperature lubricants to reduce wear of Plunger Rings die casting.
- Alignment: Ensure proper alignment with the shot sleeve to prevent uneven wear.
- Inspection: Replace rings showing cracks, scoring, or >0.2 mm wear.
What are plunger tips for die casting?
Plunger Tips for Die Casting
Plunger tips are critical components in die casting machines, designed to inject molten metal under high pressure from the shot sleeve into the mold cavity, ensuring precision and efficiency. Below are their core features and applications:
- Functions & Roles
- Material Types
- Design & Variations
- Applications
- Lubrication & Maintenance
- Industry Trends
Functions & Roles
- Metal Transfer & Pressure Application: Attached to the plunger rod, plunger tips deliver high-pressure force (up to 8,860 psi in cold-chamber casting) to rapidly fill the mold and minimize defects like porosity.
- Sealing & Flow Control: In cold-chamber systems, they seal the shot sleeve to prevent metal backflow. Their design ensures smooth metal flow to reduce turbulence and oxidation.
Material Types

- Steel Tips: Common in East Asia for lower cost but limited thermal conductivity and wear resistance; suitable for standard applications.
- Copper Alloys (e.g., beryllium copper, Cu-Ti): High thermal conductivity (for heat dissipation) and wear resistance, ideal for aluminum/magnesium alloys. Examples:
- AMPCOLOY®: Heat-resistant, thermal-shock-resistant, and durable.
- Cu-Ti Alloys: Beryllium-free (eco-friendly), high strength, and thermal efficiency, suited for HPDC (high-pressure die casting).
- Ceramic/Ductile Iron: Ceramic resists heat but is brittle; ductile iron is cost-effective for aluminum casting.
Design & Variations
- Standard Sizes: Diameters range from 61–78.7 mm (cold-chamber) for universal compatibility.
- Custom Designs: Optimized for complex molds or high-silicon aluminum alloys to improve sealing and pressure distribution.
- Self-Aligning Features: Ball-and-socket joints reduce sleeve wear and enhance sealing (e.g., patented designs with cooling channels extend lifespan).
Applications

- Hot-Chamber Casting: Used for low-melting-point metals (zinc, magnesium); tips require corrosion resistance.
- Cold-Chamber Casting: For aluminum/copper alloys, enduring extreme pressures (35–140 MPa); materials must resist thermal shock and mechanical stress.
Lubrication & Maintenance
- Lubricants: Graphite or non-graphite lubricants (e.g., VinTech) reduce friction and prevent jamming, doubling tip lifespan.
- Inspection: Regular checks for wear/cracks are critical to avoid leaks or pressure fluctuations.
Industry Trends
- Material Innovation: Western markets shift to copper alloys for efficiency, while East Asia prioritizes cost-effective steel.
- Advanced Manufacturing: Metal mold casting (e.g., beryllium copper) refines grain structures, enhancing hardness and durability vs. sand casting.
Plunger tips are vital for die casting quality and productivity. Material selection (steel, copper, or ceramic), design optimization, and proper lubrication are key considerations. Balancing cost, thermal management, and pressure requirements ensures optimal performance in diverse casting scenarios.
Haichen die casting machine
Haichen Die Casting Machine is a leading Chinese manufacturer of die casting equipment, specializing in the R&D and production of cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machines for precision casting of aluminum, magnesium, zinc, and lead alloys. Below are its core features and technical specifications:
- Product Types & Clamping Force Ranges
- Core Technologies & Advantages
- Applications & Case Studies
- Service & Certifications
Industry Leadership & Innovation
Product Types & Clamping Force Ranges
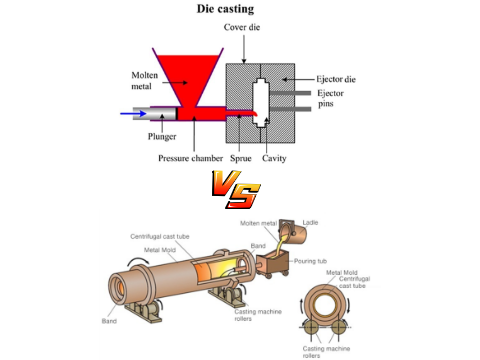
- Cold Chamber Machines (HCD-C Series):
- Clamping Force Range: 350 kN (~35 tons) to 20,800 kN (~2,080 tons).
- Applications: Automotive components (e.g., engine brackets), home appliance parts, and large-scale aluminum/magnesium alloy castings.
- Key Technologies:
- Four-stage injection control (slow speed, first fast, second fast, and intensification) for stable acceleration and high-density casting.
- Premium hydraulic components (e.g., Bosch Rexroth) and Siemens PLC control systems with multilingual interfaces (Chinese, English, Russian).
- Energy-efficient design reduces long-term operational costs.
- Price Range: 15,000to15,000to720,000 USD.
- Hot Chamber Machines (HCH Series):
- Clamping Force Range: 15 to 280 tons, optimized for zinc, lead, and other low-melting-point alloys.
- Applications: Small precision parts like door locks, hardware fittings, and medals.
- Key Technologies:
- Integrated gooseneck design combines melting and injection systems for rapid cycles.
- Semi-automatic operation; entry-level 50-ton models start at ~$18,000 USD.
Core Technologies & Advantages
- Material & Process:
- Plunger Tip: High-wear-resistant materials and precision machining ensure durability.
- Shot Sleeve: Modular design for adaptability; optimized cooling extends mold life.
- Automation & Intelligence:
- Supports robotic integration, vacuum systems, and mold temperature controllers for full automation.
- Real-time injection monitoring and servo-driven energy-saving systems (30%+ energy reduction).
Applications & Case Studies
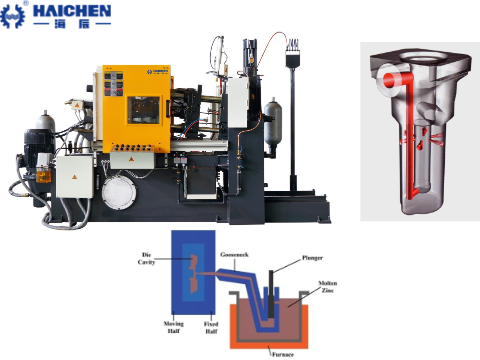
- Cold Chamber Machines:
- Automotive: Thin-walled aluminum parts (e.g., LED lamp housings), structural components.
- Home Appliances: Refrigerator/washing machine parts; maximum shot weight of 42 kg (aluminum).
- Hot Chamber Machines:
- Hardware: Zinc alloy door handles, multi-cavity molds (4 cavities) for efficiency.
- Medals: 70mm zinc alloy medals with electroplating/polishing for international markets.
Service & Certifications
- Global Support: Based in Ningbo, Zhejiang, with exports to 30+ countries (India, Russia, Mexico). Local spare parts networks.
- Certifications: ISO 9001, CE compliance (EU safety standards); cold chamber machines align with JB/T8083-2000 national standards.
- Warranty: Coverage starts at shipment; regular maintenance required (e.g., central lubrication every 500–700 cycles).
Industry Leadership & Innovation
- R&D Focus: Advances in vacuum die casting, squeeze casting, and smart manufacturing.
- Customer Feedback: Praised for stability and longevity (15+ years service life), boosting production efficiency.
Haichen combines cost-effectiveness, automation, and global service to deliver high-precision solutions for automotive, appliance, and hardware industries. For custom solutions, contact their Ningbo headquarters directly.
By the end
- For Aluminum: Tungsten carbide or ceramic-coated plunger rings offer the best longevity.
- For Zinc/Magnesium: H13 steel or graphite-embedded rings balance cost and performance.
Leading suppliers Haichen provides high-quality plunger rings tailored to specific alloys and production needs. Regular maintenance and material alignment ensure optimal efficiency and reduced downtime.
Send us an e-mail for more die casting technical details.



