Die cast aluminum vs processes:Die cast aluminum offers several advantages over other manufacturing processes, such as high precision, lightweight, and strong parts, making it ideal for applications in automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Die casting is an integral manufacturing process used for producing a variety of metal components. Aluminum is one of the materials used in die casting, and it is particularly recognized for its unique set of characteristics.
It is equally fails to compare die cast aluminum with other materials and processes.
This article will illustrate the advantages and applications associated with other processes and die cast aluminum.
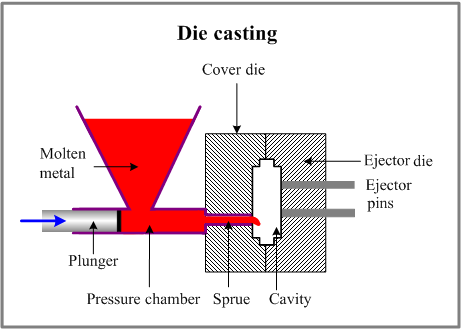
Die Casting Basics: Definition and Aluminum Die Casting Process
The Nature of Die Casting
Die casting is a metal casting process in which molten metal is injected at high pressure into a previously fabricated steel mold, or die. After cooling and solidification, high-precision part is formed. It is most beneficial when mass producing parts with intricate shapes and is able to provide them with exceptional dimensional stability and surface quality.
Key Steps in Aluminum Die Casting
Selling prices of some die casted parts can be even lower. The procedure begins with preparing steel molds from a die plate set using a CNC machine.
- Mold Preparation: Steel molds (shot and cast in H13 or similar tool steel) must be heated before insertion into die casting machine and then cooled to a temperature of 25°C to machine. After cooling, the die inserts are removed and mounted in a die construction, where the last touches are made tot he die inserts.
- Molten Aluminum Injection: The process in itself begins when the ladle pouring equipment charges the holding ladle, which is then mounted and the entire ladle holding equipment is lowered to the vertical furnace or crucible. The piston which can withstand 10 000 psi is mounted at the containing part of the mold, and the molten metal is pressurized and pushed to the ladle holding equipement at high pressure, which will internally assist in a siphon like manner.
- Cooling and Ejection: After a defined or predetermined time interval, the heated mounds are opened, and the piston mounted at the bottom is removed, and the compressed gases are able to freely leave the containing part of the molds, and cooling begins.
- Post-processing: After the cooling phase ends and the pressure starts dripping, the gas escapes to ambient air and cools off. The pads holding the not yet solidified parts would eject and the setup would be removed, after which some further manual, such as removal of the gates would be performed. After removal of the gates, the surface treatment process starts which includes anodizing and blasting with sand.

Comparison of Die Casting Process Types: Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber vs. Other
Mainstream Processes: Hot Chamber vs. Cold Chamber Die Casting
| Parameters | Hot Chamber | Cold Chamber |
| Applicable Metals | Low-melting-point alloys (zinc, tin, lead, magnesium) | High-melting-point alloys (aluminum, copper, some magnesium) |
| Working Principle | The injection system is immersed in a pool of molten metal and automatically draws in the molten metal | the molten metal is manually or automatically ladled into the cold chamber for injection |
| Production Efficiency | Very high (15–30 cycles/minute) | Low (5–15 cycles/minute) |
| Cost Structure | Low equipment cost, high maintenance cost (high-temperature corrosion) | High equipment investment, but a significant portion of material costs |
| Typical Applications | Small precision parts (gears, electronic components) | Large structural parts (engine blocks, vehicle frames) |
Other Die Casting Process Variants
- Low-Pressure Die Casting: Air pressure propels the molten metal, reducing porosity and making it suitable for thick-walled parts such as automotive wheels.
- Vacuum Die Casting: Vacuuming the mold cavity reduces gas, increasing casting density and used for high-strength components.
- Semi-solid die casting: Injecting semi-molten metal into the mold to reduce shrinkage, suitable for high-precision magnesium/aluminum parts.
Die cast aluminum vs processes
Die Cast Aluminum
Properties
Die cast aluminum is lightweight, has a high specific strength, and is a strong thermal and electrical conductive material. These attributes, especially when combined, are useful in applications that require reduction in weight and high performance, for example, the automotive and aerospace industries.
Advantages
- Lightweight: Aluminum helps in achieving a lower vehicle weight and is therefore advantageous to fuel economy and vehicle handling.
- Strength: Aluminum’s high strength to weight ratio makes it a durable choice for structural components.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminum is widely used in applications that require the removal of waste heat, for instance, in the engines of vehicles and other electronics.

Choosing the Right Process
Application Needs
The decision of using die cast parts aluminum or other alternatives hinges upon the application’s needs. Considerations include the size of the part, its complexity, the desired material characteristics, and the production scale.
Cost Considerations
In die casting’s case, the price per part is lower when the volume is higher, making this method the go-to option for mass production. If only a few parts or a prototype is needed, other methods may be best.

Aluminum Die-Casting Industry Application Examples
Automotive Manufacturing (Core Market)
- Powertrain: Critical components include cylinder blocks, cylinder heads, and crankcases. (More than 30% weight savings translates to better fuel efficiency.)
- Body Structure: Integral cast components include door frames and instrument panel brackets, reducing the overall structure weight of the vehicle and thus, increasing fuel efficiency.
- Electric Vehicle Components: Battery pack and motor housings. (Both need to be lightweight and have effective thermal management.)
Electronics and Consumer Industry
- Cooling Components:Heat sinks for CPUs and LED housings serve as Cooling components (Offers high thermal conductivity and precision molding.)
- Casing Structure: Provided to a laptop and other gadgets, a laptop chassis and other appliance housings. (Important to have a high quality surface finish and corrosion resistant).

HAICHEN: Your Partner in Die Casting Excellence
HAICHEN: Your Partner in Die Casting Excellence At HAICHEN, we manufacture die casting machines to high standards, ensuring precision and efficiency at every stage of the production process. Our machines are equipped with advanced modern features that provide for consistent production and the manufacture of high quality products. Whatever your products are, be it automotive parts, consumer electronics, or any others, HAICHEN has the solutions to fulfill your requirements.

For making the right choice for your production requirements, understanding the differences between die cast aluminum and other processes is crucial. Die cast aluminum is favored by many industries because it is lightweight, strong and has excellent thermal conductivity.



