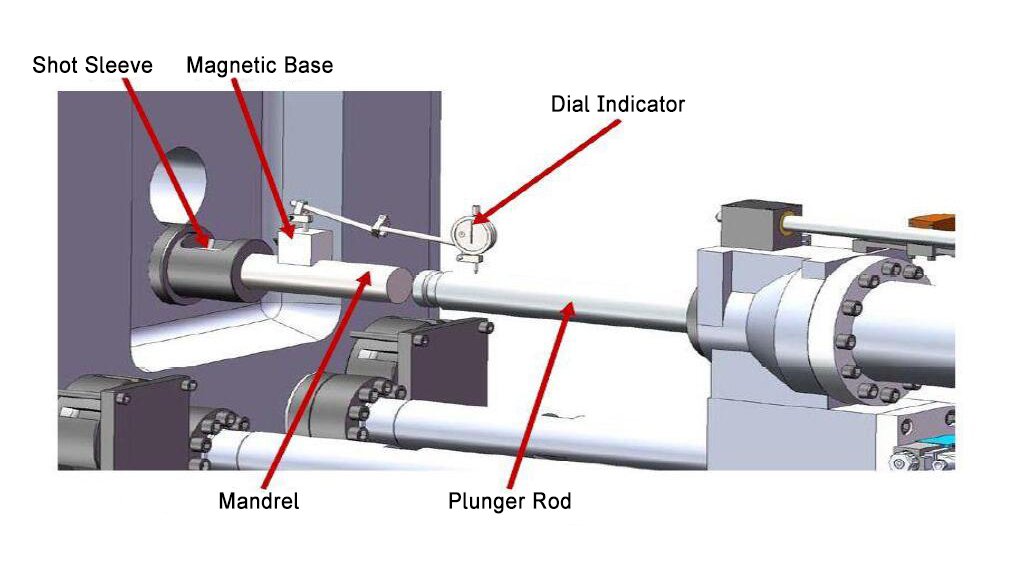
Plunger rod in die casting is categorized based on material, structural design, functional features, and application scenarios.
The plunger rod and plunger head constitute vital components of the die-casting machine. They function as the metal injector, directing molten metal into the mould. The plunger head is fabricated from specialised steel to ensure efficient execution of the casting process across a broad temperature range and under heavy-duty conditions. The plunger ring maintains constant contact with the injection sleeve, serving as a seal for the liquid aluminium akin to a hydraulic system.
Piston rods are high-pressure die-casting (HPDC) components and an important part of the die-casting system. Haichen designs and manufactures a variety of standard and custom piston rods compatible with any die-casting system.
How to distinguish between different die-cast injection plunger rods?
Below is a detailed breakdown:
- By Material
- By Structural Complexity
- By Functional Features
- By Application
- Regional Market Preferences
- Specialized Designs

By Material
- H13 Steel Plunger Rods:
- Widely used in aluminum die casting (e.g., cold-chamber machines).
- High strength, excellent thermal fatigue resistance, and mechanical stability under extreme pressure (up to 8,860 psi).
- Compatible with machines ranging from 180-ton to 800-ton capacities.
- 45# Carbon Steel Plunger Rods:
- Low-cost option for non-critical applications.
- Shorter lifespan (typically 1–3 months) due to lower wear resistance.
- Copper Alloy Plunger Rods (e.g., Nickel-Beryllium Copper C17510):
- Common in Western markets for hot-chamber die casting (zinc, magnesium).
- High thermal conductivity and wear resistance.
- Environmental/health concerns due to beryllium content.
By Structural Complexity
- Solid One-Piece Plunger Rods:
- Simple design, low cost, but lacks cooling systems.
- Suitable for low-volume or low-complexity production.
- Modular System Plunger Rods:
- Integrated cooling channels and replaceable sealing rings (e.g., Copromec’s patented design).
- Enhanced thermal management via steel tips and copper rings.
- Lifespan: 200,000–300,000 shots with optimized cooling.
By Functional Features
- Self-Aligning Plunger Rods:
- Ball-and-socket joint design to correct misalignment with sleeves.
- Reduces wear and improves sealing (e.g., Castool’s M-Loop system).
- Cooling-Enhanced Plunger Rods:
- Built-in water/oil cooling channels to prevent thermal deformation.
- Example: Con-Duct plungers with replaceable tips for thermal stability.
- Vacuum-Sealed Plunger Rods:
- Equipped with spring bushings for vacuum die casting.
- Minimizes metal leakage in high-precision applications.
By Application
- Hot-Chamber Die Casting Plunger Rods:
- For low-melting-point metals (zinc, magnesium).
- Copper alloys preferred for heat dissipation and corrosion resistance.
- Cold-Chamber Die Casting Plunger Rods:
- Used with aluminum/copper alloys under extreme pressure.
- H13 steel or copper-titanium alloys for durability.
Regional Market Preferences
- East Asian Markets: Favor cost-effective steel plungers but increasingly adopt copper alloys.
- Western Markets: Dominated by beryllium-copper alloys for thermal efficiency and process stability.
Specialized Designs

- Modular Tip Plungers: Replaceable tips (e.g., Castool’s Con-Duct) reduce downtime and costs.
- Integrated Lubrication Systems: Systems like CaroTec reduce friction and improve surface finish.
Key Selection Criteria
Choose plunger rod in die casting based on:
- Material Properties: Thermal conductivity (copper) vs. strength (steel).
- Design Complexity: Cooling systems for high-volume production.
- Application Requirements: Metal type (aluminum vs. zinc), pressure, and shot volume.
Example: H13 steel dominates aluminum die casting for its high-pressure resistance, while copper alloys excel in zinc/magnesium casting for rapid heat dissipation. Innovations like modular designs and advanced cooling (e.g., Copromec’s patents) are driving longer lifespans and efficiency.
What are the 2 types of die casting machines?
The two main types of die casting machines are Hot Chamber Die Casting Machines and Cold Chamber Die Casting Machines, categorized based on their molten metal handling mechanisms, injection systems, and applicable materials.
Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine
- Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine
- Key Differences

Hot Chamber Die Casting Machine
- Working Principle:
The molten metal reservoir (for low-melting-point metals like zinc, lead, or magnesium alloys) is integrated into the machine. A piston forces molten metal directly from the pressurized chamber into the mold cavity. - Suitable Materials:
Primarily used for metals with lower melting points:- Zinc (~420°C)
- Lead
- Magnesium alloys (~650°C)
- Advantages:
- Faster cycle times, ideal for high-volume production of small parts.
- Compact design with minimal metal exposure, reducing oxidation.
- Limitations:
- Unsuitable for high-melting-point metals (e.g., aluminum, copper) due to potential damage to the chamber components.
Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine
- Working Principle:
The metal (e.g., aluminum, copper, or brass) is melted externally in a separate furnace. Molten metal is manually or automatically ladled into a “cold” injection chamber, where a high-pressure piston forces it into the mold. - Suitable Materials:
Designed for high-melting-point alloys:- Aluminum (~660°C)
- Copper alloys (~1080°C)
- Brass
- Advantages:
- Handles high-temperature metals without damaging the injection system.
- Ideal for large, complex parts requiring high strength.
- Limitations:
- Slower cycle times compared to hot chamber machines.
- Larger footprint and higher operational costs.
Key Differences
- Metal Handling:
- Hot chamber: Integrated molten metal reservoir.
- Cold chamber: External melting and manual/automated transfer.
- Applications:
- Hot chamber: Small, high-volume parts (e.g., gears, fittings).
- Cold chamber: Larger, high-strength components (e.g., automotive engine parts).
Variations
Derivative processes like low-pressure die casting and vacuum die casting exist, but both are adaptations of the core hot/cold chamber designs.

Haichen provide hot and cold chamber machines are complementary technologies, each optimized for specific materials and production requirements in modern manufacturing.



