Aluminum pressure die casting alloy is to use the excellent characteristics of aluminum alloy.
Such as light weight, high strength, good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance.
To produce complex shapes, high precision and high performance parts through die casting technology.
Modern aluminum casting offers a variety of methods,each of the various methods have their benefits and produce high quality parts.
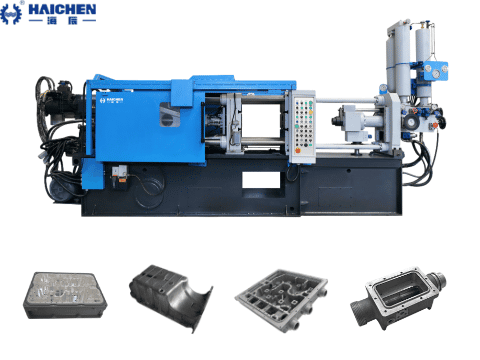
Haichen has some experience in high-pressure aluminum die-casting.
If you are struggling with choosing materials or have any other questions, feel free to ask us.
The basic requirements for Aluminum Pressure Die Casting Alloy
- Chemical composition requirements
- Mechanical property requirements
- Process adaptability requirements
- Surface and dimensional accuracy
Chemical composition requirements
According to GB/T 15114-94 and the new version of the 2023 standard.
The chemical composition of aluminum alloy die castings must comply with the provisions of GB/T 15115.
To ensure the scientific rationality of the material purity and the ratio of alloying elements.
For example, the silicon (Si) content needs to be controlled at 9.6%-12.0% and copper (Cu) from 1.5%-3.5% to optimize flow and thermal cracking resistance.

Mechanical property requirements
The tensile strength, yield strength and elongation of the single-cast specimen shall meet the standard.
The performance of the bulk specimen shall not be less than 75% of the single-cast specimen.
For example, the tensile strength of ADC12 alloy ≥ 240 MPa, and the elongation ≥1%.
The alloy for integrated die casting needs to meet the tensile strength ≥ 280 MPa and the elongation ≥7% (such as Tesla standard).
Process adaptability requirements
High silicon (Si) content (e.g., ADC12) improves melt flow and adapts to complex thin-walled structures.
The reasonable ratio of copper (Cu) and magnesium (Mg) can reduce the solidification shrinkage stress and reduce the risk of cracking.
Surface and dimensional accuracy
Surface defects (cracks, porosity, etc.) need to be strictly limited.
And the roughness is divided into Ra3.2 (grade 1) to Ra12.6 (grade 3) according to GB 6060.1.
The dimensional tolerance follows GB 6414, and the machining allowance is controlled according to GB/T 11350.

Aluminum Pressure Die Casting Alloy in the selection of different application areas
- Automotive
- Aerospace field
- Electronics & Consumer
- Construction & Industrial Equipment
Automotive
Powertrain (e.g. block, head): ADC12 or A356 is preferred, combining high thermal conductivity and fatigue resistance.
Body structure (e.g. door frame): high strength and light weight, using 6XXX or modified Al-Si-Mg alloy with an elongation of ≥7%.
Chassis parts (e.g. suspension brackets): high yield strength (≥220 MPa) is required, and Al-Mg-Si alloys are commonly used.

Aerospace field
Load-bearing structural parts (such as wing ribs): 7XXX series (such as 7075) or high-purity Al-Cu alloy with tensile strength ≥ 500 MPa.
High-temperature parts: Al-Si alloys (such as ZL105) with chromium (Cr) added can increase the strength by 30% at high temperatures.
Electronics & Consumer
Radiator housing: high thermal conductivity is required, using 4XXX series (such as 4003), silicon content ≤ 12%.
Haichen has provided aluminum die-casting solutions for radiator die-casting. If you are interested, you can check them out.

Appearance parts (such as the middle frame of mobile phones): the surface roughness requires Ra≤3.2, and ADC12 is selected with the powder spraying process.

Construction & Industrial Equipment
Aluminum formwork: using a large-scale die-casting process, the alloy needs to have good fluidity.
Such as ADC10, and the cost is reduced by 20% compared with the welding process.
Pump valve housing: corrosion resistance is preferred, ZL101A or 5052 is selected, in accordance with ASTM B108 standard.
The main types and grades of aluminum die-casting alloys
- Al-Si
- Al-Si-Cu
- Al-Mg
- Al-Zn
Al-Si
Japanese standard ADC3, American standard A360, the corresponding national standard is characterized by high silicon (5%-12%).
High silicon content, excellent fluidity, suitable for casting thin-walled complex parts (such as automobile body shells).
Al-Si-Cu
Japanese ADC10/ADC12, American A380/A383, and the national standard corresponds to YL113 and YZAlSi11Cu3.
The copper content is 1.5%-3.5%, which significantly improves the mechanical strength, but the corrosion resistance is poor,
And is widely used in complex structural parts such as engine blocks and gearbox housings.
Al-Mg
Japanese ADC5, American A518, national standard ZL303.
It contains 3%-5% magnesium and has excellent corrosion resistance.
Which is suitable for marine environments or parts that require surface treatment, but the casting performance is weak.
Al-Zn
Japanese ADC6, American A713, national standard ZL401.
The zinc content is more than 10%, and the strength is high after natural aging, but the corrosion resistance is poor.
And the surface coating protection is required, and it is often used in low-cost tools and construction hardware.

Comparative analysis of performance
- Mechanical properties
- Corrosion resistance
- Fluidity and filling capacity
Mechanical properties
Aluminum-silicon system: tensile strength 250-320 MPa, elongation 3-5%, hardness 80-100 HB.
The silicon phase is mainly strengthened, and the casting performance is outstanding, but the heat resistance is average.
Aluminum-silicon-copper system: tensile strength 320-380 MPa (such as ADC12), elongation 1-3%, hardness 85-110 HB.
The copper phase precipitation strengthens significantly, and the heat resistance is high, but the toughness is poor.
Aluminum-magnesium system: tensile strength 280-350 MPa, elongation 5-10%, hardness 70-90 HB.
Magnesium solution strengthening provides good dynamic load capacity, but casting fluidity is only 70%-80%.
Aluminum-zinc series: the tensile strength is 300-400 MPa and the hardness is 90-120 HB after natural aging, but the elongation is low (2-4%) and the corrosion resistance is poor.

Corrosion resistance
Aluminum-silicon system: medium seawater corrosion resistance, strength loss of 8%-15% in salt spray test, silicon can slow down the damage of oxide film.
Aluminum-silicon-copper system: copper is easy to cause electrochemical corrosion, and the strength loss of salt spray test is as high as 25%-38% (such as A380).
Aluminum-magnesium series: the best corrosion resistance, the salt spray strength loss is less than 5%, and the magnesium forms a dense oxide film to resist Cl⁻ erosion.
Aluminum-zinc series: the potential difference between zinc and aluminum is large, the local corrosion is serious, and the salt spray test strength loss is 30%-40%.
Fluidity and filling capacity
Aluminum-silicon: Optimal flow (benchmark 100%), suitable for large, thin-walled parts (e.g. body shell).
Aluminum-silicon-copper series: fluidity 93%-100%, taking into account strength and filling ability.
The recommended pouring temperature is 680°C, and the injection speed is 2.7 m/s.
Aluminum-magnesium system: 70%-80% fluidity, only suitable for simple thick-walled parts (such as ship parts).
Aluminum-zinc series: 85%-90% fluidity, suitable for medium-complexity parts, but the mold temperature needs to be controlled to prevent hot cracking.

Haichen Pressure Die Casting Service
Choosing an aluminum die casting alloy isn’t about a single “best” metal—it’s about fit.
Start from geometry and environment, then pick the alloy whose natural strengths (castability, tightness, corrosion, wear) align with the job.
By identifying which properties matter most for your specific application, you’ll be able to determine the aluminum die casting alloy that fits best.
For more details, visit our Die Casting Services page to learn about the solutions Haichen provides.
Ready to get an expert opinion on your project? Contact our engineering team today for a free design review and quote.
We’ll help you select the optimal alloy and ensure your part is designed for success from day one.



