Cast Aluminum is widely using in many industries due to its light weight, high strength, corrosion resistance so it’s good casting performance.
Cast aluminium is renowned for its outstanding properties, making it a favoured choice within the aluminium casting sector. It possesses high strength, exceptional durability and corrosion resistance – all essential characteristics for premium aluminium components.
The performance of cast aluminium is influenced by various casting methods and techniques. Die casting is a widely adopted approach due to its ability to produce precision aluminium castings of consistent quality.
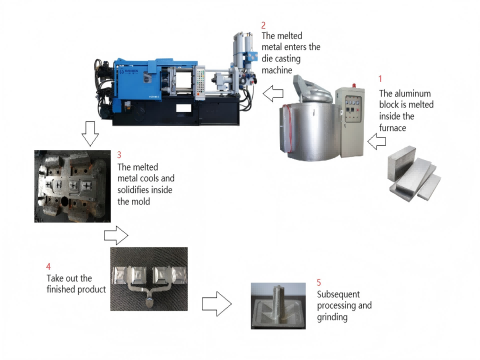
Application scope of aluminum alloy cold chamber die casting
Haichen’s die casting for you to list the following are its main areas of application and specific examples:
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace
- Building and infrastructure
- Electronic and electrical
- Industrial and energy
- Consumer and medical
- Specialty Alloys and High Temperature Applications
Automotive industry
Engine parts
Cast aluminium is widely using in engine block, cylinder head, piston, transmission housing and other key components.

Its lightweight characteristics help improve fuel efficiency and electric vehicle range.
For example, AA 390 alloy is commonly using in internal combustion engine blocks for its excellent wear resistance due to its high silicon content (16-18%).
Suspension and braking systems
Aluminium castings are also for brake calipers, suspension components, etc., combining strength and lightweight requirements.
Aerospace
Structural and power components
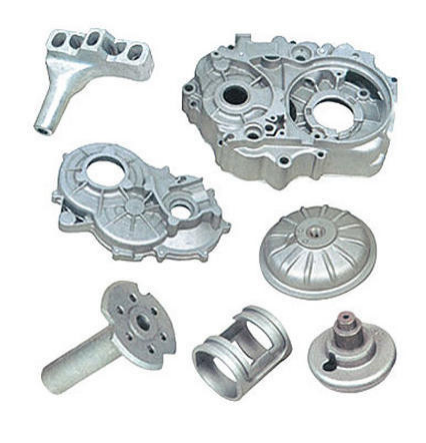

Cast aluminium is great for wing assemblies, landing gear, rocket parts, etc., due to its high strength-to-weight ratio and corrosion resistance.
For example, A356 alloy is the preferred material for aircraft parts due to its excellent combination of properties (flowability, heat resistance).
Building and infrastructure
Window and door frames and decoration
Cast Aluminum is used to make corrosion-resistant window and door frames, roofing systems and decorative elements for buildings.

Its high thermal conductivity also makes it suitable for heat dissipation structures.
Structural supports
Infrastructure such as bridges and power line supports take advantage of aluminium’s durability and corrosion resistance.
Electronic and electrical
Heat sink components
The thermal conductivity of cast aluminium makes it ideal for heat sinks, inverter housings and electronic equipment housings.

For example, cast aluminium is often using for heat sink components in laptops and smartphones.
Conductive components
Certain aluminium castings are used for electrical system components because of their conductivity.
Industrial and energy
Thermal management equipment

Cast Aluminum heaters are widely using in plastics machinery, petrochemical equipment and the electronics industry, and are characterised by high thermal efficiency and long life.
Energy equipment
Cast aluminium parts are used in base stations, power converters and other scenarios that require efficient heat dissipation.
Consumer and medical
Household products
Consumer products such as cookware, lamps and outdoor furniture take advantage of aluminium’s lightweight and corrosion resistance.
Medical Devices
Prosthetics and surgical instruments use cast aluminium for its biocompatibility and ease of machining.
Specialty Alloys and High Temperature Applications
Heat Resistant Alloys
For example, Al-Ni-Cr alloys and eutectic alloys containing zirconium (Zr) are developed for use in high-temperature, high-stress environments such as diesel engine cylinder heads.
Improved thermal stability and fatigue strength.
What materials can you cast aluminum in?
There are many different materials and tools for casting aluminium, depending on the casting process and application requirements.
Haichen lists for you the common ones in the industry:
- Sand
- Tool Steel
- High-temperature alloys (High-Temperature Alloys)
- Cast aluminium alloys (Cast Aluminum Alloys)
- 3D-Printed Sand Molds (3D-Printed Sand Molds)
Sand
Casting (Sand Casting) is one of the most commonly used methods.
Sand moulds are made by compacting the sand into the desired shape and the liquid aluminium is poured and cooled.
Sand mould is low cost and suitable for complex shapes and large castings.
Tool Steel
Die Casting and Permanent Mold Casting usually use tool steel moulds.
Cast Aluminum has a lower melting point (660°C) than steel, so tool steel moulds can withstand high temperatures.
These moulds are suitable for mass production and have a high surface finish.
High-temperature alloys (High-Temperature Alloys)
in a high-temperature environment (such as composite casting or special processes), nickel-based, molybdenum-based or tungsten-based high-temperature alloys can be used as mould materials.
They are suitable for extreme conditions due to their high melting point and oxidation resistance.
Cast aluminium alloys (Cast Aluminum Alloys)
Certain aluminium alloys can also be used as mould materials themselves.
Cast aluminium alloys have good thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance, which makes them suitable for mould making, especially for complex working conditions.
3D-Printed Sand Molds (3D-Printed Sand Molds)
Mentions the use of 3D printing technology to make sand moulds, combined with an induction heating system to cast a composite structure of aluminium and steel plates.
This advanced process improves flexibility and precision in mould design.
Other related materials and processes:Zinc
Coating:
It was mentioned that in the composite casting of aluminium with other materials (e.g. steel).
Zinc coating improves interfacial bonding, but is mainly used to treat solid surfaces rather than the mould itself.
Lost Foam Casting:
The use of a foam model to encapsulate a sand mould, where the foam vaporises after the liquid aluminium is poured, suitable for castings with complex internal structures.
Equipment selection for die-cast aluminium
Selection of suitable die casting aluminium equipment need to comprehensively consider a number of factors:
- Equipment type selection
- Production demand assessment
- Performance parameters matching
- Automation and efficiency
- Equipment quality and manufacturer selection
- Optimisation of special scenarios
Equipment type selection
Cold chamber die casting machine:
Suitable for high melting point alloys (such as aluminium, magnesium), its ejection chamber is separated from the furnace, it can avoid the aluminium liquid for a long time to contact with the high temperature caused by oxidation.
Cold chamber die casting machine production efficiency, such as Haichen HCD480-C cold chamber machine every 8 hours can die casting 600 ~ 700 times, suitable for small and medium-sized castings or cost-sensitive production scenarios.
Production demand assessment
Product characteristics: according to the casting size, complexity and precision requirements for the choice of equipment.
For example, thin-walled complex parts need high injection pressure (such as high-pressure die casting machine), and large size castings need large clamping force equipment.
Production scale: large-scale production is recommended to choose a high degree of automation equipment.
Such as fully automatic die casting machine or equipped with spray pick up mechanical system; Small batch or trial production can be given priority to consider the lower cost of the model.
Performance parameters matching
Pressure and clamping force
high-pressure casting machine (such as more than 300 tons) for high-precision needs; low-pressure casting machine is suitable for simple shapes or thick-walled parts.
Mould size
Ensure that the size of the machine table is compatible with the mould to avoid lack of space.
Injection capacity
Match the weight of the casting to avoid waste or underfilling.
Automation and efficiency
Automation equipment (such as automatic spray pickup machine, vacuum die casting machine) can reduce human intervention, improve production efficiency, suitable for automotive parts and other high-volume production areas.
Cold room die casting machine efficiency advantage is obvious, especially suitable for aluminium alloy high frequency production.
Equipment quality and manufacturer selection
Priority to choose the well-known brands (such as Haichen, Izumi, Yu Department of machinery), the stability of its equipment and technical support is more guaranteed.
The manufacturer’s quality certification (e.g. ISO standard) and customer evaluation should be verified to ensure the durability of the equipment.
After-sales service and maintenance
Select a service provider that offers installation and commissioning, regular maintenance and technical support, especially free maintenance policy during the warranty period.
Routine maintenance includes hydraulic system checking, mould cleaning and lubrication, cooling system management, etc. to prolong equipment life.
Economic considerations
Comprehensive equipment prices, energy consumption, maintenance costs and productivity, choose cost-effective models.
Aluminium alloy die casting usually does not require secondary processing, which can save processing costs and improve the economy.
Optimisation of special scenarios
Hot and humid environments need to pay attention to the rust-proof performance of the equipment, cold areas can choose a more efficient heat transfer model.
High precision areas (such as aerospace) is better to use semi-solid die casting or precision CNC equipment.

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- Why are cast aluminium parts prone to porosity?
- How to choose between die casting and sand casting?
- The difference between cast aluminium and forged aluminium?
Why are cast aluminium parts prone to porosity?
The main reason is that the gas inside the mould is not discharged or the molten aluminium turbulence involves air.
Solutions include optimising the mould exhaust design and controlling the pouring speed.
How to choose between die casting and sand casting?
Die casting: suitable for high volume, complex parts (such as automotive parts), high surface finish but high mould cost.
Sand casting: suitable for small batch, large size parts (such as machine base), low cost but rough surface.
The difference between cast aluminium and forged aluminium?
Cast aluminium: melt forming, suitable for complex shapes, low cost but slightly lower strength.
Leave a message, Haichen will solve more for you!



