The connecting rod in a die casting machine is a critical component, often part of the clamping mechanism or injection system, linking moving parts to ensure synchronized operation. Replacing it requires precision to maintain alignment, safety, and machine efficiency.
The die-cast aluminium connecting rod serves as a force transducer designed to distribute stress loads across a uniformly shaped area while minimising them. The connecting rod also forms part of the injection unit within a die-casting machine, linking the piston to the stamping components.
The die casting machine shot rod has high strength and durability and is usually used in applications that require high performance and reliability, such as automobiles and aircraft engines. Although the die casting machine shot rod has low strength and durability, it is cheaper because of its low cost.
The role and function of the injection connecting rod in die casting equipment
- Safety Precautions
- Identify the Connecting Rod Type
- Tools and Materials
- Replacement Procedure
- Common Issues & Fixes
- Maintenance Tips
- When to Replace the Connecting Rod?
Safety Precautions
- Lockout/Tagout (LOTO): Disconnect power and lock hydraulic/pneumatic systems.
- Cool Down: Allow the machine to cool to ambient temperature to prevent burns.
- Wear PPE: Heat-resistant gloves, safety glasses, and steel-toe boots.
Identify the Connecting Rod Type
- Clamping Unit Rod: Connects the toggle mechanism to the moving platen.
- Injection Unit Rod: Part of the hydraulic/pneumatic system driving the plunger.
- Linkage Rod: Transfers motion between gears or levers.
Tools and Materials
- Hydraulic jack or hoist (for heavy components).
- Torque wrench and alignment tools (dial indicator, laser alignment system).
- Replacement rod (material: H13 steel, tungsten carbide, or OEM-specified alloy).
- Anti-seize compound and high-temperature lubricant.
Replacement Procedure

Remove the Old Connecting Rod
- Drain Hydraulic Fluid: If the rod is part of a hydraulic system.
- Disassemble Surrounding Components:
- Remove bolts, pins, or retaining rings securing the rod.
- Detach linkages (e.g., toggle joints, pistons).
- Extract the Rod: Use a puller tool if corroded or stuck.
Inspect and Prepare
- Check for Wear:
- Look for cracks, bending, or surface scoring (>0.1 mm wear = replace).
- Clean Mounting Points: Remove debris from bearings, bushings, or brackets.
Install the New Rod
- Apply Lubricant/Anti-Seize: Coat threads and contact surfaces.
- Align Precisely:
- Use a dial indicator to ensure parallelism (tolerance: ±0.05 mm).
- For toggle systems, align with the moving platen and fixed crosshead.
- Secure Fasteners:
- Torque bolts to manufacturer specs (e.g., 30–50 Nm for M16 bolts).
- Use lock washers or thread-locking fluid.

Reassemble and Test

- Reconnect Linkages: Ensure all pins, bushings, and bearings are seated properly.
- Manual Movement Test: Cycle the machine manually to check for smooth operation.
- Hydraulic Pressure Test: Gradually increase pressure while monitoring for leaks or misalignment.
Common Issues & Fixes
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Misalignment | Improper installation | Recheck with laser alignment tools. |
| Premature Wear | Lack of lubrication | Apply high-temperature grease. |
| Hydraulic Leaks | Damaged seals or loose fittings | Replace seals and retorque fittings. |
Maintenance Tips
- Weekly Inspections: Check for cracks, alignment, and lubrication.
- Lubricate Joints: Use grease compatible with operating temperatures (e.g., molybdenum disulfide).
- Monitor Load Sensors: Ensure the rod isn’t overloaded during cycles.
When to Replace the Connecting Rod?
- Visible Cracks or Deformation: From thermal/mechanical fatigue.
- Excessive Play: Causes misalignment in the clamping or injection unit.
- Irregular Machine Movements: Jerky operation or uneven part ejection.
Based on Haichen’s extensive experience, when the injection stress becomes disordered, the connecting rod must be replaced.Based on Haichen’s extensive experience, when the injection stress becomes disordered, the connecting rod must be replaced.
Application of die casting machine connecting rod
The connecting rod in a die casting machine is a critical component for power transmission and mechanical linkage.
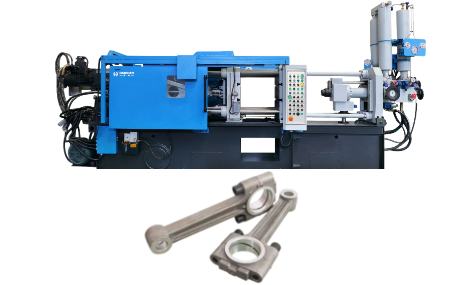
Its primary functions include:
- Mechanical Power Transmission
- Precision Mold Control and Pressure Maintenance
- Automated Component Transfer
- Core Component of Injection Systems
- Safety and Balance Assurance
- Examples of Applications
Mechanical Power Transmission
The rod transfers operator input (e.g., foot pedal force) or machine-generated power (hydraulic/pneumatic) to the mold assembly. For example, pressing a pedal rotates the connecting rod, driving the mold to close or open. In automated systems, it synchronizes with ejector pins, stripper plates, and other components for demolding and resetting.
Precision Mold Control and Pressure Maintenance
As part of the mold-clamping unit, the rod works with templates and guide rods to ensure precise mold alignment and uniform pressure distribution. In systems like Haichen die casting machines, the rod integrates with tension cylinders for automatic clamping force adjustment, ensuring stability during high-pressure casting.
Automated Component Transfer
In automated production lines (e.g., Toyota’s systems), connecting rods facilitate inter-mold material transfer. They move preheated billets or castings between mold cavities, enhancing production continuity and efficiency.
Core Component of Injection Systems
In cold-chamber die casting, the rod works with injection plungers to force molten metal into mold cavities at high speeds, ensuring complete and consistent material filling.
Safety and Balance Assurance
Symmetrical rod design and strain gauge monitoring ensure balanced clamping force distribution across the mold, preventing misalignment or overload damage in large-scale machines.
Examples of Applications
- In Pascal die casting machines, ball-lock connecting rods enable rapid mold changes by automating the connection between ejector cylinders and mold plates.
- Connecting rods in chamber lubrication systems coordinate with plungers to spray lubricant precisely, reducing friction during casting.
You need to know the connecting rod is a multifunctional part essential for power transfer, precision control, automation, and safety in die casting. Its design and performance directly impact product quality, operational efficiency, and equipment longevity.

Haichen High Quality Die Casting Machine
As a professional die-casting machine manufacturer with over 20 years of experience, Haichen’s core advantages in high-quality die-casting machines are reflected in the following aspects:
- Advanced Technology & Design Standards
- Material Adaptability & Applications
- Quality Certifications & Reliability
- Energy Efficiency & Cost Savings
- Global Support & Success Stories
- Innovation & R&D Investment
Advanced Technology & Design Standards
- High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC):
Haichen’s cold-chamber and hot-chamber HPDC machines utilize servo-controlled hydraulic injection technology, achieving injection speeds of 8 m/s (no-load). Multi-stage pressure and speed control ensure precision molding. - Intelligence & Automation:
Equipped with fully computerized systems (e.g., Siemens PLC), real-time closed-loop control, and multilingual interfaces (English, Spanish, etc.). Integrated automation (robots, vacuum systems, mold temperature controllers) enhances productivity. - Structural Design:
Cold-chamber machines feature a five-point locking mechanism and finite element analysis (FEA)-optimized stress distribution. High-rigidity nodular cast alloy templates ensure stability and mold compatibility for long-term operation.

Material Adaptability & Applications
- Material Compatibility:
- Cold-Chamber Machines: Ideal for high-melting-point alloys (aluminum, magnesium) used in automotive radiators and engine components.
- Hot-Chamber Machines: Specialized for low-melting-point alloys (zinc, lead) in products like door handles and zinc alloy medals, with tonnage ranging from 15 to 280 tons.
- Industry Applications:
Widely used in automotive (steering wheels, wheel hubs), 3C electronics, and home appliances (aluminum cookware, LED housings). Notable cases include zinc alloy door handles and magnesium alloy automotive parts.
Quality Certifications & Reliability

- Global Compliance:
ISO 9001 and CE certified, meeting JB/T industry standards and EU safety regulations. Products are exported to 30+ countries. - Core Components:
Hydraulic and electrical systems use premium European/Japanese brands (e.g., Bosch Rexroth hydraulics, Japanese seals). Critical parts (injection cylinders, templates) are made of high-strength materials for extended durability.
Energy Efficiency & Cost Savings
- Energy-Saving Features:
Servo-driven systems and variable-frequency motors reduce energy consumption, cutting long-term operational costs. - Competitive Pricing:
Price ranges from 15,000(20−tonmodels)to15,000(20−tonmodels)to720,000 (2000-ton models). Customizable configurations minimize intermediate costs.
Global Support & Success Stories

- Technical Service:
Multilingual support (Chinese, Russian, etc.), rapid engineer response, and assistance in mold design/process optimization. - Customer Feedback:
Clients praise Haichen machines for “exceeding performance expectations,” with vacuum die casting and oxygen-filled processes reducing defects and boosting yield rates.
Innovation & R&D Investment
- Cutting-Edge Processes:
Continuous R&D in vacuum die casting, semi-solid molding, and successful production of AM60B magnesium alloy automotive wheel hubs. - Production Capacity:
Ningbo production base delivers 30+ units annually, with lead times of 15–45 days for fast order fulfillment.
By the end
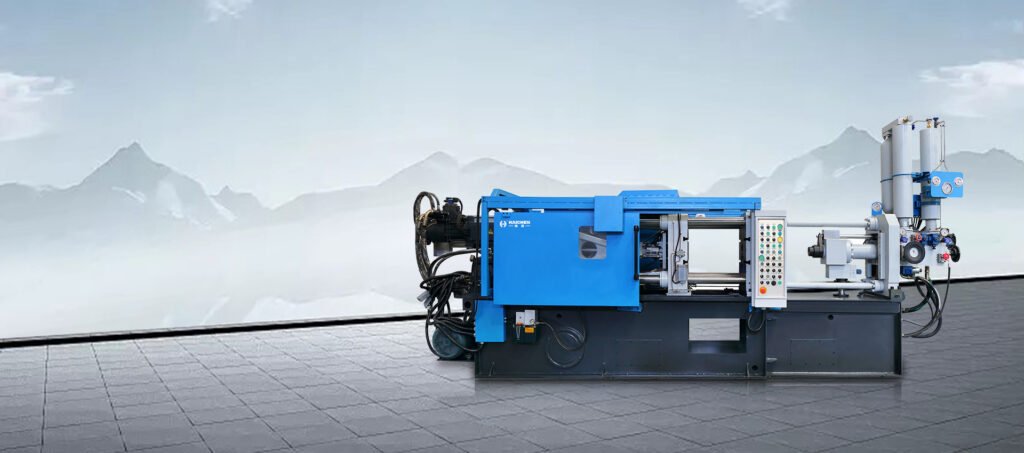

Haichen’s high-quality die-casting machines combine advanced technology, rigorous standards, diverse applications, and reliable service, making them a top choice for automotive, 3C, and other industries. Their precision, efficiency, energy-saving design, and cost optimization empower clients to enhance market competitiveness.
More we telling
Replacing a connecting rod requires meticulous alignment, proper torque, and post-installation testing. For critical applications (e.g., automotive structural parts), consult OEM guidelines from manufacturers like Haichen. Regular maintenance and alignment checks prevent costly downtime and ensure consistent casting quality.
For complex systems, consider hiring certified technicians to ensure compliance with safety and performance standards



