Die casting mold components mainly include fixed die, moving die, mold base, cavity, core, runner system, and other auxiliary components.
The parts of a casting mould comprises of a fixed die, a moving die, die plates, a cavity, a core, a runner system, along with a number of other auxiliary parts. A die casting mold is necessary to carry out the die casting process. It is important to note that the die mold’s design and fabrication will have a direct correlation to the quality of die castings produced, the production rate, and the mold’s longevity.
We will analyze die casting mold components from eight main aspects. Below is a comprehensive discussion of die casting mold components.
- Fixed die
- Moving die
- Mold Base
- Cavity
- Core
- Runner System
- Ejector pin
- Other auxiliary components
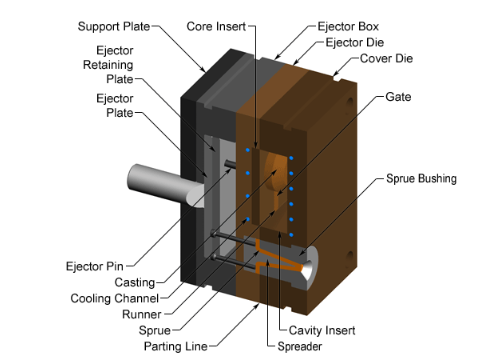
Fixed Die
- Location and Function
- Key Functional Components
- Interaction with Other Components
The fixed die is a part of the die casting mold, usually fixed to the base of the die casting machine. It forms the mold cavity together with the moving die. It uses to contain the molten metal and cool it into shape.
Core definition and function
Location and Function
- The fixed die is mounted on the fixed platen of the die-casting machine and remains stationary.
- When closed with the movable die, it forms a sealed cavity, ensuring precise, leak-free filling of the molten metal under high pressure.
- It typically includes the main cavity and the gating system inlet (such as the sprue bushing), directly connected to the die-casting machine’s nozzle or shot chamber.
Key Functional Components
- Fixed Die Insert: Embedded in the fixed die platen, it forms the main portion of the cavity and directly determines the shape of the casting.
- Sprue Bushing: Connects to the die-casting machine nozzle and guides the molten metal into the gating system.
- Guide Pillar: Mated with the guide bushing of the movable die, it ensures precise alignment of the two halves of the die.
- Core-Pulling Mechanism: Used to form lateral holes or concave-convex structures, it uses inclined guide pillars and other elements to achieve sliding motion.
Interaction with Other Components
- Interaction with the Moving Die:
When closed, it forms a complete cavity with the moving die. When the die is opened, the moving die drives the ejector mechanism to release the mold, while the fixed die remains stationary. - Connection to the Die-Casting Machine:
A fixed clamp is bolted to the die-casting machine’s fixed plate to ensure stability during high-pressure injection.

Moving Die
- Definition
- Core Functions
- Main Components of the Moving Mold
The moving die is another part of the die casting mold. It installes on the middle plate of the die casting machine and can move during the injection process to complete the opening and closing of the die.
Definition
The moving mold (also called the rear mold or movable side) and the fixed mold (fixed side) together form the main body of the die-casting mold.
The moving mold is fixed to the moving platen of the die-casting machine and moves with the platen to open and close the mold.
Core Functions
- Opening and Closing Mold: It closes with the fixed mold to form a sealed cavity, where molten metal is injected and cooled to form the mold; it separates during mold opening to remove the casting.
- Ejector Mechanism: Most ejector mechanisms (such as ejector pins and push plates) are installed on the moving mold side and are responsible for ejecting the solidified casting from the mold cavity.
- Core Pulling Mechanism: In molds requiring lateral core pulling, mechanisms such as slides and inclined guide pins are often integrated into the moving mold to form complex features.
Main Components of the Moving Mold
According to the evidence, the moving mold consists of the following key components:
Molding Components
- Moving Mold Core: Together with the fixed mold core, it forms the mold cavity and directly determines the shape of the casting.
- Inserts & Sliders: Used for complex local structures and can be dynamically adjusted via the core pulling mechanism.
Mold Base System
- Moving Clamping Plate: Secures the moving mold to the die casting platen.
- Support Pillars: Resist deformation caused by mold clamping pressure.
- Rails: Support the ejector mechanism and guide its movement.
Ejection System
- Ejector Pins: Directly contact the casting, ejecting it from the cavity (usually located on the moving mold side).
- Ejector Retainer & Ejector Plate: Secure the ejector pins and provide thrust.
- Reset Lever: Ensures the ejector mechanism returns to its original position during mold closing.
Guiding and Positioning
- Guide Posts & Bushings: Ensure precise alignment between the movable and fixed molds.
- Middle Guide Posts: Enhance guide stability in large molds.
Core-Pulling Mechanism
- Oblique Guide Pillars: Drive lateral movement of the slide.
- Clamping Blocks & Springs: Secure the slide position and assist in resetting.
Auxiliary Systems
- Cooling/Heating Channels: Control mold temperature.
- Overflow & Venting Systems: Connected to the movable mold in some molds to remove gas and debris.

Mold Base
- Core Functions and Definitions
- Key Components
- Materials and Manufacturing
The mold base is the basic structure of the die-casting mold, usually composed of steel plates and frames. It uses to integrate the various parts of the mold and ensure that the mold can be installed on the die-casting machine.
Core Functions and Definitions
- Structural Foundation: The mold frame is the supporting framework of the mold, carrying and securing all other components (such as the cavity, ejection system, and guide components), ensuring overall mold structural stability.
- Mounting Interface: This interface enables the mold to be precisely mounted on the die-casting machine, specifically aligning with the machine’s fixed platen (stationary mold half) and movable platen (movable mold half).
Key Components
- The mold plate and frame: This includes the movable and fixed mold platens (AB plates), support plates, mold feet, and backing plates, which together form a complete support system.
- Guide Components: Guide pins and guide bushings ensure precise alignment of the movable and fixed molds during opening and closing.
- Standard Parts Compatibility: Standardized ejector pins, sprue bushings, and cooling components can be integrated.
Materials and Manufacturing
- Main Materials:
Pre-hardened steels such as P-20 and AISI 4140, or high-strength mold steels such as 1.2344, SKD61, and DAC55, designed to withstand high-pressure and high-temperature cycles. - Aluminum alloy: Aluminum mold frames are used in some scenarios (such as prototypes or small batches), which are lower in cost but less durable.

Cavity
- Definition and Core Functions
- Materials
The cavity is the core part of the mold and determines the shape and size of the die casting. It is a negative space used to hold the molten metal and allow it to cool and form.
Definition and Core Functions
The cavity is the recessed space within the mold that forms the final shape of the casting.
It is formed by the closed assembly of two mold halves (a stationary mold and a movable mold). Its internal contours precisely replicate the geometry, dimensions, and surface features of the final part.
Molten metal is injected under high pressure into this cavity, where it cools and solidifies to form the desired part.
Materials
The cavity part (or cavity insert) is usually made of high-strength, heat-resistant, and wear-resistant high-quality mold steel.
Commonly used imported high-grade materials include 1.2343 (H11), 1.2344 (H13), 1.2367, SKD61 (DAC, DHA1), DAC55, Premium H13, 8407, DIVAR, STAVAX, etc.

Core
- Function
- Purpose
- Types of Cores
Function
Cores are used to form complex internal features, such as holes or grooves, in die castings. Cores are usually made of materials that can withstand high temperatures and pressures.
Purpose
- Cores create internal geometries in castings, such as holes, recesses, undercuts, or complex internal passages.
- They work alongside the cavity (which defines external shapes) to form the complete part geometry.
Types of Cores
Evidence consistently classifies cores into three types:
- Fixed Cores:
Oriented parallel to the mold opening direction.
Permanently attached to the mold and remain stationary during operation. - Movable Cores:
Oriented non-parallel to the mold opening direction.
Requires a separate mechanism (e.g., core-pulling systems) for extraction before the mold opens. - Loose Cores:
Removed manually or via auxiliary equipment after casting

Runner System
- The Runner
- The sprue
- The Inner Gate
The runner system includes main runners, branch runners and gates. They use to guide the molten metal into the mold cavity. Its design has an important influence on the uniformity of metal flow and the quality of die castings.
The Runner
- Serves as the primary channel for molten metal to flow from the injection system to the mold cavity.
- It is typically composed of multiple branch runners, ensuring uniform metal distribution in multi-cavity molds.
- Optimizing the size, shape, and placement of branch runners is crucial to reduce air pockets and ensure uniform filling.
The sprue
- The inlet channel connecting the pressure chamber to the sprue serves as the starting point for metal flow.
- The sprue is connected to the shot sleeve, guiding the metal injection.
The Inner Gate
- Located at the intersection of the sprue and the mold cavity, it controls the speed and direction of metal flow into the mold cavity.
- The Inner Gate’s cross-sectional area must be large enough to minimize filling time and must avoid the mold core.
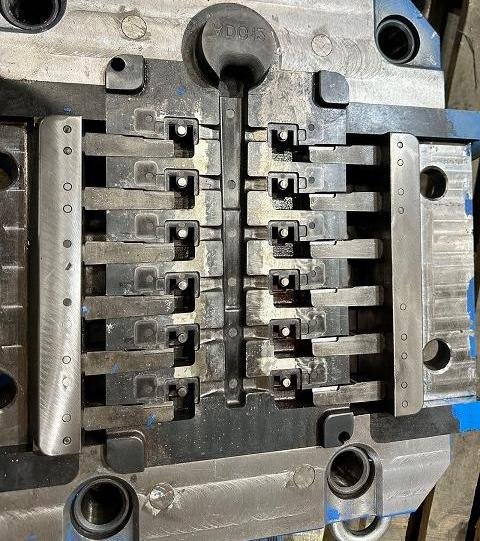

Ejector Pins
- Function and Use
- Ejector Sleeves
- Ejector Pins
- Pin Base
They locate on the moving die and are used to eject the die casting from the die after it cools. These pins need to withstand high pressure and temperature, so they are usually made of high temperature resistant materials.
Function and Use
Core Function: Ejectors are used to eject castings from the mold cavity after the metal solidifies.
They are installed on the active side of the mold (the ejector half) and are pushed by the ejector plate to force the casting out of the mold.
Ejector Sleeves
Protect and guide the ejector pins, such as the nitrided S-series sleeves.
Ejector Pins
Retract the ejector pins when the mold is closed.
Pin Base
For headless ejectors, enabling quick replacement without mold disassembly.
The main components of Haichen die-casting molds include: a fixed mold and a moving mold, a cavity, core, inserts, and a gating system. Also with an overflow and venting system; For examples, one with slider die casting mould. It need has an ejection system, including ejector pins, return pins, ejector plates, and ejector plate guide pillars/sleeves. It used to eject the solidified casting from the mold after mold closing.
Haichen Supports Mold Component Optimization
HAICHEN’s expertise helps ensure all die casting mold components work together for maximum efficiency.
- Solve Ejection Issues for The Auto Part Production
- HAICHEN’s Holistic Approach to Mold and Machine Performance
Solving Ejection Issues for The Auto Part Production
One client of Haichen had problems with a complex aluminum bracket sticking in the mold, causing damage to thin ejector pins. HAICHEN engineers analyzed the mold. They found the cooling around the pins was poor, making the local area too hot. We redesigned the cooling channel layout and suggested switching to stronger, heat-treated ejector sleeves in critical areas. These changes to the die casting mold components solved the sticking, eliminated pin breakage, and reduced cycle time by 8%.
HAICHEN’s Holistic Approach to Mold and Machine Performance
This case shows our strength. We understand that the mold and machine must work as one system. Our machines provide stable, precise clamping and injection. This protects delicate die casting mold components from shock and wear. We offer advice on mold design to match our machine’s capabilities, ensuring longer mold life and more stable production for our clients.
Other auxiliary components
- Positioning and Guide Components
- Temperature Control Components
- Vent and overflow systems
These include cooling channels, exhaust grooves, exhaust holes, etc. These components help optimize the cooling performance of the mold and improve product quality.
Positioning and Guide Components
- Locating rings and pins ensure precise mold assembly.
- Guide pillars and bushings ensure alignment between the movable and fixed molds, reducing wear.
- Middle guide posts/sleeves enhance stability in large molds.
Temperature Control Components
- Cooling channels control mold temperature
- Heating rods are used for materials requiring high-temperature molding
- Jet coolers and water jackets enhance cooling
Vent and overflow systems
- Vent slots and overflow tanks remove gases and excess metal
- Vent plugs enhance venting in deep cavity structures

Above all, the various components of the die-casting mold work together to ensure the efficiency of the die-casting process and the quality of the product. Designing and manufacturing high-quality die-casting molds requires comprehensive consideration of material selection, precision machining, cooling system design, and mold assembly and testing.



