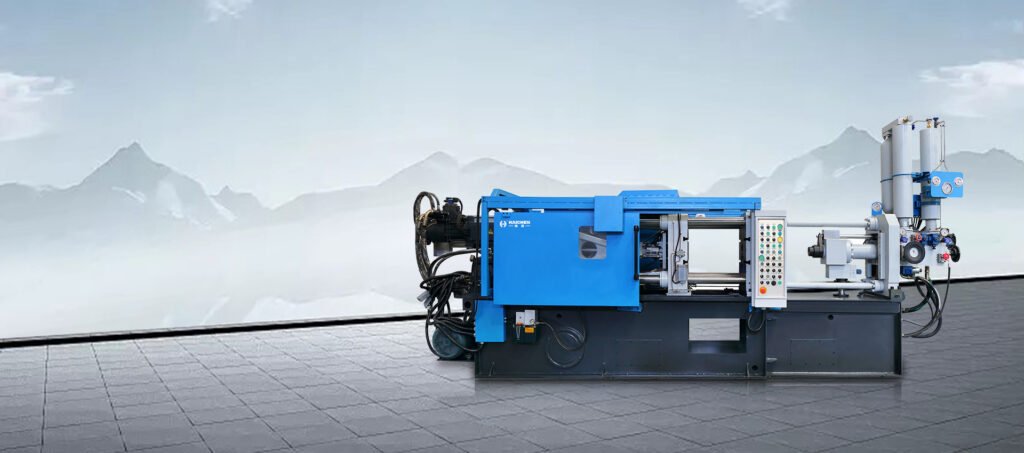
Differences Between servo valves and proportional valves in die casting are the drive mode, dynamic performance and contamination sensitivity. Servo valves use torque motors, which have low power consumption and better dynamic performance, but are more sensitive to contamination.
Both of these valves are common and important die casting parts.
Proportional valves use electromagnets, which have high power consumption and poor dynamic performance, but are low cost and have strong anti-contamination ability.
Valves used in die casting equipment
- Control Principle & Feedback Mechanism
- Dynamic Performance & Response Speed
- Contamination Resistance & Maintenance
- Energy Efficiency & Actuation
- Cost & Applications
- Die-Casting-Specific Designs

Control Principle & Feedback Mechanism
- Servo Valves:
Use closed-loop control with integrated mechanical or electrical feedback. They continuously monitor parameters like position, pressure, or speed of actuators (e.g., hydraulic cylinders) and adjust the spool position in real time. Ideal for high-precision dynamic control in critical die-casting phases (e.g., molten metal injection). - Proportional Valves:
Typically operate in open-loop (though some advanced models support closed-loop). They rely on preset parameters without real-time feedback, making them less precise but cost-effective for non-critical tasks (e.g., mold clamping).

Dynamic Performance & Response Speed

- Servo Valves:
High-frequency response (up to 200+ Hz), near-zero deadband, and millisecond-level response times. Suited for rapid, continuous adjustments (e.g., optimizing injection speed for mold filling). - Proportional Valves:
Lower frequency response (<50 Hz) and inherent deadband (~3% overlap). Modern high-end models (e.g., TFP series with VCD technology) can approach servo-like performance.
Contamination Resistance & Maintenance
- Servo Valves:
Require ultra-clean oil (NAS Class 5) due to tight internal clearances (micron-level). Vulnerable to contamination in dusty die-casting environments. - Proportional Valves:
Tolerate lower oil cleanliness (NAS Class 7-8) with larger clearances. Designs like the TFP series include fail-safe features (e.g., spool locking) for reliability in harsh conditions.

Energy Efficiency & Actuation
- Servo Valves:
Use torque motors with low power consumption (milliamperes). Advanced pilot stages (e.g., Moog’s jet-pipe design) enhance sensitivity and energy efficiency. - Proportional Valves:
Rely on proportional solenoids requiring higher current (1–2A). Some models integrate LVDT feedback and electronic closed-loop (e.g., EFB tech) to improve efficiency.
Cost & Applications
- Servo Valves:
Expensive (3–5x cost of proportional valves) and require precision filtration/controllers. Used in core processes (e.g., injection pressure/speed control). - Proportional Valves:
Cost-effective for auxiliary systems (e.g., ejectors, cooling circuits). The rule of thumb: “Use proportional valves unless servo precision is essential.”
Die-Casting-Specific Designs
- Haichen Proportional Valves:
Incorporate Haichen pilot tech for energy savings and contamination resistance, ideal for high-cycle cold chamber die casting machines. - TFP Servo-Proportional Valves:
Haichen die casting machines use VCD tech for high-pressure/high-flow precision in injection systems. Optional spool locking prevents defects from accidental pressure loss.
Table
| Feature | Servo Valves | Proportional Valves |
|---|---|---|
| Control | Closed-loop (feedback) | Open-loop/partial closed-loop |
| Frequency Response | 50–200 Hz | 10–50 Hz |
| Deadband | Zero overlap | Positive overlap (~3%) |
| Oil Cleanliness | NAS Class 5 | NAS Class 7–8 |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Typical Use | Injection speed/pressure | Mold clamping, ejectors |
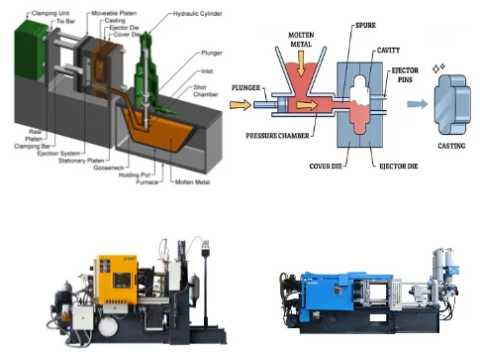
Selection Criteria
Choose based on dynamic performance needs, operating environment, and budget. Servo valves excel in precision tasks (e.g., thin-wall casting to minimize flash), while proportional valves are economical for standard applications or auxiliary functions.
Advantages of Die Casting Servo Valves
As the “intelligent core” of die-casting machine hydraulic systems, die-casting servo valves precisely regulate oil flow and pressure via electrical signals, directly determining critical parameters such as injection speed and intensification response. In high-end manufacturing fields like new energy vehicle (NEV) integrated die-casting and complex thin-wall component production, these valves

leverage millisecond-level dynamic response, nanometer-scale positioning accuracy, and closed-loop adaptive control to overcome the limitations of traditional proportional valves in precision, energy efficiency, and stability. Below is a comprehensive analysis of their core advantages:

- Ultra-Fast Response & Precision Control
- Energy Efficiency & System Stability
- Environmental Adaptability & Durability
- Advanced Process Capabilities
- Total Cost Revolution
Ultra-Fast Response & Precision Control
- Dynamic Performance: MOOG D682 series (step response: 11 ms) and Hengli 2WRCVE series (10-27 ms) enable closed-loop adjustments of injection speed with millisecond precision.
- Motion Accuracy: UBE S-DDV valves achieve full closed-loop feedback, ensuring smooth acceleration in low-speed phases (fluctuation < ±0.5%) and oscillation-free high-speed operation, with repeatability accuracy reaching 0.1 mm.
- Drive Innovation: Changmao Hydraulic’s voice coil motor direct-drive technology eliminates friction hysteresis in traditional pilot stages, boosting response speed by 30%.
Energy Efficiency & System Stability
- Energy Savings: Servo systems reduce energy consumption by 45-75% in cold-chamber die-casting machines, and 30-70% in retrofitted domestic machines using asynchronous servo solutions.
- Compact Design: Parker TFP series valves feature high energy density, shrinking valve block size by 40% while maintaining pressure fluctuations within ±0.05 MPa.
- Thermal Management: Precise control minimizes overflow losses, lowering oil temperature rise by 6°C+ and extending equipment lifespan by 20%.
Environmental Adaptability & Durability
- Contamination Resistance: UBE S-DDV valves use 0.2-0.4 mm oversized nozzles, while MOOG D680 series linear torque motors eliminate vulnerable micro-clearances, ensuring reliability in metal dust-heavy environments.
- Structural Robustness: Changmao’s simplified flow path design extends wear-resistant component lifespan to 5 million cycles, with maintenance intervals exceeding 6,000 hours.
- Extreme Condition Operation: Hengli 2WRCVE valves operate across -20°C to 80°C, with flow rates spanning 420-8,000 L/min and pressure tolerance up to 350 bar.
Advanced Process Capabilities
- Complex Molding: UBE UB-iC series achieves ultra-low-speed injection (0.05 m/s), reducing gas entrapment by 90% for near-porosity-free castings.
- Large-Scale Production: LEAP-series servo systems drive injection speeds up to 12 m/s, enabling 6,000T+ machines to produce 2 m² integrated body components.
- AI-Driven Optimization: Self-learning algorithms automatically compensate for mold wear deviations, elevating yield rates to 99.3%.
Total Cost Revolution
- Quality Gains: Real-time closed-loop control cuts defect rates by 4-7%, achieving surface roughness of Ra1.6 μm.
- ROI Acceleration: Cost-effective domestic servo systems shorten ROI periods to 12 months (vs. 24 months for imported systems).
- Maintenance Savings: Hydraulic oil replacement cycles extend by 50%, reducing annual upkeep costs by ¥150,000+ per machine.
Industrial Impact
Die-casting servo valves are reshaping manufacturing paradigms through precision, intelligence, and sustainability:
- Tesla Cybertruck and NIO ET5 integrated body components achieve 95%+ yield rates for 2 m² ultra-large castings.
- 5G heat sink housings attain wall thickness tolerances of 0.8 mm ±0.05 mm.
- As 8,000T die-casting machines proliferate, servo valve technology will drive the industry toward greener, faster, and higher-precision production.
This version maintains technical rigor while enhancing readability for global audiences.
Haichen die casting machine valves
Haichen die casting machines incorporate advanced servo valve control technology and integrate globally renowned hydraulic components to ensure high precision and reliability. Below is a detailed breakdown:
- Servo Valve Control in Injection Unit
Haichen’s cold-chamber die casting machines (e.g., HCD-C series) feature servo valve-controlled injection systems. This technology enables real-time optimization of injection speed and pressure by precisely regulating hydraulic flow and pressure. For instance, the AL-series cold-chamber machines utilize a C-type injection unit with servo valve control for high dynamic response, ideal for thin-walled or structurally complex parts. - Hydraulic Valve Sources
Haichen’s hydraulic systems rely on premium valves from international brands like Vickers (USA) and Rexroth (Germany) for directional control valves, and HNC/YUKEN for PQ valves. These high-quality components ensure stability even under high-pressure, high-frequency operations. For example, large machines with clamping forces up to 20,800 kN maintain short cycle times and high reliability. - Valves and Energy Efficiency
Servo valves significantly enhance energy efficiency. Haichen’s servo-driven systems dynamically adjust pump output to reduce idle energy consumption, achieving 20-50% energy savings compared to traditional fixed-pump systems. The C-series energy-efficient machines, for instance, deliver long-term cost reductions in energy usage. - Valve Maintenance and Durability
Haichen’s hydraulic systems include scheduled maintenance protocols:- Daily checks for seal leaks.
- Regular replacement of hydraulic oil and filters.
- Centralized lubrication systems (e.g., automatic lubrication every 500-700 cycles) controlled via valves to minimize manual intervention and extend component lifespan.
- Multilingual Support and Localization
The control interface supports multiple languages (English, Spanish, Russian, etc.), and hydraulic valves use globally standardized brands for easy replacement parts procurement, reducing downtime.

By the end
Haichen’s valve technology combines high-performance components, intelligent control algorithms, and systematic maintenance design to excel in precision casting, energy efficiency, and operational reliability.




