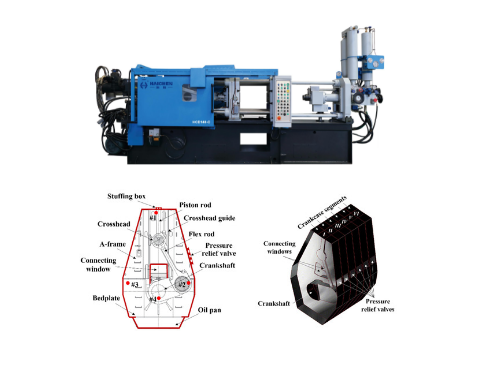
The manufacturing of crankcases requires the selection:
- Casting
- Low-pressure die-castings
- Sand casting
- Forging
Die casting is a common manufacturing process used to create crankcases, particularly for engines in vehicles like motorcycles.
The process involves injecting molten metal, usually aluminum alloys, into a reusable mold (die) under high pressure to create the desired crankcase shape.
Crankcases, which house the crankshaft and other engine components, benefit from the precision and efficiency of die casting.
Enabling the production of complex parts with high dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finishes.
Traditional casting and mechanical processing remain mainstream, but additive manufacturing has demonstrated the potential for lightweight and integrated design.
Crankcase
The crankcase is the skeleton of the engine – it houses the cylinders, numerous hoses and pipes run through the component, and countless heavy engine components are attached to it.
However, it not only supports the other components, it must also withstand the immense forces generated by combustion and piston movement.
In addition, oil heated to over 100 degrees celsius flows through the crankcase.
Extreme pressures and temperatures are one reason why a great deal of precision is required during production to ensure that a crankcase can withstand the stresses.

Crankcase manufacturing——Casting
Casting is the most popular process in crankcase manufacturing, especially for complex geometries and mass production.
- Chill Casting Technical features
- Advantages
- Case study
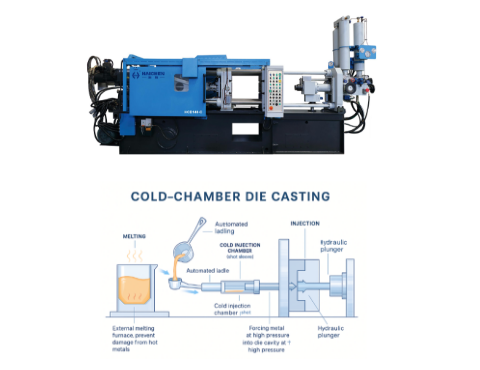
Chill Casting Technical features
The aluminum alloy melted at high temperature is injected into a water-cooled mold to quickly solidify and form a high-density structure.
For example, the aluminum alloy crankcase of the Mercedes-Benz M139 engine adopts this process, which can withstand a high load of 416 hp/500 Nm while ensuring light weight and strength.
Advantages
Grain refinement, low porosity, suitable for high-performance engines.
Case study
The weight of the crankcase of cold casting is reduced by 10%-15% compared with traditional casting, and the tensile strength is increased by 20%.

Crankcase manufacturing——Low-Pressure Die Casting (LPDC)
- Technical characteristics
- Advantages
- Applications
Technical characteristics
Liquid metal slowly fills the mold under low pressure, and forms a closed structure with the sand core.
For example, the ALUSIL® technology uses the LPDC process to produce aluminium crankcases without additional cylinder bore reinforcement and the AlSi17Cu4Mg alloy for increased rigidity (12% increase in Young’s modulus).
Advantages
Low turbulence filling reduces porosity, directional solidification optimizes microstructure.
Applications
V-arranged engine crankcases, especially for designs that require high-precision cooling channels.

Crankcase manufacturing——Die Casting technical
High-pressure injection of aluminum alloy into steel mold, rapid prototyping.
For example, an aluminum alloy crankcase reduces the crater defect rate from 8% to 0.5% by optimizing the heat dissipation design of the mold (such as the heat dissipation mesh of the lateral slider).
Challenges and optimizations
The deep cavity structure is prone to heat concentration, and the use of inlaid core design.
Such as dynamic mold insert cooling channel improves heat dissipation efficiency and prolongs the life of the mold.

Sand Casting
Compacted graphite cast iron (e.g. S415) combines high strength and thermal conductivity for use in extended-range engine crankcases.
By optimizing the gating system (sprue, sprue) and the number of sprues, sand holes and porosity are avoided.
In gravity pouring, the fishbone diagram analysis method was used to optimize the sand core fitting gap, and the proportion of core fracture defects was reduced from 15% to 0.2%.

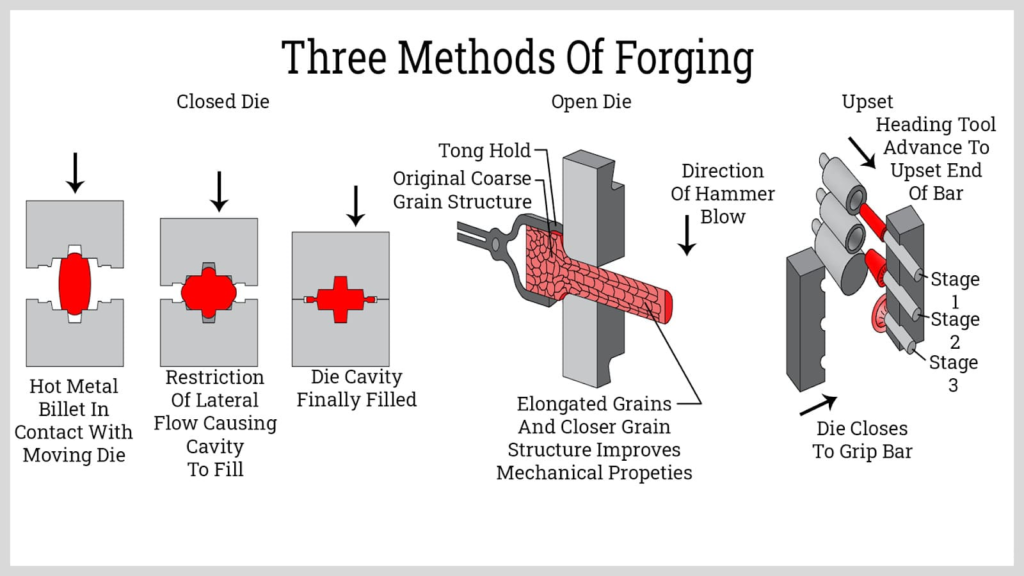
Forging
- Forged steel crankcase Marine application
- Advantages
- Lightweight forging of crankshafts Example
Forging serves primarily in applications requiring high strength and reliability.
Although manufacturers seldom use it for integral crankcases, they commonly employ it in producing crankshafts.
Forged steel crankcase marine application
The ship crankcase uses forged steel with a tensile strength of 400-1000 N/mm², must undergo explosion pressure testing, and requires explosion-proof valves.
Advantages
The grain structure of forgings is dense, and the fatigue resistance is better than that of castings.
Lightweight forging of crankshafts Example
The crankshaft of the M139 engine is made of forged steel, combined with a lightweight design (such as a hollow balance weight) to reduce inertia forces and improve speed response.
Haichen crankcase manufacturing
The crankcase is the most important component in the engine frame.
It needs to have an irregular, extremely complex, and highly precise shape, while also possessing toughness, rigidity, and high dimensional accuracy.
Haichen uses the die-casting process, which enables the production of even very complex shapes.
The reason why customers choose Haichen’s cold chamber die-casting machine is entirely due to our accumulated experience in mold design.