Hot chamber die casting machine selection tips include material selection, production requirements, cost, mold design and so on.
Hot chamber die casting machines are highly efficient casting equipment designed for low melting point alloys. They achieve fast cycles (10-20 seconds/time), high-precision production, and low material loss through an integrated furnace-injection system. Their core advantage lies in the manufacture of large quantities of small and complex parts (such as zinc alloy sanitary ware parts and 3C parts), but are limited by the melting point of the material and equipment corrosion. They complement cold chamber die casting machines and cover die casting needs from low to high melting point metals.
Choosing a suitable hot chamber die casting machine requires comprehensive consideration of multiple factors, including material properties, production requirements, equipment performance, and cost-effectiveness.

Hot chamber die casting machine selection tips: Material selection
Hot chamber die casting machines are suitable for low melting point metals such as zinc, magnesium alloys, lead and tin. These materials have good fluidity, can quickly fill the mold and form dense castings. For example, zinc alloy is one of the most commonly used materials in hot chamber die casting. Its low melting point (about 450°C) is suitable for mass production of small and complex parts. In contrast, high melting point metals such as aluminum and copper are more suitable for cold chamber die casting machines.
Zinc alloy (Zn)
Characteristics: low melting point (419°C), less oxidation and porosity problems, good fluidity, suitable for the production of thin-walled, high-surface-finish complex small parts (such as zippers, buttons).
Haichen zinc alloy medals
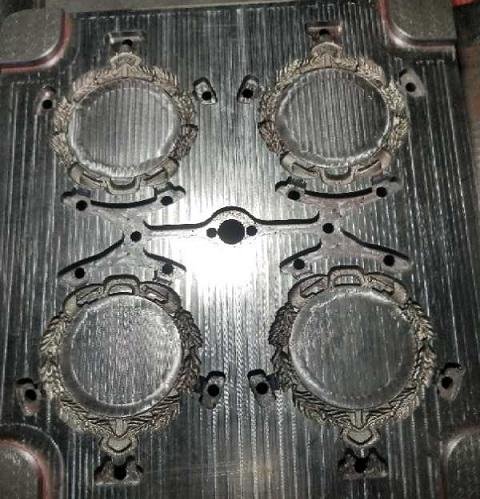

To produce zinc alloy medals, with four cavities zinc alloy medal mould, select Haichen HCD90-H series. Haichen 90ton hot chamber die casting machine. With die locking force 900KN, dosage of fluid metal per shot(Zn) 1.6kg.
Haichen die-casting machine has a high cost-performance ratio and is directly sold by the manufacturer with transparent prices. And Haichen is well-known in the die-casting machine industry for its automated die-casting production. With years of rich manufacturing experience, we have comprehensively developed various high-performance automatic die-casting technologies.
The Haichen H series high-efficiency and energy-saving zinc alloy hot chamber die-casting machine has a price range between $13000 and $36000, still, its high-efficiency and energy-saving features can save energy costs in long-term use.

Lead alloy (Pb)
Characteristics: extremely low melting point (327°C), low oxidation risk, suitable for low-strength parts (such as counterweights, radiation shielding parts).

Production requirements
The main advantages of hot chamber die casting machines are their fast production cycles and high production efficiency. Since their metal chambers directly immerse in molten metal, no additional furnace equipment is required. So faster cycle times can be achieved.
This feature makes hot chamber die casting machines very suitable for mass production of small parts, such as automotive parts, household appliance parts, etc.
Clamping force
Core parameter, usually ranging from 100-1600 tons (as specified in Chinese standard JB/T 6309.1), but there are few models exceeding 400 tons in actual production.
Clamping force needs to be calculated based on the projected area of the part and the injection pressure to ensure that the mold is stably closed under high pressure.
Injection pressure
7-75 MPa (about 70-750 kgf/cm²), too low pressure will lead to insufficient filling, too high pressure will accelerate equipment wear.
Injection speed
Dry injection speed needs to be ≥5 m/s (such as YIZUMI HM series) to achieve high-precision filling of thin-walled parts (<1mm).
Cycle time
Average 10 seconds/piece, automatic line can reach up to 1000 pieces/hour (small parts).
Mold and process requirements
- It needs to withstand high pressure and thermal cycles, and the material needs to be resistant to thermal fatigue (such as H13 steel).
- The mold needs to be equipped with an ejector mechanism, cooling system and vacuum exhaust option (to reduce pores)
Process control
- Two-stage injection: low-speed filling to avoid air entrainment, high-speed pressurization to ensure density
- Temperature control: gooseneck/nozzle needs electronic heating (±2°C accuracy) to maintain metal fluidity
- Vacuum assist: optional vacuum system (≤0.5 Pa) to improve casting density

Equipment performance of Hot chamber die casting machine selection tips
The core components of the hot chamber die casting machine include the heating furnace and pressure chamber for molten metal. Since metal chamber always immerses in molten metal. Special attention need pay to the corrosion resistance of the equipment and the thermal stability of the mechanical parts.
In addition, modern hot chamber die casting machines usually equip with advanced control systems (such as PLC). It can ensure the accuracy and stability of the injection process.
Efficient production
- Short cycle time: The average single die-casting cycle is about 10 seconds (semi-automatic machine 250 pieces per hour, fully automatic machine can reach 1000 pieces/hour).
- High-speed injection: dry injection speed> 5m/s, pressure and flow are precisely controlled by proportional valves, parameters can be set directly on the screen, shortening the debugging time.
- Speed up the clamping system: YIZUMI HM series adopts a high-speed toggle system, and the clamping speed is 10% faster than traditional models, significantly improving production efficiency.
High precision and stability
- Injection system optimization: two-stage injection control, combined with high-precision imported stroke sensors, ensures that the injection process is accurate and repeatable.
- Enhanced clamping rigidity: ductile iron template (highest rigidity design) reduces flash, and chrome-plated high-strength tie rods extend service life.
- Temperature control technology: advanced electronic heating system (nozzle/gooseneck) with energy-saving burners to achieve stable molten metal temperature.
Intelligent operation
- Siemens PLC control system: high-end human-machine interface (HMI) supports visual parameter setting, fault self-diagnosis and data storage functions to improve operation convenience.
- Real-time parameter calculation: some models can automatically optimize injection parameters (such as pressure/speed curve) to improve yield.

Cost-effectiveness
The initial investment of hot chamber die casting machine is relatively low because its structure is relatively simple and does not require additional furnace equipment.
However, due to its high production efficiency, hot chamber die casting machine can reduce the production cost per unit product in the long run.
Production efficiency advantages
- The hot chamber machine furnace is integrated with the injection system, with a faster cycle speed (15-18 times/minute), saving 30%-50% of production time compared to the cold chamber machine.
- Energy-saving features: High-efficiency models (such as the YIZUMI HM series) reduce energy consumption by optimizing the hydraulic system and PLC control, saving energy costs in the long term.
High material utilization
- Reduce metal waste and low raw material loss.
- Near-net shape process reduces subsequent processing costs.
Maintenance cost
- Applicable to low melting point metals (zinc, magnesium, etc.), reduce equipment corrosion and extend service life.
- However, high-pressure environments (100-175 MPa) may increase component wear.
Mold design
The design of the mold has an important influence on the quality of hot chamber die casting. Optimizing the mold geometry, gate angle and cooling channel layout can significantly improve the surface quality and dimensional accuracy of the casting.
Runner and gate design
- Take advantage of the direct connection between the hot chamber machine furnace and the mold to design a short runner to reduce heat loss.
- The gate position must ensure that the molten metal fills the complex cavity at high speed.
Mold draft and demolding design
A draft analysis must be performed to avoid undercuts that cause part jamming.
The ejector system must match the machine ejection stroke:
The ejection stroke (L) after mold opening must meet: L ≥ part height + core pulling distance + 10mm safety margin.
Exhaust system
- Design an efficient exhaust slot to prevent pore defects.
- The hot chamber machine needs to strengthen exhaust due to high-speed filling.
Maintenance and operation
Hot chamber die casting machines require regular maintenance to ensure the normal operation of the equipment. For example, damage to hydraulic components or lack of daily maintenance may cause equipment failure. In addition, operators need to be familiar with the working principle and operating specifications of the equipment to avoid equipment damage caused by misoperation.
Daily inspection
- Hydraulic system: monitor oil temperature (35–55°C), oil level and leakage, and replace flame-retardant hydraulic oil regularly (ISO VG46 is recommended).
- Electrical safety: Check for aging of circuits and loose terminals, and ensure that the emergency stop button functions normally.
- Lubrication management: Manually lubricate key components 1–2 times a day, and ensure that the oil level of the automatic lubrication system is sufficient.
Maintenance of core components
- Nozzles and goosenecks:
Regularly disassemble and grind or turn for repair, and replace if the stretching stroke is exceeded.
Remove the injection piston when shutting down, and keep the nozzle heated to prevent metal solidification. - Injection piston: If stuck, melt the alloy and eject it with the maximum return force, and remove it with special tools.
- Mold:
Preheat to 350°F (175°C) before injection to avoid thermal shock cracking.
Regularly record the gate thickness to avoid mold damage caused by excessive clamping force.
Regular maintenance
- Annual overhaul: Replace the injection head and seals, clean the oil tank and replace the filter.
- Hydraulic system: Perform oil analysis every 2 years to prevent valve failure caused by oil quality deterioration
Scope of application
Hot chamber die casting machines are suitable for producing small, simple-shaped parts, especially those that require high precision and good surface quality. For example, automobile engine parts, household appliance housings, etc. are ideal application areas for hot chamber die casting.
Thus when choosing a hot chamber die casting machine, a comprehensive evaluation should be conducted based on specific production needs, material properties, and cost budget. For companies that need to produce small parts in large quantities and are cost-sensitive, a hot chamber die casting machine is an ideal choice. For companies that need to produce large or high-precision parts, they may need to consider a cold chamber die casting machine.



