Industrial application of mold temperature controllers in die casting is to control mold temperature, ensure the quality of castings, improve production efficiency and extend the service life of molds.
The basic principle of MTC is to control the mold temperature and maintain stability through the circulation of heating or cooling media.
Because improper temperature control in die-casting can lead to defects such as shrinkage cavities, gas holes, and cold shuts.
In addition, MTC has more advantages over traditional methods such as gas heating, such as temperature uniformity and stability.
MTC has demonstrated irreplaceable value in addressing the demands of complex castings, reducing energy consumption and enhancing competitiveness.

The Influence of Mold Temperature Controller On aluminum Alloy Die Casting Production
With the development of large-scale transportation technology, the lightweight of automobile and aircraft has also been put on the agenda.
Industries such as automobiles and airplanes are slowly beginning to use aluminum alloy die casting referring to pure aluminum or aluminum alloy equipment components obtained by casting processing methods instead of traditional stamping parts.
Die-casting mold temperature controllers are also increasingly used in the die-casting industry, which is of vital importance to the die-casting process.
In this guide, we discuss what’s the influence of mold temperature controller on aluminum alloy die casting production.
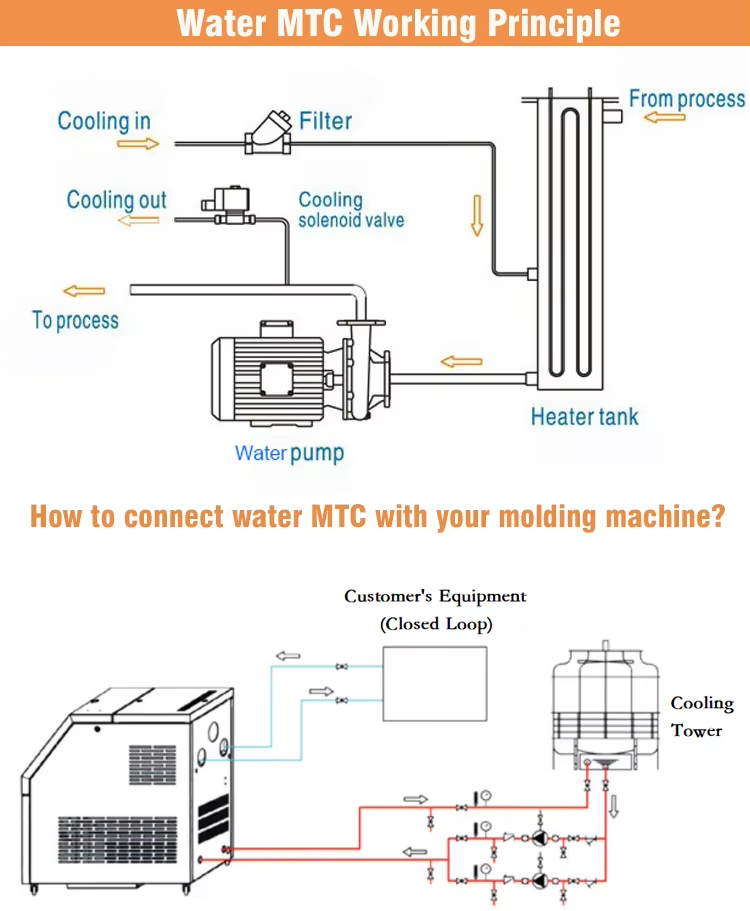
Working principle and technical composition
- Heat exchange cycle
- Sensor feedback
- PID control
- Safety mechanism
Heat exchange cycle
First, the pump drives the heat transfer medium (oil or water) from the reservoir.
Then, after flowing through the heater-cooler unit, the medium enters the mold’s flow channels, where it absorbs or releases heat.
Finally, it returns to the reservoir to complete the cycle.
Sensor feedback
The temperature sensor monitors the return oil/return water temperature in real time.
The data is transmitted to the controller.
After comparing with the set value, it triggers the heating or cooling action.
PID control
By adjusting the response speed and stability through proportional (P), integral (I).
And differential (D) parameters, it achieves high-precision temperature control within ±1℃.
Safety mechanism
Equipped with multiple safety functions such as over-temperature protection, circuit blockage detection, and motor overload protection.
The core role of mold temperature control in die-casting processes
- Quality Assurance
- Excessively high temperature
- Too low temperature
- Production efficiency optimization
Quality Assurance
The mold temperature directly affects the solidification process, internal structure and surface quality of the casting.
Uneven temperature can lead to defects such as shrinkage cavities, gas holes, cold shuts and mold sticking.
Excessively high temperature
The fluidity of the molten metal is poor, which is prone to hot cracks and bubbles, shortening the service life of the mold (due to the accumulation of thermal stress).
Too low temperature
The molten metal solidifies too quickly, resulting in cold streaks, insufficient filling, and a decrease in the density of the casting.
Production efficiency optimization
A stable temperature field can shorten the cooling time and reduce the production cycle.
For example, when maintaining the mold at 180-280℃ (aluminum alloy) through MTC, the filling efficiency is increased by more than 15%.
Avoid downtime adjustments caused by temperature fluctuations and enhance the continuity of the production line.
The service life of the mold is prolonged.
Dynamic thermal balance reduces the thermal fatigue of molds and prevents cracks and deformations.
For instance, when the temperature of an aluminum alloy die-casting mold is controlled at 180-240℃, its service life can be extended by 30%.
The application of MTC in Die Casting
- Temperature control by material
- The complex temperature control requirements of integrated die-casting
- Special process support
- Differential control of thin-walled and thick-walled parts
Temperature control by material
Aluminum alloy:
Working temperature 180-270℃, high-temperature oil circulation is required (up to 350℃) to achieve uniform heating.
Magnesium alloy:
It has a higher temperature requirement (180-300℃) and needs a high-temperature type MTC in combination with an indirect cooling system.
Zinc alloy:
Low-temperature requirement (100-200℃), suitable for water circulation MTC, temperature control accuracy ±0.5℃.

The complex temperature control requirements of integrated die-casting
Large castings (such as the front cabin size of 1.5m×1.0m) require temperature control through zonal division: the high-temperature zone utilizes oil at 320℃.
While the low-temperature zone employs water at 200℃.
Additionally, the system achieves thermal balance by integrating the machine-side cooling station.
The centralized control system (such as the Siemens WinCC platform) integrates multiple temperature control devices to achieve real-time distribution of flow, pressure and temperature.
Special process support
MTC indirectly controls the temperature through heat transfer oil (20-300℃) to prevent the mold from overheating and causing product deformation.
Differential control of thin-walled and thick-walled parts
Thin-walled parts require a higher temperature (250℃) to ensure fluidity, while thick-walled parts need a lower temperature (200℃) to accelerate solidification.
Mold temperature controllers core application scenarios
- Automobile manufacturing industry
- Motor housing and lightweight components
- Intelligent control trend
- Electronic components and precision manufacturing
- The home appliance and consumer electronics industry
- Aerospace and high-end materials
Automobile manufacturing industry
Large-scale integrated die-casting
It is used for the production of large structural components such as the front cabin, rear floor, and battery tray.
It requires the configuration of 20 to 40 mold temperature control units (with a power of 50 kW) to meet the demands of 70,000 to 160,000 kN die-casting machines.
For instance, Aode Company provides 21 sets of mold temperature control systems for die-casting islands with a capacity of over 6,000 tons.
Achieving precise temperature control of molds, pressure chambers, and punches through a wide temperature range of 20 to 320℃.

Motor housing and lightweight components
By using thermal sensors and mold temperature control units for interlocking control, the problem of temperature synchronization in complex structures is solved.
And the qualification rate of castings is improved (such as the case of pure electric vehicle motor housing die-casting).
Intelligent control trend
Enterprises such as Changan Automobile have introduced intelligent algorithms to optimize mold temperature regulation.
Solve the problem of temperature zone balance in large molds, and reduce product defects.

Electronic components and precision manufacturing
Technical requirements
High precision (±1℃), rapid response (flow rate ≥80 L/min), and dust-proof design are required to prevent dimensional deformation or surface defects of electronic components due to temperature fluctuations.
For instance, the dual-loop mold temperature control machine can independently regulate the temperature of different mold areas, making it suitable for the production of precision parts such as micro connectors and heat sinks.
Material adaptability
Zinc alloy die-casting requires low-temperature control (100-200℃), while magnesium alloys demand high-temperature stability (180-300℃).
The mold temperature control machine needs to flexibly switch between heating and cooling modes.
The home appliance and consumer electronics industry
Plastic part molding
By using a mold temperature control machine to shorten the injection molding cycle and enhance the surface finish (such as mobile phone casings and home appliance panels).
The cold and hot integrated mold temperature control machine can quickly switch temperatures, reducing energy consumption by more than 30%.
Composite material processing
In the SMC fiberglass reinforced plastic and carbon fiber RTM processes, the mold temperature control unit needs to be equipped with a blowing oil return function to meet the frequent mold changing requirements.
Aerospace and high-end materials
High-temperature alloy die-casting:
It needs to withstand an oil circulation temperature control system above 320℃, meeting the extreme process requirements of titanium alloys and nickel-based alloys.
Radiation and shock resistance design:
For the testing environment of aviation components, the mold temperature control unit needs to integrate an anti-interference control system and a high-pressure resistant pump (such as magnetic levitation pump technology).
Key points for selection and use
The alloy type matches the temperature
Mold structure and heat exchange efficiency
Safety and Maintenance
The alloy type matches the temperature
Select the medium type (oil/water) and temperature range based on the material.
For instance, magnesium alloys require an oil temperature control machine to support temperatures above 300℃.
Mold structure and heat exchange efficiency
The flow channel design needs to maximize the heat exchange area, and the channel diameter should be adapted to the flow rate requirements.
Therefore, for complex molds, it is recommended to adopt multi-loop independent temperature control to avoid local overheating.

Safety and Maintenance
Give priority to choosing equipment with automatic exhaust and blockage detection functions.
In addition, the heat transfer oil should be replaced regularly (mineral oil is prone to aging).
And the sealing performance of the pump should be monitored.



