Cast aluminum cookware is widely used in kitchens due to its excellent heat conductivity, lightweight nature, and durability.
However, concerns about its safety often arise, particularly regarding potential health risks.
Below is a detailed analysis of the safety of cast aluminum pots, addressing common questions and misconceptions.
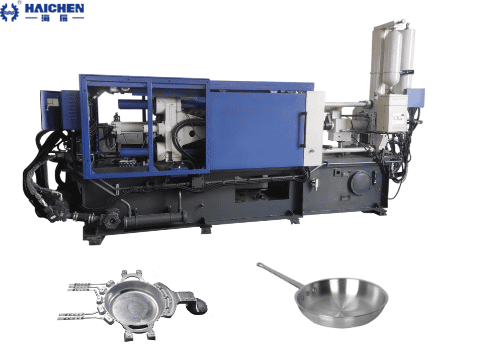
Answers to the safety of aluminum alloy die-cast cookware
- Aluminum and Health Concerns
- Types of Cast Aluminum Cookware
- Safety Considerations
- Benefits of Cast Aluminum Cookware
- Tips for Safe Use
Aluminum and Health Concerns
- Aluminum Exposure: Aluminum is a naturally occurring metal found in food, water, and air. While excessive aluminum exposure has been linked to health issues (e.g., neurological disorders), the amount leached into food during cooking is minimal.
- Cooking Factors: Acidic foods (e.g., tomatoes, citrus) or prolonged cooking in uncoated aluminum pots can increase leaching. However, the levels are generally well below safety limits set by health organizations.

Types of Cast Aluminum Cookware
- Uncoated Cast Aluminum: Bare aluminum pots and pans are lightweight and conducts heat well but is more prone to leaching and discoloration with acidic foods.
- Anodized Aluminum: An electrochemical process creates a hard, non-reactive surface, reducing leaching and making it safer for cooking acidic foods.
- Non-Stick Coated Aluminum: A non-stick coating (e.g., Teflon) is applied to prevent food from sticking and minimize aluminum contact. However, the coating must be free of harmful chemicals like PFOA.
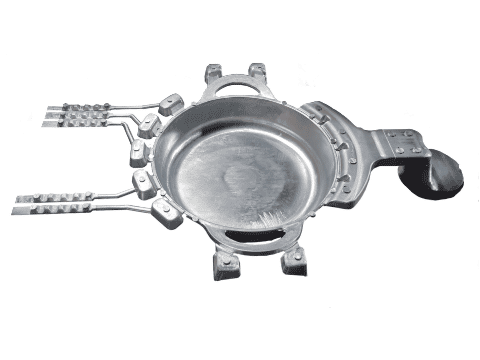
Safety Considerations
- Regulatory Standards: In many countries, aluminum cookware is regulated to ensure safe levels of metal leaching. For example, the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) have established guidelines for aluminum exposure.
- Anodized and Coated Options: These are considered safer than uncoated aluminum, as they prevent direct contact between food and the metal.
- Avoiding Scratches: Damaged coatings or scratched surfaces can increase leaching and expose food to aluminum. Regularly inspect and replace damaged cookware.
Benefits of Cast Aluminum Cookware
- Heat Conductivity: Aluminum heats evenly, reducing hot spots and improving cooking results.
- Lightweight: Easier to handle compared to cast iron or stainless steel.
- Durability: Resistant to rust and corrosion, especially when anodized or coated.

Tips for Safe Use
- Avoid Acidic Foods: Use stainless steel or anodized aluminum for cooking acidic dishes.
- Hand Wash: Avoid harsh detergents or abrasive scrubbers that can damage coatings.
- Inspect Regularly: Replace cookware with worn or scratched surfaces.
- Choose Quality Brands: Opt for reputable brands that comply with safety standards.
Haichen Complete Die-Casting Process for Aluminum Alloy Cookware
- Raw Material Preparation
- Smelting and Die-Casting
- Custom Aluminum Pot Molds
- Trimming and Shaping
- Heat Treatment and Annealing
- Surface Treatment and Teflon Coating
- Accessory Installation
- Quality Control and Inspection
- Packaging and Distribution

Raw Material Preparation
Gas Furnace
Select aluminum alloy billets with uniform density, excellent thermal conductivity, and solidification properties as raw materials.
Smelting and Die Casting
Characteristics of Die Casting Ladle
The aluminum alloy billet is melted into a liquid state and then pressed into a mold using a cold chamber die casting machine to form an aluminum pot.
Custom Aluminum Pot Molds
Aluminum Pot Die Castings
Molds are manufactured according to design drawings, usually made of steel, and consist of a cavity and a core.
Edge Trimming and Shaping
Using a hydraulic trimming machine to trim the external gate and backing material of the aluminum pot, followed by polishing and shaping with a polishing machine.
Heat Treatment and Annealing
The aluminum pot undergoes heat treatment to improve mechanical properties and eliminate internal stress.
Surface Treatment and Teflon Coating
An oxide protective layer is formed through grinding, polishing, and anodizing, followed by a Teflon coating to enhance durability and non-stick properties.
Accessory Assembly
Handles, lids, and other accessories are configured and installed according to the different uses of the aluminum pot products.
Quality Control and Inspection
Each aluminum pot undergoes rigorous quality inspection to ensure that dimensions, surface finish, and overall quality meet standards.
Packaging and Distribution
Finished aluminum pots are carefully packaged by workers to prevent damage during transportation.
By the end
Cast aluminum cookware is generally safe for everyday use, especially when anodized or coated. While uncoated aluminum may leach small amounts of metal into food, the levels are typically within safe limits. By following proper care guidelines and choosing high-quality products, you can enjoy the benefits of cast aluminum cookware without significant health concerns. For those with specific health conditions or concerns, consulting a healthcare professional is advisable.
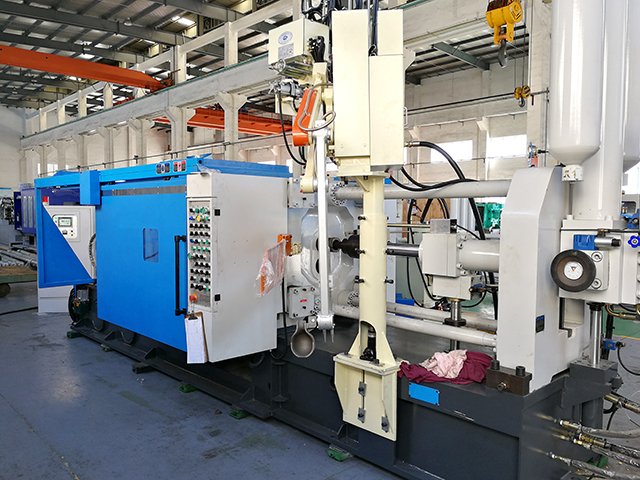

Haichen has extensive experience in the Argentine cold-chamber aluminum alloy die-casting cookware market.
Welcome to call us for more details.



