Not all aluminum pans are created equal. Yes, they’re all pans and serve the same purpose. But there’s a significant difference between a great Cast aluminum cookware and an average one. This isn’t just in price (which is obvious when comparing pans at the store), but also in quality, which sometimes isn’t immediately apparent until you use it at home.
Aluminium is an excellent heat conductor, making it an ideal choice for cookware. The table below compares aluminium with other metals. The thermal conductivity of metals is measured in watts per metre per kelvin (W/m.k). Aluminium has a thermal conductivity 16 times that of stainless steel.
At the same time, the low price of aluminium is an important factor in its popularity in the cookware sector. Compared to alternatives such as copper, cast iron or stainless steel cookware, aluminium cookware is usually only a fraction of the price.
Die Casting aluminum cookware production line
Cast aluminum cookware is generally safe, but proper use and maintenance matter. Here’s what you need to know:

- Safety & Aluminum Exposure
- Best Practices for Cooking
- Care & Maintenance
- Health Research & Alternatives
Safety & Aluminum Exposure
- Leaches minimal aluminum: Normal cooking releases tiny amounts, which health agencies like the FDA and WHO consider safe.
- Potential risks: Acidic foods (tomatoes, citrus) or salty dishes can corrode bare cast aluminum, increasing aluminum absorption. Nonstick or anodized coatings reduce this risk.
Best Practices for Cooking
- Avoid acidic/salty foods in bare pans: Use coated or anodized cast aluminum for these dishes.
- Prevent scratches: Metal utensils can damage the surface, so use wood or silicone tools instead.
Care & Maintenance
- Clean gently: Hand wash with mild soap—no harsh scrubbing—to preserve the cookware’s protective layer.
- Check for damage: Deep scratches or pitting may increase aluminum leaching; replace heavily worn pans.

Health Research & Alternatives
- FDA stance: Regular use poses no significant risk, as dietary aluminum intake from cookware remains low.
- Safer options: Stainless steel, cast iron, or ceramic cookware work well for those wanting to minimize aluminum exposure.
Bottom Line
✅ Safe for everyday cooking if you avoid acidic foods in uncoated pans and maintain them properly.

How cast aluminum cookware made?
The manufacturing process of cast aluminum cookware primarily involves die casting techniques, where molten aluminum or aluminum alloy is poured into molds and undergoes subsequent processing. Here’s a detailed breakdown:

- Raw Material Preparation & Mixing
- Mold Design & Filling
- Casting & Solidification
- Post-Casting Processing
- Quality Control & Testing
Raw Material Preparation & Mixing
- Alloy composition: Manufacturers blend aluminum with metals like copper or magnesium to boost hardness and durability.
- Melting: Workers melt the alloy in large furnaces at 1200°F (649°C). Precise ratios ensure optimal thermal conductivity and strength.
Mold Design & Filling

- Mold types: Factories use steel or iron molds with two parts: a cavity (for shaping) and a plug (to create hollows for handles or lids).
- Gating system: Workers pour molten aluminum through a gating system to fill the mold evenly. Engineers design thicker sections (e.g., cookware bases) to improve heat retention.
Casting & Solidification
- Cooling: The molten aluminum solidifies inside the mold, forming a rough cookware shape.
- Demolding: After cooling, technicians remove the cast piece and trim excess material (e.g., sprues or flash).
Post-Casting Processing
- Trimming & Machining: Grinding or CNC machines remove excess material. Workers polish surfaces for smoothness.
- Surface Treatments:
- Non-stick coatings: Factories spray or electrostatically deposit coatings like PTFE, ceramic, or Greblon C3+, then cure them at high temperatures.
- Hard-anodizing (optional): Electrochemical oxidation creates a scratch-resistant, corrosion-proof layer.
- Magnetic base: Some manufacturers add a stainless steel layer for induction compatibility.
- Assembly: Workers attach handles or knobs using rivet-free designs for durability.
Quality Control & Testing
- Performance tests: Labs test thermal shock resistance (rapid heating/cooling), corrosion resistance, and coating adhesion.
- Safety checks: Manufacturers ensure compliance with FDA or EU standards for food contact materials.

Key Advantages of Cast Aluminum Cookware
- Thermal efficiency: Thick, even walls distribute heat uniformly, reducing hot spots.
- Durability: Cast structures resist warping and scratching better than stamped or rolled aluminum.
- Versatility: Cookware works on most stovetops (gas, electric, induction with added base).
Maintenance Tips
- Use non-abrasive cleaners and avoid metal utensils to protect coatings.
- Hand wash non-stick surfaces; check oven-safe temperatures based on coating type.
This process balances traditional casting methods with modern coatings to create lightweight, high-performance cookware.
Haichen Cast aluminum cookware machine
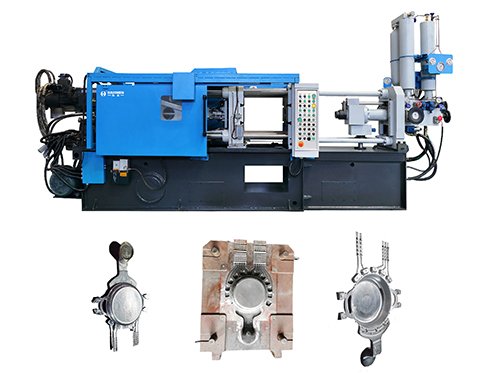
As a leading manufacturer of cold-chamber die-casting machines, Haichen excels in aluminum cookware production with advanced technology and extensive industry expertise. Below is a detailed breakdown of its machinery and processes:
- Core Technologies & Equipment
- Production Workflow
- Product Advantages
- Applications & Market
- Services
Core Technologies & Equipment
- Cold-Chamber Die Casting:
- High-pressure (50.4–127.3 MPa) injection of molten aluminum into molds ensures superior product density, strength, and resistance to deformation.
- Ideal for complex shapes like pots, pans, and griddles.
- Machine Tonnage & Applications:
- 220–300-ton models: Suitable for small cookware (e.g., sandwich grills, 700g–3kg).
- 580-ton models: Produce large cookware (pots, frying pans) with thick walls for even heat distribution and durability.
- Control Systems:
- Siemens PLC automation with multi-language interfaces (Chinese, English, Russian).
- Real-time injection curve monitoring for precision molding.
Production Workflow

- Material Preparation:
- Aluminum ingots are melted and fed into the cold-chamber machine. Custom molds adapt to product designs (e.g., pot bodies, handles).
- Die Casting:
- High-speed, high-pressure forming creates rough components.
- Post-Processing:
- Trimming/Polishing: Hydraulic trimming removes burrs; polishing ensures smooth edges.
- Heat Treatment: Stress-relief annealing improves mechanical properties.
- Surface Coating:
- PTFE (Teflon) non-stick coatings applied for durability and food safety compliance.
- Quality Control:
- Rigorous checks for dimensions, surface finish, and coating integrity. Defective items are reworked or scrapped.
Product Advantages

- Performance: Thick-walled designs resist warping; excellent thermal conductivity saves energy.
- Customization: Interchangeable molds support diverse designs (e.g., handles, lids).
- Certifications: CE/ISO 9001 certified; complies with GB/T 21269-2023 standards (no harmful lead leaching).
Applications & Market
- Case Studies: Haichen’s machines produce cookware (saucepans, skillets, milk pots) for global manufacturers.
- Cost Efficiency: Integrated production lines reduce intermediate costs. Energy-saving features (e.g., C-Series models) lower long-term operational expenses.
Services
- Custom Solutions: Adjustable parameters (injection speed, pressure stages).
- After-Sales Support: 1-year warranty with global technical assistance.

Overall: Haichen’s cast aluminum cookware machinery combines cutting-edge cold-chamber die-casting technology, flexible customization, and stringent quality control to deliver efficient, safe, and competitive solutions for global manufacturers. Its equipment meets diverse production needs while adhering to international safety and performance standards.



