Zinc is highly suitable for die casting due to its exceptional properties and process advantages, as supported by extensive evidence.
Zinc alloy die casting is very popular in the manufacturing of parts for the construction and industrial sectors, but its most common application is still in the automotive industry. In fact, many parts in cars can be manufactured using die casting, we can also tell modern die casting technology was originally developed for the automotive industry.
Zinc alloys are suitable for parts manufacturing due to their ductility, impact strength and low melting point. In addition, because the material has a low melting point, the casting process can be carried out at lower temperatures. Therefore, zinc alloys are referred to as ‘hot chamber die casting’.
Key Advantages of Zinc for Die Casting
- Superior Fluidity and Castability
- Mechanical and Physical Properties
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Design Flexibility
- Environmental and Economic Benefits
- Comparison with Other Materials
Superior Fluidity and Castability
Zinc alloys exhibit high fluidity when molten, enabling intricate geometries, fine details, and tight dimensional tolerances . This makes them ideal for thin-walled components (as thin as 0.4 mm) and complex shapes without compromising precision.

Mechanical and Physical Propertie
- Strength and Durability: Zinc alloys like Zamak 3 and ZA-8 offer excellent tensile strength (up to 374 MPa), impact resistance, and ductility, outperforming many aluminum and magnesium alloys .
- Wear and Corrosion Resistance: Zinc’s natural corrosion resistance and compatibility with protective coatings (e.g., electroplating) enhance longevity in demanding environments .
Cost-Effectiveness
- Lower Melting Point: Zinc’s low melting point (~387–480°C) reduces energy consumption and extends die life (up to 10× longer than aluminum dies) .
- High Production Efficiency: Fast cycle times (as low as 15 seconds) and minimal post-processing (e.g., no secondary machining for surface finishes) lower per-unit costs .
Design Flexibility
Zinc allows for near-net-shape casting, enabling lightweight designs with reduced material waste . Its compatibility with hot-chamber die casting (unlike aluminum) further simplifies production of small, intricate parts .
Environmental and Economic Benefits
Zinc is 100% recyclable, and its long tool life reduces resource consumption over time . Alloys like Zamak 3 dominate North American markets due to their balanced cost-performance ratio .

Comparison with Other Materials
- Aluminum: While lighter, aluminum requires higher pressures/temperatures, shorter die life, and more post-processing. Zinc excels in surface finish, fluidity, and dimensional stability .
- Magnesium: Though lighter, magnesium is costlier, harder to cast, and less durable under stress .
- Plastics: Zinc offers superior strength, heat resistance, and recyclability, making it preferable for high-stress applications .

Common Zinc Alloys
- Zamak 3: The most widely used alloy (North America) for its balance of castability, strength, and cost .
- ZA-8: High-aluminum alloy with superior creep resistance, suitable for hot-chamber casting .
Limitations
Zinc’s higher density (6.6 g/cm³) makes it heavier than aluminum (2.7 g/cm³) or magnesium (1.8 g/cm³), which may be a drawback for weight-sensitive applications .

Zinc is an excellent choice for die casting, particularly for applications requiring precision, durability, and cost-efficiency. Its advantages in fluidity, die longevity, and recyclability make it a versatile and sustainable option across industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods
Technical advantages of zinc alloy die casting
Zinc alloy die casting offers numerous technical advantages, making it a preferred manufacturing method across various industries. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its key benefits:

- High Production Efficiency and Extended Mold Life
- Superior Fluidity and Thin-Wall Casting Capability
- Outstanding Mechanical Properties
- Design Flexibility and Precision
- Cost-Effectiveness
- Surface Finish and Treatment Versatility
- Innovative Alloys and Process Advancements
- Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
High Production Efficiency and Extended Mold Life
- Zinc alloys have a low melting point (~385–390°C), enabling rapid filling of molds and shorter cycle times .
- Mold longevity is exceptional: zinc molds can withstand 750,000 to 2 million cycles, far exceeding aluminum (250,000 cycles) and magnesium (500,000 cycles) .
- Hot-chamber die casting (commonly used for zinc) minimizes downtime and maintenance due to lower operating temperatures and pressures .
Superior Fluidity and Thin-Wall Casting Capability
- Zinc alloys exhibit excellent fluidity, allowing the production of ultra-thin walls (as low as 0.3 mm) and intricate geometries that are challenging for other alloys like aluminum or magnesium .
- High-vacuum die casting further enhances this capability, producing components with better sectional integrity and reduced porosity .
Outstanding Mechanical Properties

- High tensile strength (up to 396.4 MPa in high-vacuum processes) and hardness (HBS 98.5) .
- Superior impact resistance, second only to brass among common die-casting alloys .
- Excellent wear resistance and creep resistance, particularly in ZA alloys with higher aluminum content .
Design Flexibility and Precision
- Complex, near-net-shape components can be cast with tight dimensional tolerances (±0.075 mm) and smooth surface finishes, reducing post-processing .
- Design freedom enables integration of multiple features (e.g., threads, hinges) into a single casting, minimizing assembly steps .
Cost-Effectiveness
- Lower tooling costs compared to aluminum and magnesium due to reduced mold wear and extended tool life .
- Material savings from thin-wall designs and minimal machining requirements .
- High production rates (e.g., 1,000 cycles in 8 hours) reduce per-unit costs for large batches .
Surface Finish and Treatment Versatility

- Components have smooth surfaces ready for direct use or secondary treatments like electroplating, painting, powder coating, and laser engraving .
- Zinc’s compatibility with coatings enhances aesthetics and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for automotive and consumer electronics .
Innovative Alloys and Process Advancements
- High-fluidity zinc alloys (e.g., HF alloy) enable casting of sub-0.45 mm walls while maintaining mechanical properties comparable to ZAMAK 3 and 7 .
- ZA alloys (e.g., ZA-8, ZA-27) offer higher strength and lower density for specialized applications .
Energy Efficiency and Sustainability
- Lower melting temperatures reduce energy consumption compared to aluminum and magnesium .
- Zinc alloys are fully recyclable, with minimal material loss during reprocessing .
Applications Across Industries
Zinc die casting is widely used in automotive (engine components, HVAC systems), electronics (heat sinks, EMI shielding), consumer goods (hardware, decorative items), and medical devices, leveraging its precision, durability, and cost efficiency .
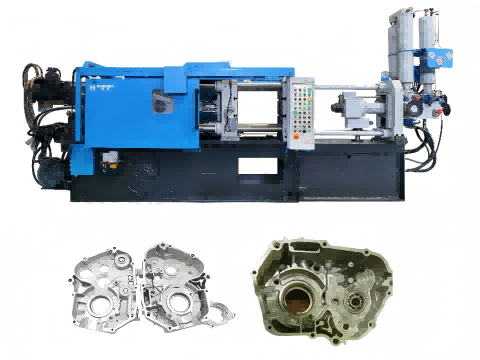
In summary, zinc alloy die casting combines high performance, design flexibility, and economic efficiency, supported by advancements in alloy development and process technologies. These advantages position it as a leading choice for high-volume, precision-driven manufacturing.
Haichen zinc die casting machine
Haichen offers a range of zinc die-casting machines designed for various industrial applications, primarily utilizing hot-chamber die-casting technology due to zinc’s low melting point (around 420°C). Here’s a detailed breakdown:
- Key Models and Specifications
- Technical Advantages
- Industry Applications
- Contradictions and Clarifications
- Global Reach
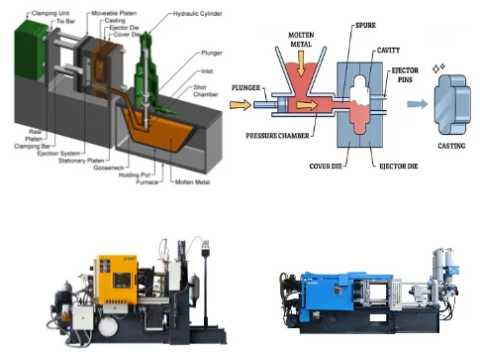
Key Models and Specifications
- Hot Chamber Machines (HCH Series)
- Tonnage Range: 15–280 tons, with common models like 50T, 90T, and 280T .
- Applications: Ideal for zinc alloy parts like door handles, lock cylinders, medals, and thin-walled LED housings. These machines feature high-speed production, precision, and energy efficiency .
- Features:
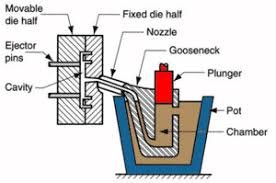
- Multi-stage pressure and speed control for optimized filling .
- Integrated furnace (gooseneck design) for continuous molten zinc supply .
- Multilingual control interfaces (English, Spanish, Russian, etc.) for ease of use .
- Cold Chamber Machines
- Tonnage Range: Up to 3,000 tons, including models like the 680T horizontal cold chamber machine .
- Applications: Used for specialized zinc parts requiring higher clamping forces or larger molds, though this is less common for zinc (typically reserved for aluminum/magnesium). Evidence suggests Haichen adapts cold chamber machines for zinc in specific cases .
- Features:
- Four-stage injection control (slow, first fast, second fast, intensification) for precision .
- Advanced hydraulic systems with components from global brands (Vickers, Siemens PLC) .
Technical Advantages
- Automation and Customization: Haichen provides auxiliary equipment (automatic ladles, sprayers, robots) to enhance production line automation .
- Quality Assurance: Machines comply with ISO 9001 and CE standards, with rigorous testing and real-time monitoring systems .
- Material Compatibility: Optimized for zinc alloys like Zamak 3, ensuring high fluidity and dimensional stability .
Industry Applications
- Automotive: Lock cylinders, structural components .
- Consumer Goods: Medals, door handles, pipe fittings .
- Electronics: LED housings with thin walls (1.3–1.4 mm) .
Contradictions and Clarifications
While hot chamber machines are standard for zinc, some evidence mentions cold chamber use for zinc . This may apply to niche scenarios (e.g., large parts or hybrid production lines), but hot chamber remains the primary recommendation for efficiency and cost-effectiveness .
Global Reach
Haichen exports globally, with strong markets in Mexico, India, Russia, and China, particularly in automotive and construction sectors .

Haichen’s zinc die-casting solutions prioritize hot-chamber machines for most applications, offering speed and precision, while cold chamber options cater to specialized needs. Their machines are customizable, certified, and backed by 20+ years of expertise .
Contact us anytime for more details on zinc die casting technical details.



