The platen material selection and design of die-casting machine is a comprehensive engineering problem, involving multiple fields such as material science, mechanical engineering and cost control. 5 types of the material: H13, 3Cr2W8V, SKD61, 4Cr5MoSiV, Copper alloy.
The die-casting machine platen is the core component in die-casting technology, which directly affects the quality and production efficiency of die-casting parts. This article will discuss the material selection . And design of die-casting machine platen to ensure the efficiency and stability of the die-casting process.
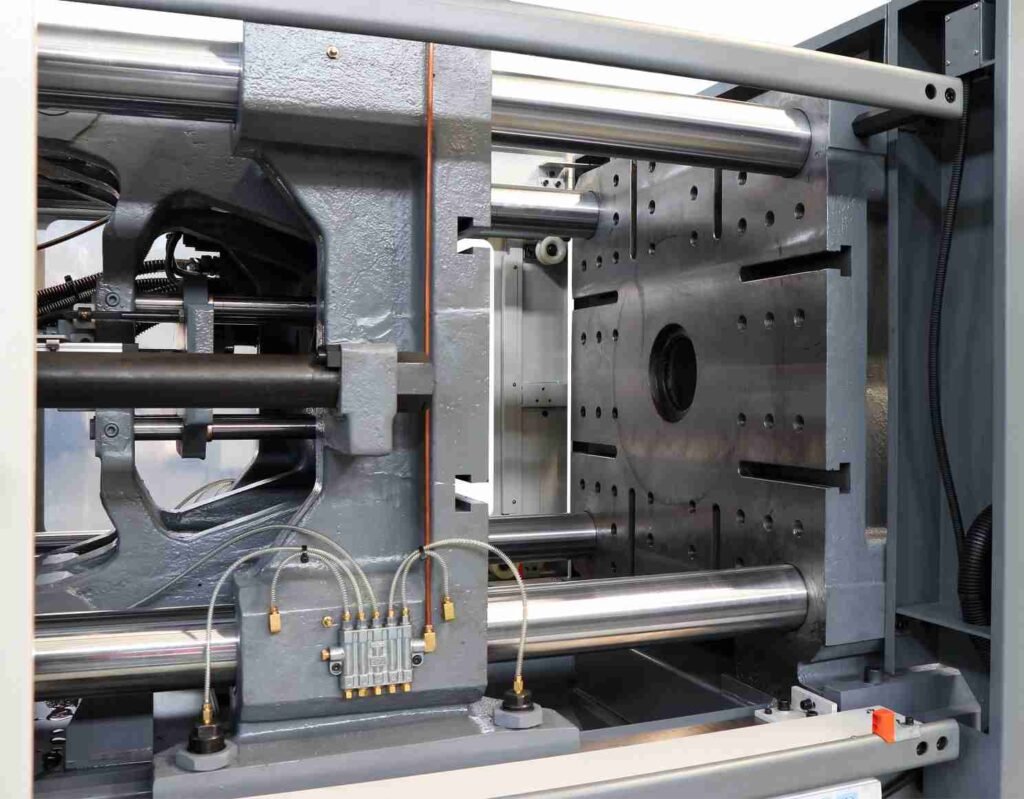

What materials should be selected for die-casting machine platen
When choosing die-casting machine template materials, it is recommended that you comprehensively consider the actual working environment of the mold. Expected service life, production needs and cost budget. The following are the characteristics and applicable scenarios of several common materials for your reference:
H13 die steel
Due to its good toughness and resistance to high temperature softening (red hardness).H13 has become a common choice for aluminum alloy die-casting molds. It is suitable for manufacturing parts that withstand high temperature and high pressure but are not directly impacted, such as cores and sprue bushings. This material has achieved a good balance between cost and performance. The hardness can reach 50-55 HRC after quenching, which can effectively extend the life of the mold.
3Cr2W8V
The advantage of this material is its outstanding heat resistance and fatigue resistance. It is especially suitable for die-casting production of aluminum alloys and copper alloys. And is commonly used in cold chamber die-casting machines. The tungsten (1.5-2.0%) and chromium (7.75-8.75%) in its composition enable it to remain stable at a high temperature of 600℃. But attention should be paid to the effect of heat treatment process on performance.
SKD61
Although the price is relatively high, SKD61 performs well in scenarios that require high strength and high wear resistance. The hardness after quenching can reach 60-62 HRC, which is suitable for mass production. Its thermal expansion coefficient is moderate, which can reduce the problem of dimensional deformation at high temperature. But the quenching temperature needs to be controlled during processing.
4Cr5MoSiV
This material has enhanced heat resistance and wear resistance through molybdenum and vanadium elements. And is particularly suitable for molds that need to resist high temperature and mechanical stress at the same time. It is recommended to use a heat treatment process of 790℃ preheating + 1010℃ quenching + 550℃ tempering to achieve a hardness of ≥60 HRC.
Copper alloy
Under high temperature and high pressure conditions (such as over 600℃). The rapid heat dissipation ability of copper alloy can reduce mold thermal fatigue. Its conductivity also helps to maintain dimensional accuracy. But attention should be paid to the tendency of intergranular corrosion that may occur during long-term use.
Special steel (such as DH-3840841H, etc.)
This type of customized material is usually developed for specific needs, such as precision parts such as automobile transmission gears. When selecting, the geometric complexity of the parts and the production batch must be strictly matched. It is recommended to consult the supplier directly to obtain heat treatment parameters.
Final decision recommendation:
Please prioritize the three core indicators of the mold:
- Working temperature: Focus on heat resistance when exceeding 500℃ (such as 3Cr2W8V)
- Wear strength: High hardness materials (such as SKD61) are preferred for mass production
- Cooling requirements: Copper alloy inserts can be used locally in high heat load areas. It is also recommended to conduct more than 2,000 thermal cycle tests on new molds to verify fatigue resistance.

Key factors in platen material selection
As a core component that withstands high pressure, the material properties of the template directly determine the quality of die castings and the life of the equipment. Engineers need to comprehensively evaluate the following six characteristics to achieve a balance between durability and production efficiency:
Rigidity requirements for mechanical properties
The template must have a high hardness of more than HRC 50 to resist high-pressure deformation (such as the application of H13 tool steel), and the material must have sufficient toughness to prevent the risk of fracture under high-pressure conditions. Studies have shown that insufficient material strength will cause the dimensional deviation rate of castings to increase by more than 12%.
Dynamic balance of thermal properties
Given that the mold temperature during the die-casting process often reaches 200-260℃ (aluminum alloy process), the material must meet dual characteristics:
- Low thermal expansion coefficient (≤13×10⁻⁶/K) to ensure dimensional stability
- High thermal conductivity (>30 W/m·K) to accelerate heat dissipation. The thermal stress caused by sudden temperature changes is the main cause of mold failure. Reasonable material selection can extend the life by 30%.
Practical considerations of corrosion protection
In the face of chemical erosion in aluminum alloy melt, it is recommended to use alloy steel with a chromium content of >11%. Experiments show that at a pouring temperature of 650℃ and an injection speed of 3m/s, the corrosion potential of the material can be increased by 31dumV, significantly reducing the risk of pitting corrosion.
Cost control of processing performance
Good cutting performance (such as tungsten steel W300) can reduce manufacturing hours by 40% and reduce tool loss by 25% when processing complex surfaces. This is directly related to the frequency of mold maintenance. For example, the average maintenance interval of materials with poor machinability is shortened to 8,000 molds.
Dynamic model of cost-effectiveness
Although the initial cost of tool steel is 35% higher than that of cast iron, its life cycle cost advantage is significant:
| Material type | Single maintenance cost | Average service life |
| Ordinary cast iron | ¥12,000 | 15,0000 molds |
| H13 tool steel | ¥18,000 | 45,0000 molds |
In mass production, tool steel can reduce the cost of a single mold by 62%.
New challenges of environmental adaptability
In coastal high humidity environments, it is recommended to use nickel-based alloys (such as Inconel) with surface coatings. Salt spray tests show that its corrosion resistance is 5 times higher than that of conventional materials. At the same time, the special requirements of thermal expansion coefficients due to temperature fluctuations in different regions need to be considered.
Common platen materials and their properties
In the field of industrial manufacturing, the choice of platen material directly affects the durability and production efficiency of the equipment. The following is a comparison of the actual characteristics of five commonly used materials:
Steel
Alloy steels such as 4140, 4340 and H13 are the first choice for heavy machinery platens due to their excellent mechanical strength and heat treatment stability. In automotive mold manufacturing, this type of steel can withstand working pressures of more than 1000MPa. However, regular anti-rust treatment should be taken, especially in high humidity environments.
Cast iron
The cost is about 30% lower than that of steel and is suitable for medium and low load scenarios with limited budgets. Its compressive strength is about 60% of that of steel. It is widely used in auxiliary platens of textile machinery, but microcracks may occur in long-term impact environments.
Aluminum alloy
It weighs only 1/3 of that of steel and is particularly suitable for platens of inspection equipment that need to be moved frequently. Although it is not as wear-resistant as steel (wear rate is 2-3 times higher), it can effectively reduce the overall load on the optical instrument calibration platform.
Copper alloy
The excellent thermal conductivity makes it an ideal choice for hot pressing process, with a thermal conductivity of up to 400W/(m·K). However, the material cost is 4-5 times that of steel, and it is usually only used in precision thermal processing such as semiconductor packaging.
Composite materials
The strength/weight ratio of carbon fiber reinforced plastic (CFRP) exceeds that of metal materials, and can reduce weight by 40% in aerospace fixtures. However, the cost per square meter exceeds US$200, and machining requires special tools. In the 5G base station RF test, its dielectric constant is stable between 2.0-2.5, ensuring signal transmission accuracy.

Key elements of platen design
The design of the platen needs to consider size and shape, cooling system, fastening and positioning, and convenience of maintenance and replacement. A well-designed platen can ensure the accuracy and efficiency of the die casting process. An effective cooling system helps control the platen temperature and prevent overheating. Proper fastening and positioning ensure the stability of the platen, while convenient maintenance and replacement reduce downtime.
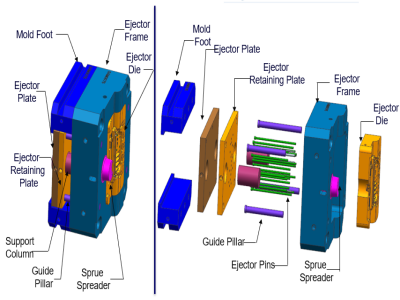
Balance between platen material and design
It is crucial to find a balance between the material and design of the die casting machine platen. On the one hand, the material needs to have enough strength and hardness to withstand high pressure and wear; on the other hand, the design must ensure that the platen can work stably under high pressure and high temperature. This balance ensures the long-term reliability and efficient production of the die casting machine.
The material selection and design of the die casting machine platen are the key to ensure the quality of die casting. By carefully selecting materials and optimizing the design, we can improve the performance of the die casting machine, reduce production costs, and improve the economic benefits of the entire production process. This is not only a technological advancement, but also a manifestation of industrial art.




