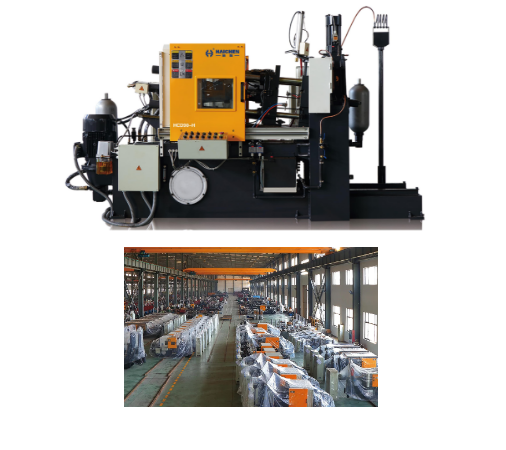
Precision die casting development of include history, technical characteristics, key technological breakthroughs, application cases, current challenges and future trends.
The development of precision die casting is a multi-disciplinary process.
The coordinated progress of technology, materials, design and market has jointly promoted its core position in high-precision manufacturing.
In the future, with the further development of new materials, automation and intelligent technologies, precision die casting will play a key role in more fields.

What is Precision Die Casting?
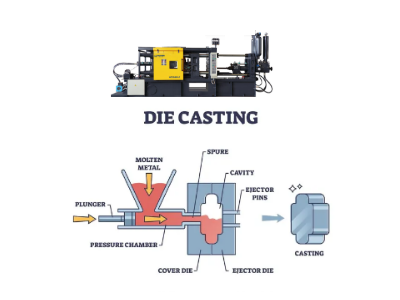
Precision die casting is a high-pressure manufacturing method that forces molten non-ferrous metals (like aluminum, zinc, magnesium) into hardened steel molds (dies) to create complex.
High-volume metal parts with tight tolerances, excellent surface finishes, and intricate details, minimizing the need for secondary machining and offering cost-effectiveness for large runs.
This process ensures dimensional accuracy and consistency, making it ideal for industries requiring lightweight yet strong components.
Haichen are committed to enhancing production efficiency and implementing effective project management to shorten the mold development cycle.
With a professional processing and mold maintenance team as well as abundant software and hardware resources, Haichen is committed to providing fast, high-quality and competitive services to meet the needs of customers.

Overview of the Development of Precision Die Casting
- High precision and repeatability
- Excellent surface quality
- Material diversity
- Cost-effective
Precision die casting is a metal forming process in which molten metal is injected into a steel mold (the mold consists of two halves of hardened tool steel) through high pressure.
Which is suitable for the efficient production of non-ferrous metals such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper, etc.
Haichen can provide hot chamber die casting machines as well as cold chamber die casting machines.
High precision and repeatability
Tolerances can be controlled within ±0.02 mm, which is suitable for forming complex geometries.
Excellent surface quality
The surface of the casting is smooth, which can be directly used in the end product, reducing the need for post-processing.
Material diversity
Actually,different materials can be adapted by hot chamber (low melting point metals such as zinc) or cold chamber (high melting alloys such as aluminum) processes.
Cost-effective
Suitable for large-scale production, low cost per piece.
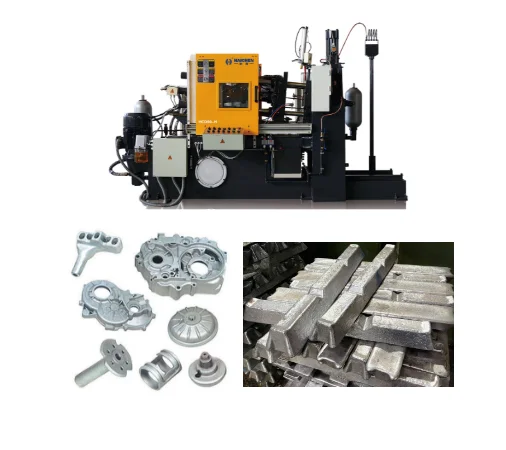

Timeline of historical development
- Early 19th century
- Early 20th century
- Mid-20th century
- 21st century
Early 19th century
Die-casting technology originated in the printing industry, and in 1838 Sturges and Chubb patented the first manual die-casting machine for lead casting.
Late 19th century
In 1885, Ottmar Mergenthaler invented the Linotype typesetting machine to promote the industrialization of lead-tin alloy die casting.
Early 20th century
It’s all known,he material expands to zinc alloys (1910s) and aluminium alloys (1914), and the field of application shifts from printing to industrial parts (e.g. bearings, weapon components).
Mid-20th century
Cold chamber die casting technology matured, and aluminum and magnesium alloys were widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Such as General Motors’ Acurad process in 1966 to optimize compactness.
21st century
The rise of intelligent and high-pressure die casting (HPDC) technology, combined with vacuum-assisted.
Semi-solid molding and other processes, promotes lightweight and complex structure manufacturing.

Key technological breakthroughs
- Material innovation
- Process improvements
- Equipment Upgrades
Material innovation
High-performance alloys:Whereas,magnesium alloys, high-alumina-zinc-based alloys to improve strength and corrosion resistance.
Then,metal matrix composites (e.g., aluminum-silicon carbide) meet the needs of automotive lightweighting.
Non-traditional materials:Exploration of nickel-based alloys and titanium alloys expands high-temperature application scenarios.
Process improvements
Vacuum die casting:Therefore,reduces porosity defects and improves mechanical properties for automotive structural parts such as door frames.
Semi-solid die casting:Uses metal paste to improve fluidity and achieve high-precision molding of thin-walled parts, such as electronic housings.
Equipment Upgrades
Intelligent Control:For example, Yizumi’s NEXT² series die-casting machines are equipped with Dolphin intelligent systems to optimize the clamping force and injection speed.
High-pressure die casting (HPDC):Secondly,pressures can be increased to more than 1000 bar to support the integrated molding of large structural parts such as electric vehicle chassis.
Application case
- Automotive industry
- Aerospace
- Electronic field
Automotive industry
Engine block, gearbox housing, body structural parts (such as Tesla integrated chassis), aluminum alloy die-casting weight reduction of more than 30%.
Aerospace
Then,turbine blades, aircraft mounts, magnesium alloy components to reduce fuel consumption.
Electronic field
Mobile phone shells, radiators, connectors, zinc alloy die-casting to ensure electromagnetic shielding and precision heat dissipation.
In addition, Haichen has also handled many other cases, such as zinc die-cast door handles, etc.

Current Technical Challenges
- Surface Accuracy
- Complex structure molding
- Material limitations
Surface Accuracy
Defects such as porosity and cold insulation still rely on process optimization (e.g., vacuum-assisted) and mold design improvements.
Complex structure molding
Thin-walled (<1 mm) or deep-cavity parts are prone to underfilling.
And the runner design needs to be optimized with simulation software.
Material limitations
The high melting point of iron-based alloys leads to short mold life.
And the research and development direction focuses on coating technologies (such as PVD anti-erosion coatings).
Future Development Trends
- Industry 4.0 Integration
- Automated production
- Environmental protection and sustainable development
Industry 4.0 Integration
IoT monitors mold temperature and pressure in real time, and AI predicts defects and adjusts parameters to improve yield.
Automated production
Robots are used for picking, deburring, reducing manual intervention and improving safety.
Haichen offers a variety of models of robotic arms for customers to choose from.

Environmental protection and sustainable development
Recycled materials:The proportion of recycled aluminum and zinc will be increased to more than 80% to reduce the consumption of primary resources.
Green process:low-energy servo motors, exhaust gas treatment system to reduce carbon emissions.
Lightweight and multi-functional
Super large die-casting:Die-casting machines of more than 6,000 tons support the integration of the body and reduce the welding process.
Composite die-casting:carbon fiber reinforced aluminum alloys are used in aerospace structural parts.
Haichen Precision Die Casting
Precision die casting has evolved from a printing industry auxiliary technology in the 19th century to a core process in modern manufacturing.
Its development history reflects the deep integration of materials science, mechanical engineering and digital technology.
In the future, with the advancement of intelligent and green manufacturing.
Precision die casting will further release its potential in the fields of new energy vehicles and aerospace.
And promote the efficiency and sustainability revolution of industrial manufacturing.




