Process Cost of Die Casting alloys has several parts:
- Material cost
- Tool cost
- Manufacturing cost
- Post-processing cost
- Alloy selection
The process cost of die-castings involves multiple factors, including material cost, mold cost, manufacturing cost, post-treatment cost, etc.
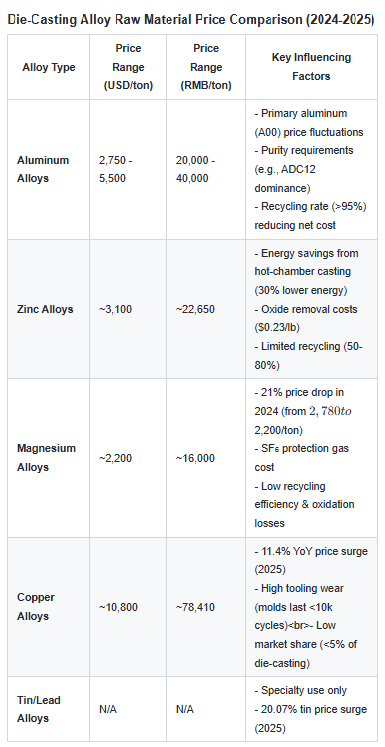
Material cost is a major component, and the price fluctuates according to market conditions and the weight and volume of the casting.
Manufacturing costs are influenced by machine size, cycle time and labor force.
Due to harsh operating conditions and the demand for high-quality materials, mold costs may be very high.
Post-processing costs, such as fine machining, may account for 2% to 10% of the total cost of the parts.
Material cost
These are mainly based on the weight of the alloy used and the current market price.
Alloys like aluminium have a lower cost per cubic inch, while magnesium, zinc and ZA alloys may have advantages in applications.
Tool cost
Die-casting molds, especially high-pressure die-casting molds (HPDC), are very expensive due to the high temperatures, thermal shock and mold cleaning they are exposed to.
Mold materials, such as H13 or SKD61, also contribute to the cost.

Manufacturing cost
This includes machine operation, energy consumption, labor and auxiliary materials.
Then,the size and cycle time of the die-casting machine (the time required to complete one casting cycle) directly affect these costs.
Post-processing cost
These include any finishing processes, such as machining, coating or other final treatments for die-castings.
These costs vary greatly depending on the complexity and volume of the organization.
Alloy selection
The selection of alloys affects both material costs and process costs.
Compared with alloys that require cold chamber casting, alloys that can be cast in hot chambers may need smaller machines and faster speeds.
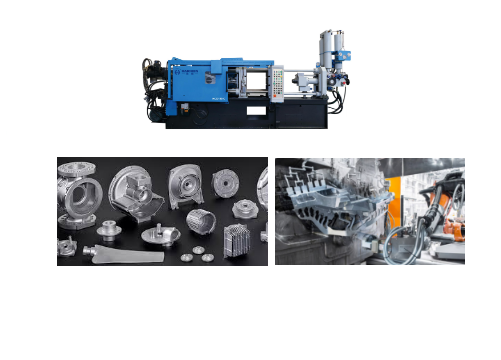
Die Casting alloys Common type
Die Casting alloys is a metal casting process in which molten non-ferrous metal alloys are injected into molds under high pressure to quickly produce parts with high precision and complex shapes.
Common Die Casting alloys include:
- Aluminum alloy
- Magnesium alloy
- Zinc alloy
- Copper alloy
- Lead and Tin alloys
Aluminum alloy
Aluminum is one of the most commonly used materials in die casting due to its light weight, high strength and excellent casting properties.
Common aluminum die-casting alloys include ADC12, ADC10, ADC14, etc.
These alloys are usually combined with elements such as copper and silicon to enhance their mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Magnesium alloy
Magnesium alloy has an extremely high strength-to-weight ratio and is an ideal choice for lightweighting.
Common magnesium die-casting alloys include AZ91D, AM60, AS41B, etc.
These alloys are widely used in the automotive and electronics industries.
Zinc alloy
Zinc alloy has excellent fluidity and casting properties, and is often used to manufacture precision parts such as connector housings, gears and chains.
Common zinc die-casting alloys include Zamak 2, Zamak 3, Zamak 5, etc.
Copper alloy
Copper alloy features high hardness and good electrical conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require high mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
Such as mechanical parts and electronic components.
Lead and Tin alloys
These alloys are typically used in special applications, such as components with high density and corrosion resistance requirements.
Shaping and repair welding is required to ensure that they meet the design requirements.

How does Haichen reduce the Process Cost of Die Casting alloys
- Optimize raw material procurement
- Improve equipment and mold utilization
- Improving the production process
- Reduce transportation costs
- Improve production efficiency
Optimize raw material procurement
Through industry associations, enterprise cooperation and necessary regulatory means.
Jointly maintain the stability of the magnesium alloy price market and ensure the sustainable development of the industry.
Improve equipment and mold utilization
Increase investment in simulation technology, simulation software, and design to improve the efficiency of mold design and manufacturing, and reduce mold trial time and cost.
Improve the durability and reuse rate of molds, and reduce the tooling cost per product.
Improving the production process
Develop high-strength, high-thermal conductivity and heat-free magnesium alloys suitable for integrated die castings to meet the high performance requirements of magnesium alloy materials in different fields.
Improve process and mold design to improve product quality and reduce costs.
Reduce transportation costs
Choose to build factories as close as possible to reduce product transportation distances and costs.
Improve production efficiency
Use high-pressure casting technology to produce high-volume thin-walled parts to improve production efficiency.
Using low-pressure casting technology, the filling is stable.
And it is more suitable for forming large and complex magnesium alloy castings.




