Die casting crucibles are key components in die-cast furnaces, applied for the melting and holding of metals such as aluminum, zinc, or magnesium. Proper replacement and installation guarantee safe operation, consistent quality of metal, and long life of the equipment.
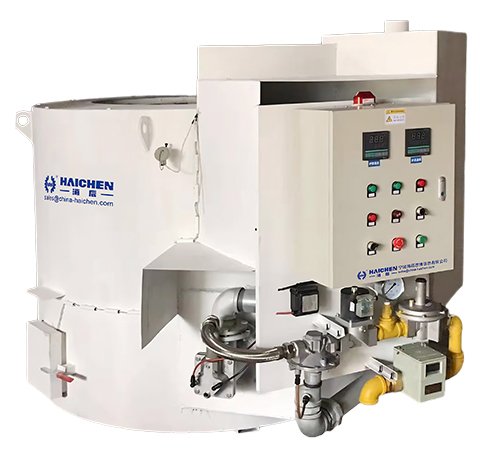
The melting and holding crucible furnace is specifically designed for the efficient melting and holding of non-ferrous metals such as aluminium, brass, zinc, lead, and tin alloys.
The Haichen furnace body incorporates advanced temperature control and insulation technology to ensure minimal energy loss and enhanced heating precision. Crucible materials can be customised, including graphite, cast iron, and silicon carbide, delivering reliable performance for diverse industrial applications.
They’re great for high-pressure die casting, sand casting, gravity casting, and metal mold casting.
How do we replace crucible for die casting machine?
Below is a step-by-step guide:
- Preparation
- Removal of the Old Crucible
- Installation of the New Crucible
- Post-Installation Testing
- Maintenance Tips
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Recommended Crucible Suppliers
Preparation

- Safety First:
- Wear heat-resistant gloves, face shields, and fireproof clothing.
- Ensure the furnace is cooling down (below 100°C) to prevent thermal shock.
- Disconnect power and lock out/tag out (LOTO) the machine.
- Tools and Materials:
- Replacement crucible (material must match the alloy: graphite for aluminum, steel-lined ceramic for zinc/magnesium).
- Lifting equipment (e.g., hoist, tongs).
- High-temperature refractory cement or sealant.
- Torque wrench and alignment tools.
Removal of the Old Crucible
- Empty Residual Metal:
- Drain all molten metal from the crucible during operation, or chip out solidified metal after cooling.
- Loosen Fasteners:
- Remove bolts or clamps securing the crucible to the furnace base.
- Extract the Crucible:
- Use lifting tools to carefully lift the crucible out of the furnace. Avoid mechanical impact to prevent damage to the furnace lining.
Installation of the New Crucible

- Inspect the Furnace:
- Check the furnace lining for cracks, wear, or residue. Clean with a wire brush if needed.
- Apply Sealant:
- Coat the base and seating area with high-temperature refractory cement to ensure a tight seal.
- Position the Crucible:
- Lower the new crucible into the furnace using lifting tools. Ensure it sits evenly on the base.
- Secure Fasteners:
- Tighten bolts or clamps evenly in a cross-pattern to avoid warping. Follow manufacturer torque specifications (typically 20–30 Nm).
- Align with Pouring System:
- Adjust the crucible to align with the ladle or injection system (for hot chamber machines).
Post-Installation Testing
- Dry Run:
- Heat the furnace slowly (50°C increments) to season the crucible and cure the sealant.
- Leak Test:
- Fill with a small amount of metal and check for leaks.
- Monitor Performance:
- Observe temperature stability and metal flow during initial production runs.
Maintenance Tips
- Preheating: Always preheat new crucibles to 200–300°C before use to prevent thermal shock.
- Avoid Contamination: Never mix metals (e.g., aluminum and zinc residues react explosively).
- Regular Inspections: Check for cracks, erosion, or warping weekly. Replace crucibles showing >5% wall thickness reduction.
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Cracking | Thermal shock or mechanical stress | Preheat properly; avoid rapid cooling. |
| Metal Leakage | Poor sealant application | Reinstall with fresh refractory cement. |
| Uneven Heating | Misalignment or warped crucible | Realign or replace the crucible. |
Recommended Crucible Suppliers
- Morgan Advanced Materials: High-performance graphite crucibles for aluminum.
- ZIRCAR Ceramics: Refractory crucibles for zinc and magnesium.
- SGL Carbon: Durable silicon carbide crucibles for high-temperature alloys.
What is the use of crucible in casting?
In die casting, the crucible serves several critical functions that directly impact the casting process and final product quality:
- Melting and Temperature Maintenance
- Pressure Transfer and Flow Control
- Integration with Injection Systems
- Challenges and Material Requirements
Melting and Temperature Maintenance
The crucible acts as a container to melt and hold molten metal at the required temperature. For example:
- In low-pressure die casting, the crucible is positioned beneath the mold. Molten metal is pushed upward through a feed tube into the mold cavity.
- In hot chamber die casting machines, the crucible is integrated with the injection system, ensuring metal remains in a ready-to-inject state.
- For magnesium alloys, steel crucibles exploit the compatibility between magnesium and steel to minimize oxidation.
Pressure Transfer and Flow Control

By applying gas pressure (e.g., dry air, nitrogen, or argon) to the crucible, molten metal is forcing into the mold:
- Low-pressure casting typically uses 7–15 psi to ensure smooth filling without turbulence.
- In vacuum die casting, pressure differences between the crucible and mold drive metal flow.
- Excess molten metal can flow back into the crucible after injection, improving material efficiency (up to 95%).
Integration with Injection Systems

In hot chamber machines, the crucible is directly connected to the plunger mechanism:
- When the plunger descends, molten metal flows from the crucible into the injection chamber and through the nozzle into the mold.
- This design minimizes air exposure, reducing oxidation defects.
Challenges and Material Requirements
Crucibles face durability issues due to prolonged exposure to molten metal:
- Erosion of components like feed tubes or crucible walls can introduce impurities (e.g., iron contamination in aluminum alloys).
- Advanced materials like boron nitride coatings or refractory ceramics are used to enhance thermal/chemical resistance and lifespan.
By the end
The crucible is both a molten metal reservoir and a pressure-transfer medium, directly influencing mold filling quality, material efficiency, and defect prevention. Its design and material selection must balance operational demands (e.g., pressure ranges, alloy types) with durability requirements.
High quality crucibles for Haichen die casting machines
As a professional die-casting machine manufacturer, Haichen’s hot chamber die-casting machine is indeed equipping with high-quality crucibles. The following is a specific analysis:
- Warranty terms for crucibles
- Material selection and design requirements for crucibles
- Indirect manifestation of technical advantages
- Application scenarios and adaptability
Warranty terms for crucibles

It is clearly mentioned that within the warranty scope of the hot chamber die-casting machine, the warranty period of the crucible is 2 months (“CRUCIBLE | 2 MONTHES”), which directly indicates that the crucible is one of the standard configuration parts of Haichen’s hot chamber die-casting machine.
The existence of the warranty terms shows that we Haichen have a certain confidence in the quality and durability of the crucible and provide guarantees for its performance.
Material selection and design requirements for crucibles
HAICHEN die-casting machine crucibles must meet the following key standards:
High temperature resistance and corrosion resistance

The crucible must be made of high heat-resistant materials (such as graphite or ceramic-based composite materials) to withstand the smelting environment of low-melting-point metals such as zinc alloys and lead alloys.
Capacity matches production needs
The crucible capacity needs to be adjusted according to the tonnage of the machine model.
For example, the tonnage of the medium hot chamber die casting machine covers 30 tons to 90 tons, corresponding to different molten metal volume requirements.
Heating method compatibility
Haichen hot chamber die casting machine adopts immersion heating (the molten metal is heated directly in the crucible), so the crucible needs to be compatible with gas or resistance heating systems.
Indirect manifestation of technical advantages
The key components of Haichen die casting machine (such as Shot Sleeves) are made of high temperature resistant steel and optimized design to cope with high pressure and high speed environment. This quality control logic for core components may also apply to the manufacture of crucibles.
The hydraulic and electrical systems of Haichen die casting machine use components from well-known brands in Europe, America and Japan, and the structural design is optimized through finite element analysis, which indirectly reflects the support of its supply chain and process level for the quality of crucibles.
Application scenarios and adaptability
Haichen hot chamber die casting machine is mainly suitable for die casting of low melting point metals such as zinc alloys and lead alloys (such as door handles, 3C parts, etc.).
The melting temperature of such alloys is usually 400-500°C, so the crucible needs to remain structurally stable during long-term thermal cycles to avoid deformation or corrosion, which is consistent with the 2-month usage period requirement in the warranty terms.

More telling
Proper crucible replacement and installation are critical for safe, efficient die casting operations. Always follow manufacturer guidelines and prioritize regular maintenance to extend crucible lifespan.
Leave us a message to get more die casting technology information.



