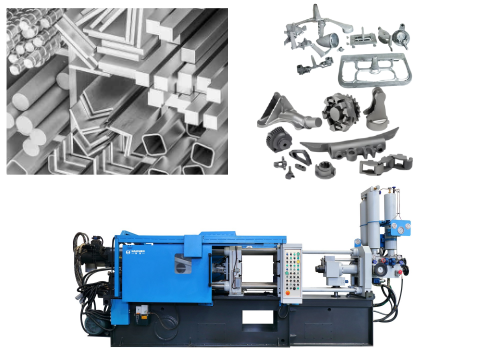
Aluminum die casting is a process under high pressure, in which molten aluminum is injected into a steel mold (die). The resultant product comprises accurate and intricate parts with a good surface finish and dimensional stability. It suits the needs of high-volume production because of its efficiency and repeatability.
It is ideal for high-volume production due to its efficiency and repeatability.
Conventional process and characteristics of aluminum alloy die casting
- Key Process Steps
- Design Considerations
- Aluminum Alloys
- Advantages
- Limitations
- Applications
- Post-Processing
- Environmental & Safety
- Comparison with Other Methods
Key Process Steps
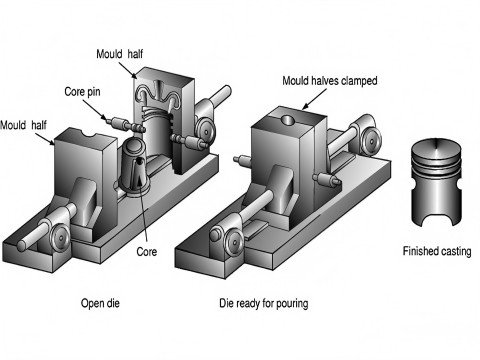
- Die Preparation:
- Two hardened steel dies (cover and ejector) are machined to form the part cavity.
- Dies are heated and coated with lubricant to facilitate ejection and prevent sticking.
- Melting:
- Aluminum alloys (e.g., A380, ADC12) are melted in a furnace (~660°C). Alloys often include silicon for fluidity and copper/magnesium for strength.
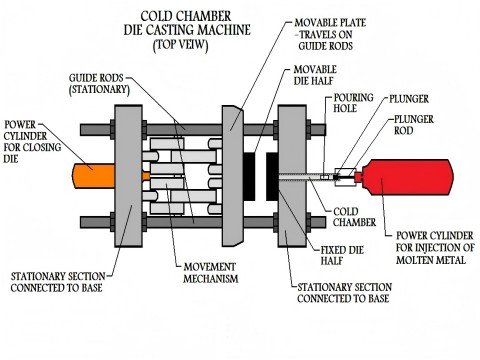
- Injection:
- Cold Chamber Process: Molten aluminum is ladled into a chamber, and a hydraulic piston injects it into the die at high pressure (10–175 MPa).
- High-speed injection ensures complete filling before solidification.
- Cooling & Solidification:
- Dies are water-cooled to rapidly solidify the metal (milliseconds to seconds).
- Ejection:
- Dies open, and ejector pins push out the casting. Cycle repeats immediately.
- Trimming & Finishing:
- Excess material (flash, gates) is removed.
- Secondary operations: machining, polishing, plating, or powder coating.
Design Considerations
- Die Design: Includes runners (channels), gates (entry points), and vents to allow air escape.
- Vacuum Assistance: Reduces porosity by evacuating air from the die cavity.
- Lubrication: Release agents applied to dies enhance part ejection and die longevity.
Aluminum Alloys
- Common alloys: A380 (high fluidity, strength), A383 (thin walls), ADC12 (Japan standard).
- Silicon content (7–12%) improves flow; copper/magnesium enhance mechanical properties.
Advantages
- High production rates (up to hundreds of parts/hour).
- Excellent dimensional accuracy (±0.1 mm).
- Complex geometries with fine details.
- Smooth surfaces (Ra 1–2.5 μm).
- Recyclability of aluminum scrap.

Limitations
- High initial die cost (suitable for large batches only).
- Part size restricted by machine capacity.
- Internal porosity may require X-ray inspection or vacuum processes.
Applications
- Automotive: Engine blocks, transmission housings, brackets.
- Consumer Electronics: Housings, heat sinks.
- Industrial: Pump components, power tools.
Post-Processing
- Heat Treatment: T5/T6 tempering improves strength.
- Quality Control: X-ray, CT scans, or pressure testing to detect defects.
Environmental & Safety
- Recyclability reduces waste; energy-intensive melting requires efficient furnaces.
- Safety protocols for molten metal handling and high-pressure machinery.
Comparison with Other Methods
- Vs. Sand Casting: Higher precision, smoother finish, but higher tooling cost.
- Vs. Permanent Mold Casting: Faster cycle times due to pressure injection.

Aluminum die casting Process have balances cost, speed, and quality, making it a cornerstone of modern manufacturing for lightweight, durable components. Advances in vacuum-assisted and semi-solid casting continue to expand its applications.
What are the 3 basic methods of aluminum alloy castings?
The three basic methods of aluminum alloy castings are die casting, sand casting, and permanent mold casting. Each method has distinct characteristics, advantages, and applications:
- Die Casting (High-Pressure Die Casting, HPDC)
- Sand Casting
- Permanent Mold Casting (Gravity Die Casting)
Die Casting (High-Pressure Die Casting, HPDC)
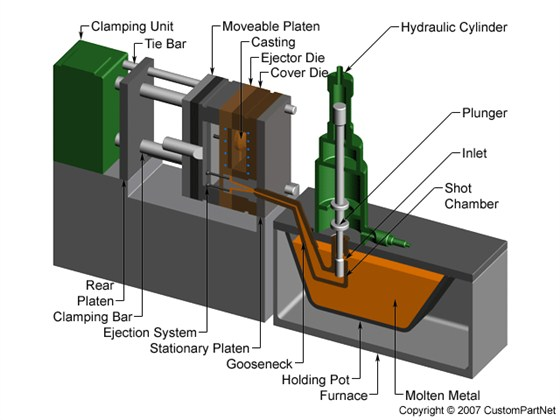
- Process: Molten aluminum is injected under high pressure (10–175 MPa) into a reusable steel mold (die).
- Key Features:
- High production speed (hundreds of parts per hour).
- Excellent dimensional accuracy (±0.1 mm) and smooth surface finish.
- Ideal for complex, thin-walled parts (e.g., automotive components, electronics housings).
- Advantages:
- High repeatability for large batches.
- Minimal post-processing required.
- Limitations:
- High initial die cost (economical only for high-volume production).
- Internal porosity may require vacuum-assisted processes.
Sand Casting
- Process: Molten aluminum is poured into expendable sand molds created from a pattern.
- Key Features:
- Low tooling cost (suitable for prototypes or small batches).
- Accommodates large, heavy parts (e.g., engine blocks, pump housings).
- Rough surface finish and lower dimensional accuracy compared to die casting.
- Advantages:
- Flexible design changes (easy to modify sand molds).
- Cost-effective for low-volume or one-off production.
- Limitations:
- Slower production rate (molds are destroyed after each cast).
- Labor-intensive and less precise.
Permanent Mold Casting (Gravity Die Casting)

- Process: Molten aluminum is poured into reusable steel or iron molds under gravity or low pressure.
- Key Features:
- Better surface finish and dimensional accuracy than sand casting.
- Suitable for medium-volume production (e.g., automotive wheels, housings).
- Longer mold life compared to sand casting.
- Advantages:
- Reduced porosity compared to sand casting.
- Faster cycle times than sand casting.
- Limitations:
- Higher tooling cost than sand casting.
- Less suited for highly complex geometries compared to die casting.
Comparison Summary
| Method | Best For | Production Volume | Surface Finish | Tooling Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | High-volume, complex parts | Very High | Excellent | High |
| Sand Casting | Large parts, prototypes, low volume | Low | Rough | Low |
| Permanent Mold | Medium-volume, simple to moderate complexity | Medium | Good | Moderate |
Applications
- Die Casting: Automotive transmission housings, consumer electronics.
- Sand Casting: Engine blocks, marine components, artistic castings.
- Permanent Mold: Automotive pistons, cookware, aerospace parts.
Each method balances cost, precision, and production volume, allowing manufacturers to choose the optimal process based on part requirements. Die casting dominates high-volume precision needs, while sand and permanent mold cater to flexibility and moderate-scale production.
Haichen high performance die casting machine
Haichen HDC series cold chamber die casting machines: A new generation, dual closed-loop full real-time control injection system adopts and integrates with the SIEMENS control system to realize closed-loop control of casting pressure as well as injection speed and boost pressure.
Its features include:
1.0.5ms real-time control cycle to ensure high-precision response;
2.±1bar boost pressure repeatability to ensure casting consistency;
3.Ten-stage injection speed + six-stage boost pressure configuration to meet complex process requirements;
4.Built-in intelligent quality management and remote networking functions to monitor production parameters in real time.
Choose Haichen to make your Aluminum Die Casting Process better.~



