Both tie bars vs. alternative clamping systems in die casting serve the dual purpose of providing structural support and ensuring the precise alignment of the mold. However, tie bars are preferred for their robustness and simplicity, while toggle-action and hydraulic clamping systems add precision and may be more energy-efficient.
During the injection process in die casting, clamping systems are pivotal in securring the mold to avoid any form of disintegration.
Tie bars, which have always been common in the industry, are now being displaced with other clamping systems.
Manufacturers can gain better understanding and make better decisions if they learn the implications of tie bars and alternative clamping systems.
This article seeks to focus on the advantages and applications of tie bars and alternative clamping systems.

Tie Bars: Definition and Working Principle
The moving and fixed platens in die-casting machines are connected by high-strength metal rods called tie bars. They keep the die locked in position by means of preload and counteract the massive expansion forces resulting from the injection of molten metal.
Tie bars serve the following core functions:
- Force Transmission and Stability: Tie bars maintain the cavity alignment and distribute the clamping force uniformly. They ensure that the cavity remains aligned along the parting surface of the die. A design of slenderness ratio ≤ 20:1 will ensure that the die does not break.
- Dynamic Precision Control: Balance of clamping force due to thermal expansion of the molds can be countered by the adjustment of the tie bar nut. An automatic adjustment system can be fitted that maintains the balance of forces to a range of 0.02 mm/m.
- Shock Absorption and Life Optimization: Changes in design that include “unloading grooves” help to redistribute high-stress concentrations which leads to better resistance to fatigue.

Key Technical Parameters of Tie Bars
| Parameter Category | Requirements and Optimization | Directions Impact |
| Material | Selection: Alloy steel (H13 hot work die steel), tungsten steel; | High-temperature strength and tempering resistance (>500°C) |
| Structural | Design: Diameter/length ratio ≤ 20:1 | Prevent bending and fracture |
| Installation | Specifications: Deviation between the center of expansion force and the clamping center ≤ 5mm | Avoid tie bar deformation caused by uneven loading |
| Sealing | Requirements: Independently seal the cooling channels and tie bar holes | Prevent coolant infiltration and corrosion |

Tie Bars vs. Alternative Clamping Systems
- Traditional Tie Bars
- Alternative Clamping Systems
Traditional Tie Bars
Function
Traditional Tie Bars Function Tie bars are rigid bars that link the stationary and moving parts of the platen of a die casting machine. They supply the necessary clamping force to keep the mold shut during the injection phase. This ensures that the molten metal is forced into the cavity at high pressure and prevents leakage.

Advantages
- High Clamping Force: Tie bars are effective in providing a significant clamping force and are therefore, confidently used in large-scale die casting processes.
- Precision: As the control provided to the mold is precise, the quality of castings and tolerances is high.
- Reliability: When in good operating conditions, tie bars are dependable and have a long service life.
Limitations
- Complexity: The use of tie bars can be difficult and labor-intensive when it comes to installation and maintenance.
- Space Requirements: The use of tie bars also increases the space requirements of the machine. This is a disadvantage in machine shops with limited floor space.
Alternative Clamping Systems
Hydraulic Clamping
These systems use a hydraulic pump to generate the clamping force. They are designed to be capable to provide uniform and variable clamping force during the injection phase.
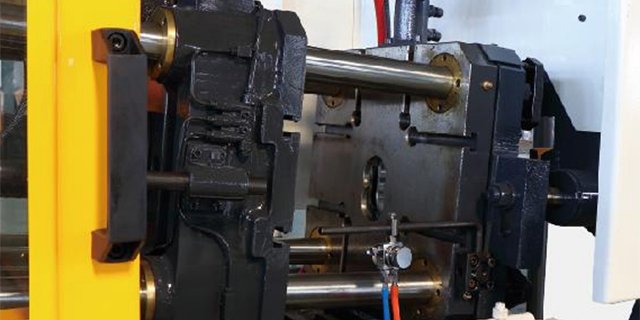
Advantages
- Flexibility: Hydraulic clamping systems offer a wide adjustable range of clamping force, making them applicable to a variety of molds including smaller and more complex ones.
- Space-efficient: Compared to traditional tie bars, they take up less space, making them suitable for facilities with limited square footage.
- Ease of maintenance: Unlike tie bars, there systems are more straightforward and less cumbersome to maintain and adjust.
Limitations
- Initial cost: Compared to traditional tie bars, the initial investment for these clamping systems is significantly higher.
- Maintenance requirements: While easier to maintain, these systems are more prone to requiring regular checks and maintenance.
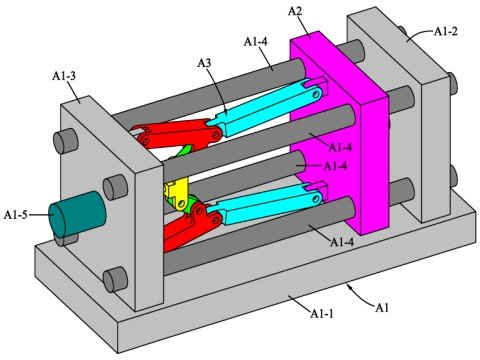
Choosing the Right Clamping System
Application needs
What tie bars and alternative clamping systems are to be used is heavily dictated by the specific requirements of the application. Considerations include, but are not limited to, the overall dimensions of the mold, the expected production volume, and the space available.
Machine compatibility
Ensure that the chosen clamping system is suitable with the die casting machine. HAICHEN has a variety of machines with both traditional tie bars and alternative clamping systems to suit diverse needs.

HAICHEN’s Technical Solutions for Clamping Systems
HAICHEN offers both tie bar and alternative clamping systems in its die casting machines. We match the right system to customer needs and ensure reliable operation through precise control and strong design.
- HAICHEN Practice with Tie Bar Systems
- HAICHEN Application of Direct Hydraulic Clamping
- Customer Case: System Choice and Results
HAICHEN Practice with Tie Bar Systems
HAICHEN uses high-strength alloy steel tie bars on medium to large machines. We optimize the stress design with computer analysis. Our machines have an automatic stress balance system on the tie bar nuts. This system checks and adjusts the preload on each tie bar in real time. It keeps the force difference between the four tie bars within ±3%. This prevents mold flash and early tie bar wear caused by uneven loading.
HAICHEN Application of Direct Hydraulic Clamping
For customers who need fast mold changes or have limited space, HAICHEN offers a direct hydraulic clamping option. This system uses large hydraulic cylinders to clamp the mold directly, with no tie bars. It gives a very wide space for mold opening. HAICHEN’s hydraulic system uses fast servo valves and closed-loop pressure control. It can build and lock the full clamping force in milliseconds. This is ideal for high-speed production of thin-wall parts.
Customer Case: System Choice and Results
An auto parts maker ordered several HAICHEN machines for the same production line to make different products.
- Different Needs: For large parts like transmission housings, they needed very rigid clamping. HAICHEN provided tie bar systems. For small precision parts like sensor housings, they needed quick mold changes in tight spaces. HAICHEN provided direct hydraulic clamping systems.
- Results: The tie bar machines kept very accurate clamping under full load. The time between mold maintenance increased by 30%. The hydraulic machines cut mold change time by 50%. The open space also allowed for more complex robots, raising automation levels.

Understanding the differences between tie bars and alternative clamping systems is essential for making the right choice in die casting operations. By considering the specific needs of your application and the compatibility with your machine, you can select a clamping system that ensures efficient and high – quality production.



