Die-casting moulds (dies) are defined as those special tools which shape molten metal into components under high pressure with very close tolerances assumed as the most common definition of die castings.
The type of mold selected will depend upon such factors as production volume, part complexity, material to be used, and cost requirements.
Below is a listing comprised of the major types of die-casting molds together with their characteristics and normal applications.
Ten characteristics of current die casting molds
- Single-Cavity Moulds
- Multi-Cavity Moulds
- Unit Die Moulds
- Family Moulds
- Hot Runner Moulds
- Cold Runner Moulds
- Overflow Moulds
- Vacuum-Assisted Moulds
- Hybrid Moulds
- Insulated Runner Moulds
Single-Cavity Moulds
- Description: Contains one cavity, producing a single part per casting cycle.
- Applications: Low-volume production, prototyping, or large/complex parts (e.g., engine blocks).
- Pros: Lower tooling cost, simpler design, and easier maintenance.
- Cons: Low output efficiency compared to multi-cavity systems.

Multi-Cavity Moulds
- Description: Multiple identical cavities produce several parts in one cycle.
- Applications: High-volume production of small parts (e.g., automotive brackets, connectors).
- Pros: Higher productivity and reduced per-part cost.
- Cons: Higher initial cost and complex maintenance.

Unit Die Moulds
- Description: Modular design with interchangeable inserts for different part geometries.
- Applications: Prototyping or small batches of varied designs (e.g., custom fittings).
- Pros: Cost-effective flexibility for multiple designs.
- Cons: Limited to similar-sized parts; inserts may wear unevenly.
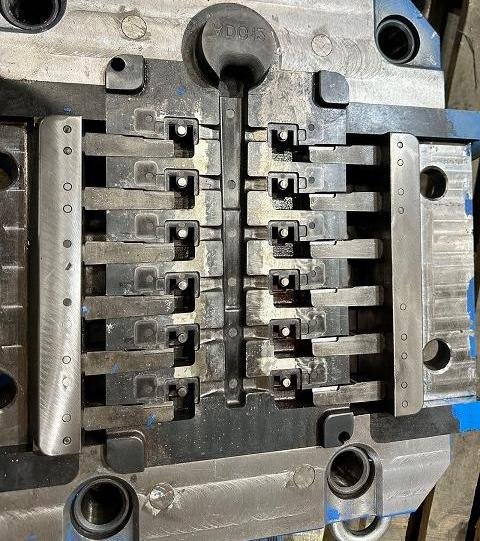

Family Moulds
- Description: Combines cavities for different parts used in the same assembly (e.g., gearbox components).
- Applications: Automotive, electronics, and appliances.
- Pros: Eliminates need for separate moulds; ensures part compatibility.
- Cons: Risk of scrap if one cavity fails; complex design.

Hot Runner Moulds
- Description: Uses heated channels to keep molten metal liquid, eliminating solidified runners.
- Applications: High-precision parts (e.g., medical devices, aerospace components).
- Pros: Minimal material waste, faster cycles, superior surface finish.
- Cons: Expensive upfront cost and maintenance.
Cold Runner Moulds
- Description: Unheated runners deliver metal to cavities; runners solidify and are recycled.
- Applications: General-purpose casting (e.g., industrial fittings).
- Pros: Lower initial cost and simpler operation.
- Cons: Higher material waste and slower cycles.
Overflow Moulds
- Description: Includes overflow wells to trap excess metal, ensuring full cavity filling.
- Applications: Parts requiring flawless surfaces (e.g., decorative hardware).
- Pros: Reduces porosity and incomplete filling.
- Cons: Increased scrap and complex tooling.
Vacuum-Assisted Moulds
- Description: Uses vacuum systems to remove air from cavities, minimizing porosity.
- Applications: High-strength parts (e.g., automotive transmission components).
- Pros: Enhances part density and mechanical properties.
- Cons: Higher equipment costs and maintenance.
Insulated Runner Moulds
- Description: Insulated runners retain heat to keep metal semi-liquid between cycles.
- Applications: Medium-volume production of aluminum/zinc parts.
- Pros: Reduces heat loss and material waste.
- Cons: Limited to specific alloys and geometries.
Hybrid Moulds
- Description: Combines features of hot/cold runners or other systems for optimized performance.
- Applications: Complex parts needing balanced cost and quality (e.g., automotive sensors).
- Pros: Customizable for specific needs.
- Cons: High design complexity and cost.
Key Factors in Mould Selection
- Production Volume: High-volume runs favor multi-cavity or hot runner moulds; low-volume uses single-cavity.
- Part Complexity: Intricate designs may require vacuum-assisted or overflow systems.
- Material: Aluminum alloys often pair with insulated runners; magnesium may need specialized coatings.
- Cost: Balance upfront tooling costs with long-term efficiency (e.g., hot runners save material but are pricier).
- Surface Finish: Overflow or vacuum systems enhance aesthetics and reduce post-processing.

Haichen Aluminum alloy road stud mold
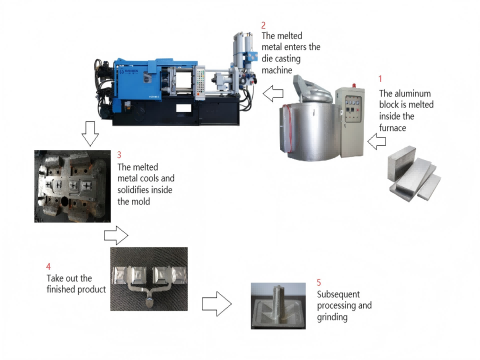
Haichen four-cavity moulds operate in conjunction with cold-chamber die-casting machines. Each cycle produces four road studs in just 50 seconds, achieving daily output exceeding 5,000 units.
Surface Quality and Material Utilisation
Die-cast components exhibit surface roughness Ra of 0.8–3.2 μm, eliminating secondary processing. Material utilisation reaches 80%, with blank recovery exceeding 90%.
Aluminium Road Stud Production Line
Haisen Die-Casting Machine Technological Innovations and Practical Applications
High-Efficiency Batch Production Solution for Road Studs
Equipment Configuration: HCD 880-C cold-chamber die-casting machine with 8800 kN clamping force, suitable for producing 15×15 cm aluminium road studs.
- Technical Highlights
- Production Capacity
- Vacuum Die Casting
- Intelligent Temperature Control System
Technical Highlights:
Four-stage injection control: Magnetic scale positioning and PLC-regulated injection speed precision eliminate gas defects, achieving 99% yield.
Intelligent cooling system: Multi-channel water cooling within moulds, combined with finite element thermal analysis, reduces cooling time by 30% while minimising thermal distortion.
Production Capacity:
Single production line exceeds 1.8 million units annually, serving infrastructure projects across the Middle East and Southeast Asia.
Innovative Technology Applications
Vacuum Die Casting:
Reduces internal porosity in road studs, enhancing impact strength by 30% for severe cold-weather applications.
Intelligent Temperature Control System:
Real-time mould temperature monitoring with automatic cooling water flow adjustment ensures batch consistency.

HCD Machinery Core Value Proposition
HCD’s solutions extend beyond supplying machinery to deliver stable, comprehensive turnkey production platforms for road stud manufacturers.
The robustness of the HCD 880-C model ensures sustained, high uptime critical for meeting tight project deadlines.
Furthermore, the deep integration of process control technologies—from injection curves to vacuum and temperature management—transforms raw parameters into actionable process intelligence. This enables manufacturers to achieve immediate excellence in quality and output while digitally fine-tuning and documenting future product lines, thereby securing long-term competitiveness within global infrastructure supply chains.
Materials for manufacturing road studs
Aluminium alloy road studs form a vital component of modern road safety and traffic management systems. Their superior reflective properties provide clear route guidance for drivers at night or in low-light conditions, while their robustness ensures long-term stability under vehicle pressure and harsh environmental conditions. Widely deployed on roads, motorways and car parks, these devices effectively enhance driving safety by clearly delineating lanes and warning of hazardous areas.
By the end
Die casting moulds are engineered to meet specific production goals, from rapid prototyping to mass manufacturing. Innovations like vacuum assistance and hybrid systems continue to push the boundaries of part quality and efficiency. Selecting the right mould type ensures optimal performance, cost savings, and minimal waste, making it a critical decision in die casting projects.
Contact Haichen for more die casting technical details~!




