Good casting design basic rules is critical to producing high quality, functional and durable castings during the manufacturing process. Here are some basic rules for good casting design.
- Simple geometric shapes
- Prioritize graphics
- Material Selection
- Avoid sharp thickness changes
- Avoid sharp corners and edges
- directed solidification
- Setting of risers and gating systems
- Consider manufacturing and assembly
- Reduce internal defects
Good casting design basic rules
Simple geometric shapes
- Castings should consist of geometrically simple bodies, such as cylinders, cones, cubes or spheres.
- This helps to simplify the mold design and manufacturing process.
Prioritize graphics
- Use prioritize graphics in preference to curved surfaces that follow simple curves.
- This reduces the risk of stress concentrations and deformation.
Material selection of good casting design basic rules
- The most suitable casting material is selected according to the type of stress expected.
- For example, for shock or vibration stresses, “brittle” flake graphite cast iron should not be used.
Avoid sharp thickness changes
- The wall thickness of the casting should be as uniform as possible, avoiding sudden thickness changes, which can lead to uneven cooling and defects.
Avoid sharp corners and edges
- Avoid Sharp corners and edges in the design as they can become stress concentration points that can lead to cracks and fractures.
Directional solidification
- The design should take into account the solidification direction of the casting to ensure that the liquid metal can fill the mold smoothly and reduce defects caused by shrinkage.
Setting of risers and gating systems
- Properly set up risers and gating systems to ensure a smooth flow of metal and to provide the necessary make-up contraction during solidification.
Consider manufacturing and assembly
- The design should consider the convenience of manufacturing and assembly in order to reduce production costs and improve product quality.
Reduce internal defects of good casting design basic rules
- Reduce the internal defects of castings, such as porosity, shrinkage holes, etc. through optimized design, so as to improve the overall quality of castings.
What is the basic concept of casting?
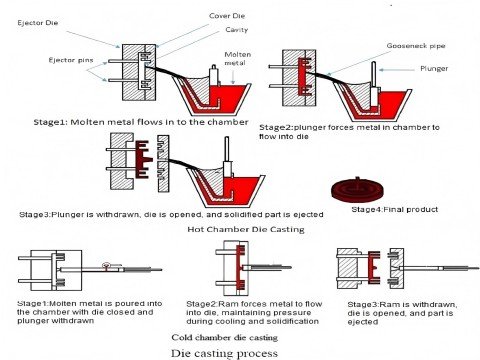
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold containing a cavity of the desired shape and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part, also known as the casting, completes the process after it is shot out of the mold or broken.
What are the basic requirements of casting?
The basic requirements for casting can be summarized in a number of ways, including material selection, process flow, quality control, and defect handling. These requirements ensure the functionality, reliability and suitability of cast parts.
- Material Selection
- Process Flow
- Quality Control
- Defect Handling
Material Selection
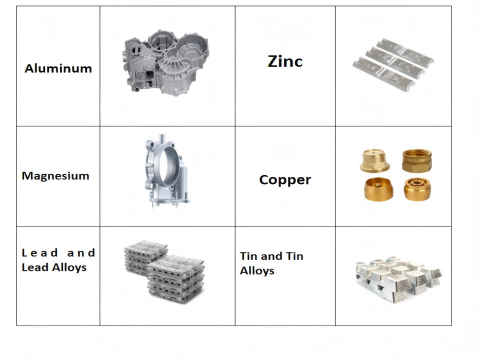
The selection of casting materials needs to be determined according to the load, operating conditions and environment, and in accordance with the requirements of the relevant standards or specifications.
Process Flow
The casting process consists of several steps, such as mold making, melting, pouring, cooling and post-treatment. Common casting methods include sand casting, disappearing mold casting, centrifugal casting and pressure casting, etc.
Quality Control
- Dimensional accuracy: The casting must meet specified dimensions.
- Surface finish: The surface should be smooth enough for the application.
- Internal quality: Free from defects like porosity, inclusions, and cracks.
Defect Handling
If there are defects in the casting, such as surface cracks or internal porosity, they can be repaired by machining (e.g., grinding), welding, or filling with plastics.
What to Consider in Metal Casting Design?
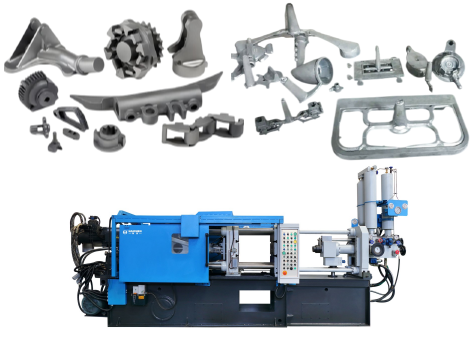
- Part Geometry and Complexity
- Material Selection
- Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
- Surface Finish
Part Geometry and Complexity
Shape and Size: Ensure the part’s shape is suitable for casting. Avoid extremely thin walls, which may be difficult to fill with molten metal.
Undercuts and Draft Angles: Minimize undercuts that can complicate mold design and part removal.
Material Selection
Metal Type: Choose a metal based on the part’s intended use.
Alloy Properties: Consider the mechanical properties like strength, toughness, and thermal conductivity.
Dimensional Accuracy and Tolerances
Different casting processes have different levels of dimensional accuracy.
Surface Finish
Some casting processes provide better surface finishes than others. For example, die – cast parts usually have a smoother surface than sand – cast parts.
Haichen die casting machine

Haichen, a manufacturer which is specialized in cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machines and widely recognized for efficiency and precision in the production of high-quality cast parts. We are commonly used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods for manufacturing components from materials like aluminum, zinc, and magnesium.
If there is any information about the die casting want to know, welcome to consult us.
By following these good casting design basic rules, you can create a casting design that is both functional and cost-effective while minimizing defects and maximizing the ease of production.



