Pressure die casting steps:
- Preparation
- Injection and solidification
- Ejection and finishing
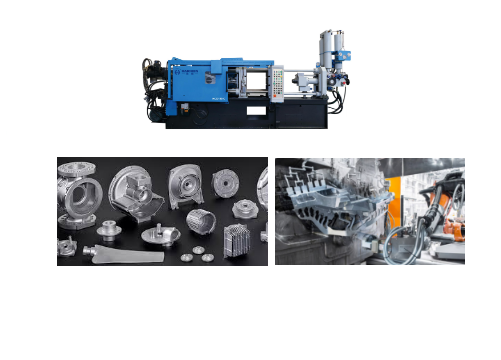
Pressure die casting is an advanced metal casting process that is widely used to produce metal parts with high precision, high strength, and high surface finish.
Moreover, it is widely adopted in manufacturing because it can quickly produce precise parts with consistent dimensions in high volumes.
It allows for complex shapes with intricate details and thin walls, and the castings generally have a smooth surface straight out of the mold.
It can handle tight tolerances, and produces much less waste than other similar methods. It’s compatible with a wide range of non-ferrous metals, and cost-effective when it comes to mass production.
Haichen’s high-pressure die casting machines are divided into hot chamber die casting machines and cold chamber die casting machines, with complete models that can meet the needs of different producers for large and small outputs.
What is Pressure Die Casting?
Pressure die casting is a die casting type that uses a metal mold—typically crafted from premium, heat-resistant steel grades—into which manufacturers inject non-ferrous metals like aluminum or zinc.
Basically, manufacturers machine the mold cavity (or die) into the required shape, then force molten metal into it under pressure and high velocity.
The two main types of pressure die casting are low- (LPDC) and high-pressure (HPDC) die casting.

Beyond these, die casting can also be classified by chamber type: hot or cold. In hot chamber die casting, the casting machine heats the metal internally.
The pressure die casting process starts with an engineered closed steel die cavity, where manufacturers forcefully inject molten metal under pressure.
The machine itself has an injection mechanism on one end that uses both hydraulics and pressurized gas to propel a piston forward, and, on the other end, a clamping mechanism that uses hydraulics and mechanical toggles.
The design ensures the machine can survive intense pressure during injection, and the die remains firmly closed as the metal part hardens.
Impressively, this process can convert molten metal into a solid, near-net-shape part within just a few seconds. You can see all the different parts involved in the below diagram.

Die casting mould preparation
Firstly, before starting high-pressure die casting, the mold must be prepared. This involves cleaning the mold and applying lubricant.
The lubricant helps control the mold temperature and forms a thin film between the molten metal and the mold, facilitating the release of the cast part afterward.
Secondly, Haichen will inspect the mold for defects, damage, or loose components (such as locks and positioning devices).
The mold cavity should be cleaned to ensure no impurities are present.

Pressure die casting Injection and solidification
After the mold is prepared, molten metal is injected into the mold cavity. Depending on the material used, either hot chamber or cold chamber injection systems can be selected.
The hot chamber system is suitable for low-melting-point metals such as zinc and magnesium, while the cold chamber system is used for high-melting-point metals such as aluminum and brass.
Haichen’s die casting machines are high-pressure injection systems, where molten metal is injected into the mold cavity under high pressure (typically 10-175 MPa) to fill every gap in the mold.
High pressure ensures rapid filling of complex shapes and compensates for shrinkage during solidification.
During the injection process, metal is rapidly filled into the mold cavity under high pressure to ensure complete filling of the mold and avoid defects.
Ejection and finishing
Firstly, after metal is injected into the mold, it cools and solidifies rapidly. The cooling rate is crucial for preventing defects such as porosity, cracks, or deformation.
During solidification, the mold remains closed to ensure uniform solidification. Once solidification is complete, the mold is opened, and the ejection mechanism (such as ejector pins or sliders) removes the cast part from the mold.
Haichen can also provide auxiliary equipment like robotic arms to assist manufacturers in automating this step.
Finally, flash and burrs are removed through mechanical processing (e.g., milling, grinding) or chemical treatment (e.g., acid washing) to remove excess material from the die-cast part.

How to monitor and ensure the quality of castings in the process of pressure die casting?
- Mould Inspection & Maintenance
- Parameter setting and real-time monitoring
- On-line inspection and automated quality control system
- On-site inspection and non-destructive testing
- Raw material selection and handling
- Operation & Maintenance
- First Article Inspection vs. Intermediate Inspection
- Dimensional Measurement & Visual Inspection
Mould Inspection & Maintenance
Mold is a key factor that affects the size and surface quality of a casting.
Before the die casting process begins, the mold should be rigorously inspected and tested to ensure that the mold dimensional accuracy and surface finish meet the requirements.
The wear or damage of any mold can directly affect the quality of the casting.
So regular maintenance and upkeep of the mold is also crucial.

Parameter setting and real-time monitoring
Proper parameter setting is the key to ensuring the stability and consistency of the die casting process.
Before the operation of the die-casting machine, it is necessary to reasonably set the processing parameters.
According to the requirements of the product and the characteristics of the process, including injection speed, injection pressure, injection rate, injection temperature, etc.
By optimizing these parameters, it is possible to ensure that the castings are dimensionally stable and have a good surface quality.
In the die-casting process, the die-casting machine should be monitored in real time, and the pressure, temperature, speed and other data should be recorded.
By monitoring the data, anomalies can be detected in time and machine parameters can be adjusted to maintain the stability and consistency of the die casting process.
On-line inspection and automated quality control system
In modern manufacturing, the adoption of on-line inspection and automated quality control system is the key.
By monitoring the quality of castings in real time.
Process parameters can be discovered and adjusted in time to improve production efficiency and product consistency.

On-site inspection and non-destructive testing
On-site inspection of finished die-casting products is an important part of quality control.
The inspection content should include the size, surface quality, pores and pores of the product to ensure that the product meets the design requirements and customer needs.
Through strict on-site inspection, unqualified products can be found and eliminated in time, and the pass rate of products can be improved.
In addition, using non-destructive testing techniques such as X-ray or ultrasonic.
Defects such as porosity, inclusions or underfilling within the casting can be detected in a timely manner.

Raw material selection and handling
Select high-quality aluminum alloy or other alloy raw materials to ensure that their chemical composition meets the requirements of the standard.
And avoid defects such as poor fluidity or shrinkage porosity caused by raw material problems.
Strict screening and pretreatment of raw materials are carried out to remove impurities and foreign substances in them to ensure the purity of molten metal.

Operation & Maintenance
Regularly maintain and maintain the die casting machine and mold to ensure that it is in good working order and reduce casting defects caused by equipment problems.
Strengthen staff training, improve the skill level and sense of responsibility of operators.
And ensure the stability and reliability of the die casting process.
First Article Inspection vs. Intermediate Inspection
During the production process, inspectors will inspect the first article of each batch to ensure quality and consistency.
To ensure that the first piece of the product meets the specified quality standards.
Regular intermediate inspections are conducted to ensure the stability of the quality of the die castings produced.
Dimensional Measurement & Visual Inspection
Use measuring tools (e.g., calipers, micrometers, projectors, etc.) to measure the size of the die casting to ensure that the dimensions meet the requirements.
Inspect the appearance of die castings, including surface defects, porosity, cracks, etc.
High pressure die casting features
- High Speed
- High precision and dimensional stability
- High productivity
- Strong material adaptability
Firstly, Haichen has two types of high-pressure die-casting machines: hot-chamber die-casting and cold-chamber die-casting.
In hot-chamber die-casting, the metal melting process occurs within the furnace of the die-casting machine.
The injection system of the die-casting machine directly injects the molten metal into the die cavity.This method is suitable for low-melting-point alloys.
In contrast, in cold-chamber die-casting, the metal melting process occurs in an independent furnace outside the die-casting machine.
A ladle or an automatic device transfers the molten metal into the injection system of the die-casting machine.
High Speed
Pressure die casting operates at extremely high pressures (typically 700 to 2500 bar) and fast filling speeds (0.5 to 120 m/s).
Ensuring that the molten metal fills the mold cavity quickly and completely.
Achieving high-quality molding even for thin-walled or complex-shaped parts.
High precision and dimensional stability
Due to high pressure and fast filling, the casting has high dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
Usually up to grade 5~8, which is suitable for mass production.
High productivity
High-pressure die casting enables very fast cycle times, making it ideal for high-volume production.
Strong material adaptability
Suitable for a variety of metals, including aluminum, zinc, magnesium, copper and other alloys.
Especially in the automotive, aerospace and other fields of wide application.