Furnace in the casting process is a critical equipmentthat melt metals and alloys, ensuring that they reach the necessary temperature and consistency in order to be molded.
The role and critical importance of the furnace in die-casting processes. It is responsible for melting metals or alloys to precise temperatures and maintaining stable temperatures throughout the casting process. This is paramount, as temperature directly influences the fluidity of molten metal, its ability to fill intricate moulds, and the final microstructure and properties of the castings. Whether for aluminium, zinc, magnesium, lead, or any other metal, a suitable furnace ensures the molten metal remains in optimal casting condition, thereby minimising defects and enhancing quality.
The role of a furnace is not only melting, but also includes temperature regulation, chemical composition control, and material storage.
Definitions and core functionality
Main use: The furnace heats and melts the raw metal (ore, scrap or alloy) to remove impurities (gangue) and convert it into a liquid state for pouring into a mold.
Key Functions
Melting: The conversion of solid metals into a molten form by extreme heat, such as induction, combustion, or arcing.
Temperature control: Maintain or increase the molten metal temperature to compensate for heat loss during transfer, ensuring optimal pouring conditions.
Homogenization: Mixing molten metal to obtain a uniform chemical composition and reduce fluctuations, which is essential for alloy consistency.
Refining: Removes impurities and adjusts the alloy composition.
Storage: Acts as a buffer between the melting and casting stages, ensuring a steady supply of molten metal.

Furnace structural components
Furnace shell: Made of steel or aluminum alloy to ensure rigidity and heat resistance.
Linings/crucibles: refractory materials that are resistant to high temperatures (e.g. silica, alumina).
Induction coil: high-purity insulated copper coil that generates an electromagnetic field.
Cooling system: water-cooled components (e.g. coils, yokes) to prevent overheating.
Control system: Automatic temperature adjustment by PLC and sensors (e.g. thermocouples).

Classified by heating method
- Resistance furnace
- Electric arc furnace
- Induction furnace
Resistance furnace: Heat is generated by a resistive heating element (such as a silicon carbon rod).
With high temperature control accuracy, making it suitable for small batch production or laboratory environments.
Electric arc furnace: uses the arc to melt metal at high temperatures, commonly found in aluminum die casting plants, suitable for large-scale production, but has high energy consumption.
Induction furnace: Heating metal by electromagnetic induction, with fast melting speed and less oxidation, especially suitable for high melting point metals such as copper and magnesium.
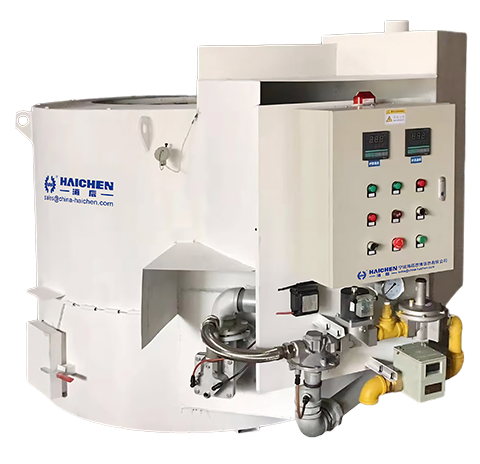

Furnace in the casting Classified by fuel type
- Diesel/gas furnace
- Electric heating furnace
Diesel/gas furnace: direct heating by burner, low initial cost, but there are problems such as workshop pollution, molten aluminum and iron pollution.
Electric heating furnace: clean and environmentally friendly, with high thermal efficiency, but it needs to have a stable power supply, which is suitable for scenarios with strict environmental protection requirements.
Classified by function and structure
- Crucible furnace
- Centralized melting furnace
- Crucible-free electric melting holding furnace
Crucible furnace: Conventional furnace type, simple operation but slow melting speed, easy to lead to the oxidation of molten aluminum and the mixing of impurities.
Centralized melting furnace: suitable for large-scale continuous production, but it is necessary to pay attention to the selection of refractory materials and the utilization of thermal energy.
Crucible-free electric melting holding furnace: using SIC heating elements and high-strength refractory materials.
It has both melting and heat preservation functions, stable temperature of molten aluminum and low defective rate of casting, representing the future energy-saving trend.
Furnace in the casting for special applications
- Double-push induction furnace
- Tilting induction furnace
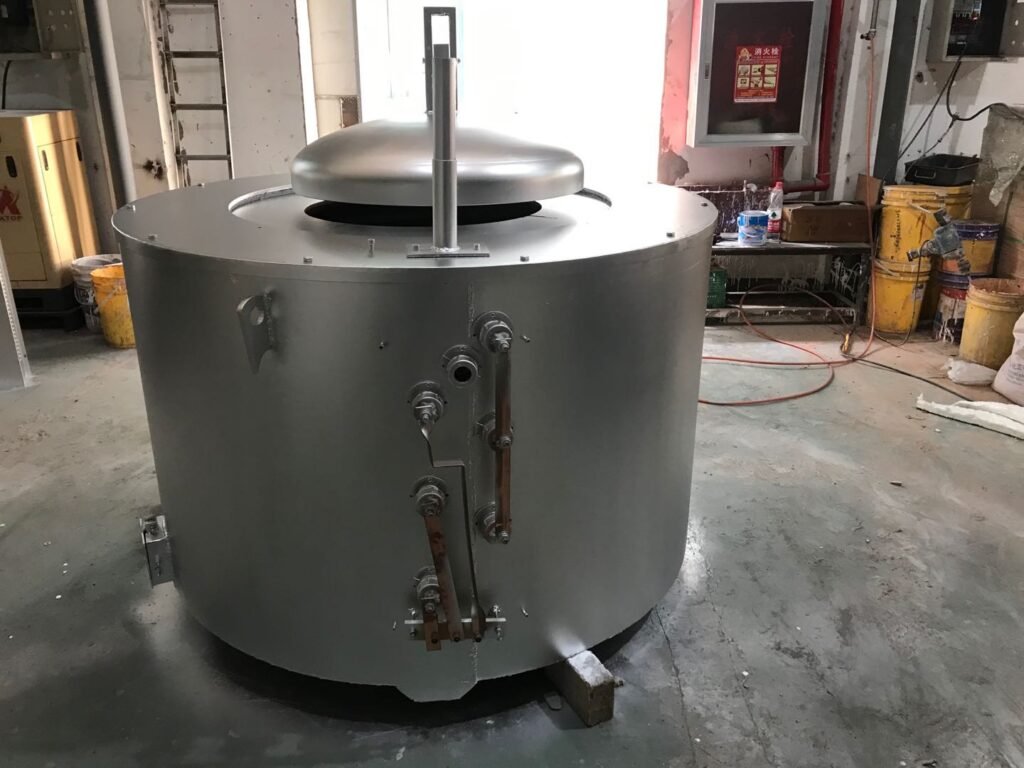

Double-push induction furnace
For copper rotor die casting, with a pneumatic cylinder pushing the crucible for small-scale or prototype production.
Tilting induction furnace
Suitable for large-scale continuous casting, it can handle a variety of raw materials.
Such as sheared copper cathode, and is equipped with nitrogen protection to reduce oxidation.
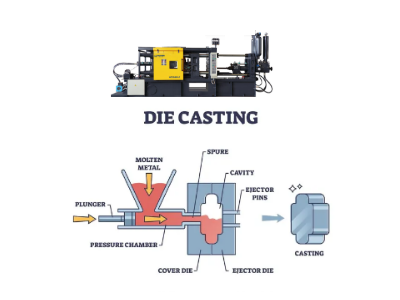
The working principle and technical parameters
- Working principle
- Key technical parameters
Working principle

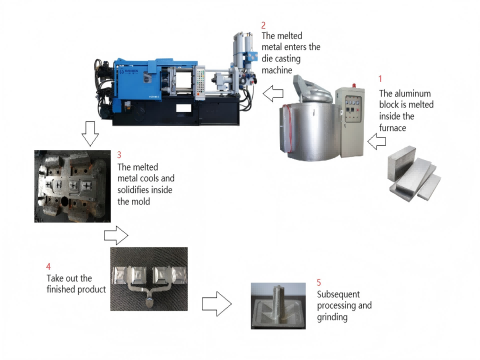
Melting stage
The metal absorbs heat through heat conduction, convection, or radiation in the furnace, and forms a liquid state after reaching the melting point.
For example, electric arc furnaces are heated by burners or arc radiation.
And induction furnaces generate heat by electromagnetic eddy currents.
Holding stage
To maintain a stable temperature of the molten metal.
It is usually necessary to be equipped with a temperature sensor and an automatic control system.
Conveying stage
The molten metal flows into the press chamber of the die casting machine through a pump or gravity to complete the high-pressure injection.

Key technical parameters
Melting rate: from tens of kilograms to several tons per hour, depending on the furnace size.
Temperature control accuracy: within ±5°C, which directly affects the shrinkage and surface quality of castings.
Energy consumption index: the energy efficiency of the electric furnace can reach more than 90%, and the thermal efficiency of the gas furnace is about 40-60%.
Refractory life: A high-quality liner can withstand thousands of melting cycles, reducing downtime and maintenance costs.
The foundry furnace is the core equipment of metal processing, integrating melting, refining and temperature management.
Its design and operation vary depending on the alloy, the scale of production, and technological advancements.



