High Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) of Aluminum is a manufacturing process that injects molten aluminum into a steel mold cavity under high pressure and speed to rapidly produce complex metal components.
High-pressure aluminum die casting (HPDC) is a high-throughput near-net-shape manufacturing process for aluminum parts. Through a combination of a cold-chamber injection system and steel molds, it enables the high-productivity production of complex-shaped components.
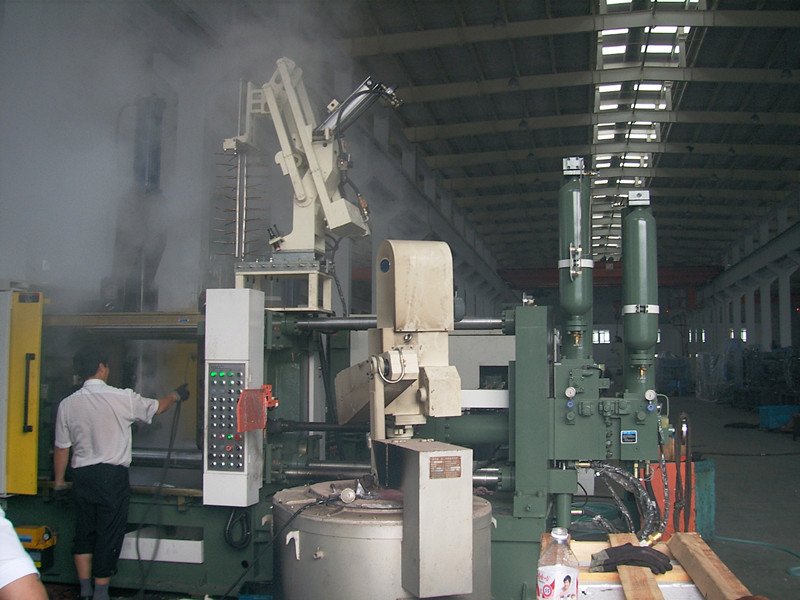

This process excels in scenarios requiring complex geometries, low unit cost for high-volume production, and moderate mechanical performance—particularly suitable for the automotive, consumer electronics, power tool, and housing manufacturing industries.

High Pressure Die Casting Practical Application
Below are its core principles, technical details, and applications:
- Process Principles
- Process Steps
- Advantages
- Limitations
- Technological Advances
Process Principles
- High Pressure & Rapid Injection:
- The process forces molten aluminum into the mold at pressures ranging from 1,000–25,000 PSI (~7–172 MPa) and speeds of 30–100 m/s, ensuring complete filling of intricate geometries, including thin walls (as thin as 0.5 mm).
- High pressure minimizes shrinkage and improves dimensional accuracy.
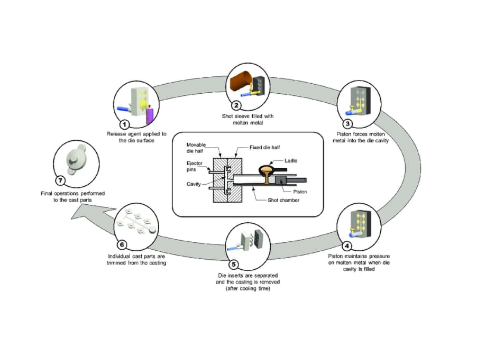
- Tooling & Equipment:
- Manufacturers use hardened steel molds (split into fixed and moving halves) for tens of thousands of cycles, though initial mold costs remain high.
- Cold-chamber die casting machines handle aluminum (melting point ~660°C/1220°F) to isolate molten metal from the injection system, reducing thermal stress on equipment.
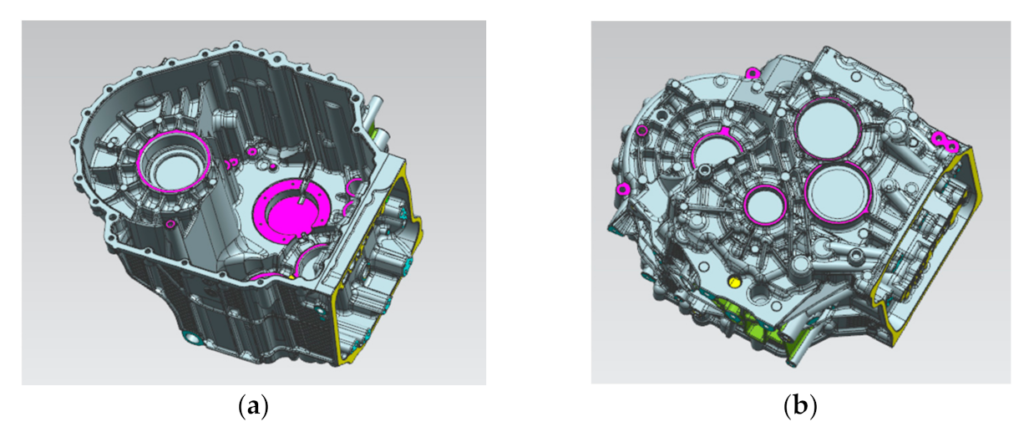
Process Steps
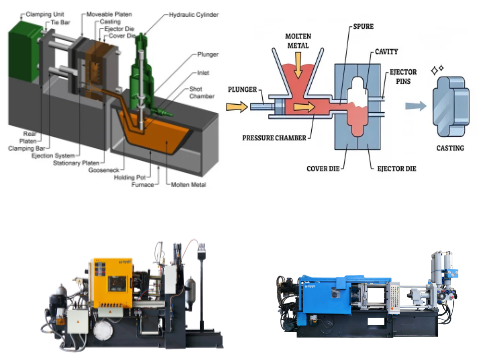
- Melting: A furnace heats aluminum alloy to a molten state (~670–710°C/1240–1310°F).
- Injection: Operators ladle the molten metal into the shot chamber, and a hydraulically driven piston injects it into the mold.
- Cooling & Ejection: The metal rapidly solidifies (seconds to tens of seconds), after which the mold opens, and ejector pins remove the part.
- Post-Processing: Most parts require only deburring, trimming, or drilling.
Advantages
- High Efficiency: Mass production (e.g., automotive parts) achieves cycle times as short as 30–60 seconds.
- Precision & Surface Quality: Tight tolerances (±0.1 mm) and smooth surfaces (Ra 1.6–3.2 μm) reduce post-processing costs.
- Material Properties: Aluminum’s lightweight (2.7 g/cm³), high strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance support lightweighting in electric vehicles and aerospace.
Limitations
- High Tooling Costs: Complex molds cost 50,000–50,000–1M+, limiting HPDC to high-volume production (typically 10,000+ units/year).
- Gas Porosity: Turbulent filling traps air, causing internal voids. Vacuum-assisted HPDC (vacuum levels >90%) addresses this issue, enabling heat-treatable or weldable parts.
Applications
- Automotive: Aluminum HPDC dominates 70%+ of demand for engine blocks, transmission housings, and structural components like Tesla’s gigacast chassis.
- Consumer Electronics: Factories produce smartphone frames, heat sinks, and housings with thin walls and precision.
- Aerospace: Engineers use it for non-load-bearing components and lightweight enclosures.
Technological Advances

- Vacuum Die Casting: This method reduces porosity, allowing high-integrity structural parts (e.g., automotive safety components).
- Mega Casting Machines: Machines with clamping forces up to 9,000–12,000 tons (e.g., Tesla’s IDRA Gigapress) produce ultra-large integrated parts (e.g., EV underbodies), cutting assembly steps and weight.
High Pressure Die Casting of aluminum combines high-speed, high-pressure molding with aluminum’s material benefits to deliver complex, lightweight, and cost-effective components. It is a cornerstone of modern manufacturing, particularly in industries prioritizing efficiency and sustainability.
What is the die casting tolerance of aluminum?
- Standard Tolerance Ranges
- Precision Tolerance Ranges
- Tolerance Formulas
- Tolerance Variations by Standard
Standard Tolerance Ranges
- General Standards:
According to NADCA (North American Die Casting Association) and industry norms, the linear dimensional tolerance for aluminum die casting is typically ±0.010 inches (0.25 mm) per 1 inch (25.4 mm), with an additional ±0.001 inches (0.025 mm) for each subsequent inch.- Example: For a 5-inch (127 mm) dimension, total tolerance would be:
±0.010 + 4×0.001 = ±0.014 inches (\~±0.35 mm).
- Example: For a 5-inch (127 mm) dimension, total tolerance would be:
- Parting Line Tolerance: Depends on projected area. For a 75 in² (483.9 cm²) part, parting line tolerance is ±0.012 inches (0.30 mm), leading to a combined tolerance of ±0.026 inches (~0.66 mm) when added to linear tolerance.
Precision Tolerance Ranges
- High-Precision Processes:
With optimized tooling (e.g., repeated sampling, mold re-cutting) and strict process control, tolerances can reach ±0.002 inches (0.05 mm) per inch, plus ±0.001 inches per additional inch.- Example: For a 5-inch dimension:
±0.002 + 4×0.001 = ±0.006 inches (\~0.15 mm).
- Example: For a 5-inch dimension:
- Extreme Cases: Specialized processes (e.g., high-precision molds and CNC finishing) may achieve ±0.005 inches (0.127 mm) or even ±0.01 mm (~±0.0004 inches), but costs increase significantly.
Tolerance Formulas
- General Tolerance Formula:
ε = ±(2.15×10⁻³ × L + 0.2) mm, where L = dimension length (in mm).- Example: For 100 mm:
±(0.215 + 0.2) = ±0.415 mm.
- Example: For 100 mm:
- Precision Formula:
ε = ±(1.15×10⁻³ × L + 0.1) mm.
Tolerance Variations by Standard
- NADCA: Accounts for projected area, parting line shifts, and moving die components (MDC). For example, MDC tolerance for a 75 in² part is ±0.024 inches (0.61 mm).
- ASTM: Aligns with NADCA for linear, parting line, and flatness tolerances.
- Chinese GB/T 15114: Defaults to CNS 4022/4025 standards. Typical tolerances are IT13–IT15, while high precision reaches IT10–IT11 (~±0.05–0.1 mm).
Key Factors Affecting Tolerances
- Material Behavior: Aluminum’s thermal expansion (24 µm/m·°C) requires shrinkage compensation during cooling.
- Tooling Complexity: Moving components (e.g., sliders, ejector pins) introduce tolerance stacking risks.
- Surface Finish: Standard roughness ranges from Ra 3.2–6.3 µm, while high precision achieves Ra 0.8 µm.
Recommendations
- General Applications: Use standard tolerances (±0.010 inches/inch).
- High-Precision Needs: Apply NADCA’s precision guidelines and collaborate closely with suppliers.
- Cost Considerations: Ultra-tight tolerances (e.g., ±0.01 mm) may double tooling costs; evaluate necessity carefully.
For critical projects, consult die casting suppliers early and reference the latest NADCA or GB/T standards during design.
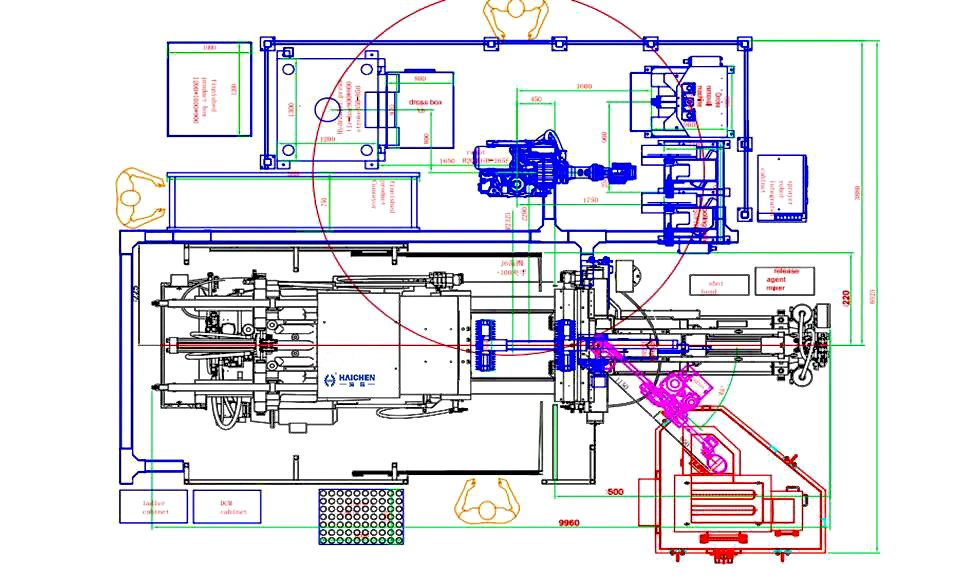
Haichen machine high Pressure Die Casting of aluminum
Haichen Machinery, a leading Chinese manufacturer of die-casting equipment, has over 20 years of expertise in high-pressure aluminum die casting. Its cold chamber HPDC machines are renowned for precision, efficiency, and versatility.
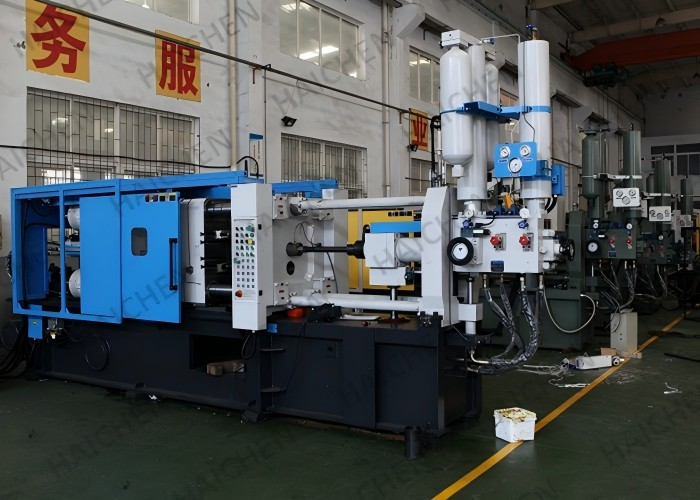

- Equipment Models and Technical Specifications
- HPDC Process Features
- Applications
- Technological Advantages
- Partnerships and R&D
- Industry Comparison
Equipment Models and Technical Specifications
Haichen’s HCD-C Series cold chamber HPDC machines are core products for aluminum die casting, with clamping forces ranging from 350 kN to 20,800 kN (approx. 35 to 2,080 tons). Examples include:
- HCD580-C: Clamping force of 5,800 kN, injection force range of 222–559 kN, adjustable injection speed (suitable for complex aluminum parts).
- HCD200-C (200-ton model): Casting pressure of 50.4–127.3 MPa, maximum aluminum shot weight of 1.8 kg, and multi-stage pressure/speed control (ideal for thin-walled precision components).
HPDC Process Features
- High-Speed Injection: Molten aluminum is injected into molds at 4 m/s under pressures of 50–250 MPa, ensuring cavity filling and minimizing porosity.
- Four-Stage Control: Slow shot, first fast, second fast, and intensification stages optimize melt flow stability, enhancing part density (up to 99.5%) and surface finish (Ra ≤1.6 μm).
- Smart Control: Siemens PLC systems enable real-time injection curve monitoring and closed-loop control, supporting multi-language interfaces (English/Chinese/Russian).

Applications
- Automotive: Engine blocks, structural components (e.g., battery housings for EVs), and lightweight parts (cycle time as low as 30 seconds).
- Thermal Management: Integrated aluminum heat sinks for electronics and HVAC systems.
- Consumer Goods: Thick-walled cookware with uniform heat distribution.
Technological Advantages
- Energy Efficiency: Dual-pump hydraulic systems and servo drives reduce energy consumption by 30% (noise ≤75 dB).
- Material Compatibility: Supports aluminum alloys (melting point >700°C) and magnesium alloys. Cold chamber design prevents thermal damage to injection systems.
- Digital Integration: Cloud-based production management systems enable remote monitoring and process optimization.
Partnerships and R&D
Haichen collaborates with global leaders like Mitsubishi Heavy Industries and SHW, using German/Japanese hydraulic components. Its Ningbo facility (5,000 m²) produces 4,000 machines annually, with R&D focused on innovations like vacuum-assisted HPDC.
Industry Comparison
Compared to traditional casting, Haichen’s HPDC aluminum parts offer:
- 30% higher strength-to-weight ratio vs. steel.
- Near-net-shape precision (minimal post-machining).
- Scalability: Cost-effective for high-volume production (e.g., automotive batches of 100,000+ units).
By the end
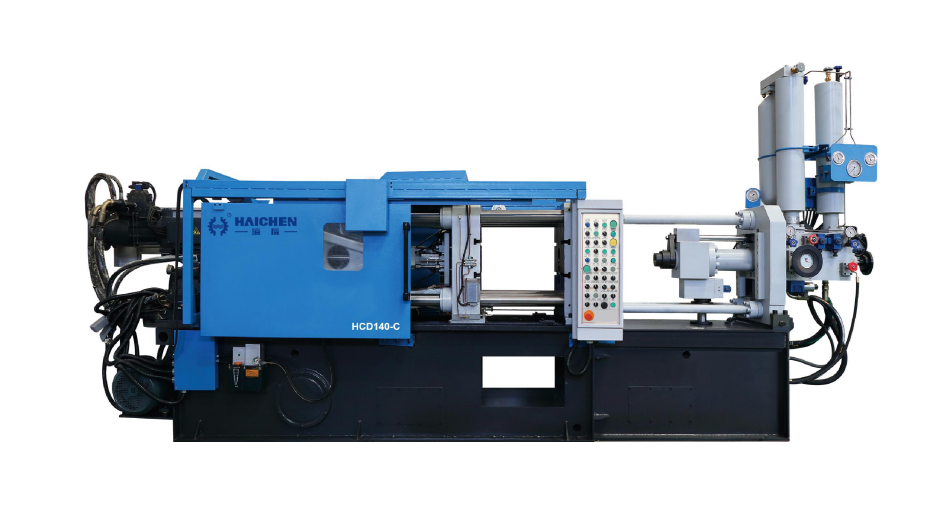

Haichen’s HCD-C Series combines multi-stage pressure control, intelligent systems, and energy-saving designs to lead in automotive, electronics, and consumer goods HPDC. Its focus on R&D (e.g., hybrid HPDC-vacuum technology) positions it as a key innovator in lightweight, high-performance aluminum manufacturing.



