Precision die casting is an advanced manufacturing process used to make metal parts with very close tolerances, high dimensional accuracy, and excellent surface finishes. It applies special methods, tools, and checks to fulfill high standards for detailed shapes, often removing the need for extra machining later.
Precision die casting has a very short forming cycle. Very high injection frequency, fully automated process, able to attain high precision. And low waste in one forming process. These can attain great cost and time advantages when brought in mass production.
Thus it has taken over as the preferred metal forming process for high-volume manufacturing (especially in such industries as automobiles, electronics, and home appliances).

Key points of high-precision die-casting design
- Core Characteristics
- Materials Used
- Key Advantages
- Applications
- Technologies Enhancing Precision
- Comparison with Other Processes
- Quality Assurance
Core Characteristics
- Tight Tolerances: Achieves tolerances as precise as ±0.02–0.05 mm (depending on part size and material).
- High Pressure: Uses pressures up to 200 MPa to ensure complete mold filling and minimize porosity.
- Advanced Tooling: Multi-slide molds, hardened steel dies, and vacuum-assisted systems to reduce air entrapment.
- Fine Surface Finish: Surface roughness (Ra) as low as 0.8–1.6 µm, often eliminating post-casting polishing.
Materials Used

- Aluminum Alloys (e.g., A380, ADC12): Lightweight, corrosion-resistant, and ideal for automotive/electronics.
- Zinc Alloys (e.g., Zamak 3, ZA-8): Excellent fluidity for intricate details.
- Magnesium Alloys (e.g., AZ91D): Ultra-lightweight for aerospace and portable devices.
Key Advantages
- Complex Geometries: Produces thin walls (down to 0.5 mm), internal channels, and fine features (e.g., threads, logos).
- Cost Efficiency: High-volume production reduces per-unit costs; minimal post-processing saves time.
- Consistency: Repeatable quality across thousands of parts due to automated process controls.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio: Ideal for lightweight yet durable components.

Applications
- Automotive: Engine sensors, transmission housings, fuel injectors.
- Electronics: 5G antenna housings, heat sinks, micro-connectors.
- Medical: Surgical instruments, implantable device components.
- Aerospace: Lightweight brackets, drone frames, avionics housings.
Technologies Enhancing Precision
- Vacuum-Assisted Die Casting: Removes air from the mold to reduce porosity and improve structural integrity.
- Real-Time Process Monitoring: Sensors track pressure, temperature, and injection speed to optimize quality.
- CNC Machining Integration: Combines casting with machining for critical features (e.g., bearing seats).

Comparison with Other Processes
| Factor | Precision Die Casting | Investment Casting | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tolerances | ±0.02–0.05 mm | ±0.1–0.25 mm | ±0.005–0.01 mm |
| Cost (High Volume) | Low per-unit | Moderate | Very high |
| Part Complexity | High (thin walls, fine details) | Moderate | Limited by tool access |
| Lead Time | Short (once tooling is ready) | Long (wax patterns required) | Medium to long |
Quality Assurance
- X-Ray/CT Scanning: Detects internal defects like porosity or inclusions.
- CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine): Verifies dimensional accuracy.
- ISO Certifications: Ensures compliance with industry standards (e.g., ISO 9001, IATF 16949).
When to Choose Precision Die Casting
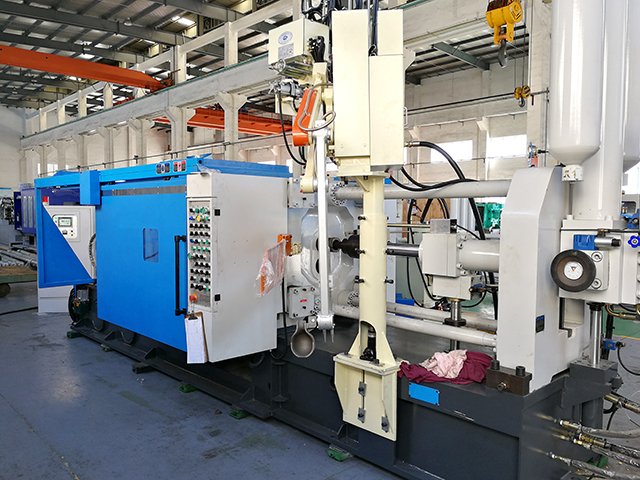

- High-Volume Production: Parts needed in batches of 10,000+ units.
- Complex Designs: Thin walls, intricate shapes, or integrated functional features.
- Lightweighting Goals: Critical for automotive, aerospace, and consumer electronics.
Difference between precison die casting and high pressure casting
In low pressure die casting, molten metal is injected into the die casting mould at low pressure. A characteristic of the process is that the cavity of the mould continues to fill during solidification or shrinkage phase which greatly improves dimensional accuracy, indicating that the process provides an effective means for compensating volume reduction. Other benefits include better consistency of molten metal from top to bottom as well as reduced porosity and oxide formation.
Die casting is a common manufacturing process that can create metal parts with great accuracy and fine finishes. The process works by forcing molten metal under pressure into a mould cavity, then letting it solidify into the needed shape. There are basically two types of die casting: low-pressure die casting and high-pressure die casting. These methods offer different benefits and fit various uses.
How precise is die casting?
Die casting is renowned for producing parts with high dimensional accuracy and excellent surface finish, making it suitable for applications requiring tight tolerances and intricate geometries. However, its precision depends on factors like material choice, part design, tooling quality, and process controls. Below is a detailed breakdown of die casting precision:

- Dimensional Tolerances
- Surface Finish
- Factors Influencing Precision
- Comparison with Other Processes
- Applications Requiring High Precision
- Tips to Enhance Precision
Dimensional Tolerances
- Typical Tolerances:
- Aluminum Alloys: ±0.1–0.3 mm (±0.004–0.012 in) for small to medium parts.
- Zinc Alloys: ±0.05–0.15 mm (±0.002–0.006 in) due to better fluidity.
- Magnesium Alloys: ±0.15–0.25 mm (±0.006–0.010 in).
- High-Precision Tolerances:
- Vacuum-Assisted Die Casting: Achieves ±0.02–0.05 mm (±0.0008–0.002 in) for critical features.
- Secondary Machining: Can refine tolerances to ±0.01 mm (±0.0004 in) for bearing seats or mating surfaces.
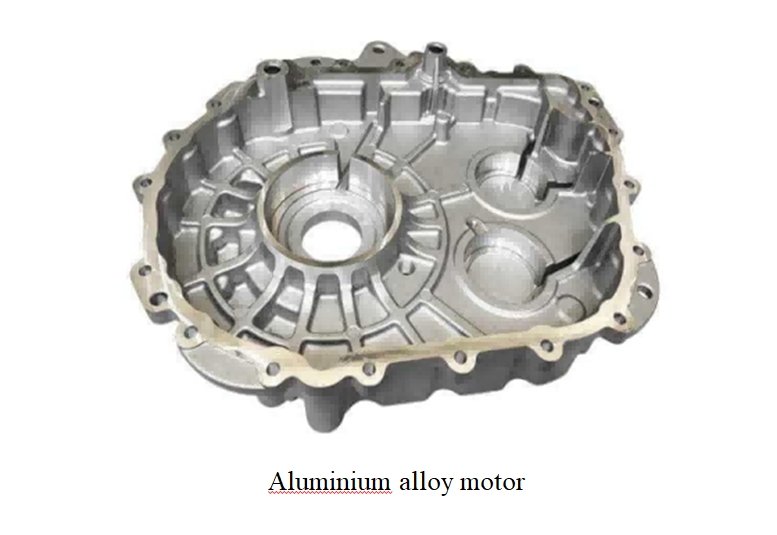

Surface Finish
- As-Cast Finish:
- Aluminum: 1.6–3.2 µm Ra (smooth, but may require polishing for cosmetic parts).
- Zinc: 0.8–1.6 µm Ra (naturally smoother due to material properties).
- Post-Processing:
- Polishing, bead blasting, or coatings (e.g., anodizing) can achieve mirror-like finishes (<0.4 µm Ra).
Factors Influencing Precision
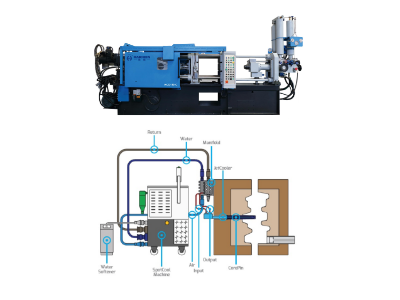
- Tooling Quality:
- Hardened steel molds (e.g., H13) with precise CNC machining ensure consistent part dimensions.
- Multi-slide molds and conformal cooling channels reduce warping.
- Process Control:
- Stable injection pressure (up to 200 MPa), temperature, and cycle time minimize variability.
- Vacuum systems reduce porosity, improving structural integrity.
- Material Fluidity:
- Zinc alloys flow better than aluminum or magnesium, enabling thinner walls (±0.5 mm) and finer details.
- Part Size:
- Larger parts (e.g., automotive housings) may have looser tolerances (±0.5 mm) due to thermal expansion.
Comparison with Other Processes
| Process | Tolerance | Surface Finish (Ra) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Die Casting | ±0.05–0.3 mm | 0.8–3.2 µm | Complex, high-volume parts |
| CNC Machining | ±0.005–0.02 mm | 0.4–1.6 µm | Prototypes, critical features |
| Plastic Injection Molding | ±0.1–0.5 mm | 0.8–3.2 µm | Lightweight, non-metallic parts |
| Investment Casting | ±0.1–0.25 mm | 3.2–12.5 µm | Medium-volume, intricate parts |
Applications Requiring High Precision

- Electronics: Connector housings, heat sinks, and 5G antenna components (±0.05 mm).
- Automotive: Fuel injectors, sensor housings, and transmission valves (±0.1 mm).
- Medical: Surgical tool components and implantable device parts (±0.02 mm with machining).

Tips to Enhance Precision
- Design Optimization: Avoid sharp corners, uniform wall thickness, and draft angles (1–3°) to reduce stress.
- Advanced Tooling: Use multi-cavity molds with vacuum systems for defect-free parts.
- Process Monitoring: Real-time sensors and AI-driven analytics adjust parameters to maintain consistency.
Die casting offers good to excellent precision (±0.05–0.3 mm) for most industrial applications, rivaling processes like investment casting while excelling in speed and cost-efficiency for high volumes. For ultra-critical tolerances (<±0.05 mm), secondary machining or hybrid processes (e.g., squeeze casting) are recommended.
Haichen best precision die casting machine factory
- Company Background and Technical Capabilities
- Core Product Types
- Technological innovation and advantages
- Market and application cases
- After-sales service and support
Company Background and Technical Capabilities

Experience and Positioning:
Haichen is a die-casting machine manufacturer with more than 20 years of experience, exporting high-pressure die-casting machines (HPDC) to overseas markets since 2005.
Its products include hot chamber die-casting machines and cold chamber die-casting machines, suitable for precision casting of various alloys such as aluminum, zinc, lead, and magnesium.
R&D and Certification:
The company has passed ISO 9001 and CE certifications, and follows Chinese national standards (such as GB/T 21269-2023) and EU safety standards.
Its design uses computer-aided (CAD/CAE) and finite element analysis, and key components are rigorously tested to ensure high precision and reliability.
Core Product Types
Cold Chamber Die Casting Machine (HCD Series):
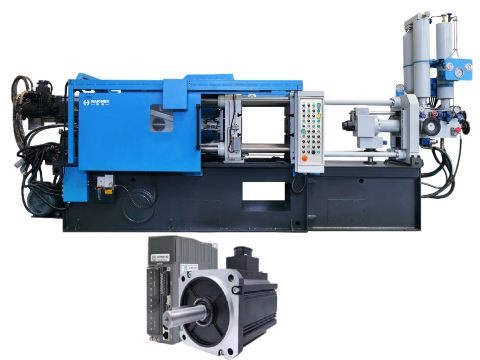
Applicable Materials:
High-temperature alloys such as aluminum, magnesium, and copper (melting temperature exceeds 700°C), and the furnace needs to be separated from the machine to avoid high temperature effects.
Technical features:
Four-stage injection control (slow, first fast, second fast, boost injection), with magnetic scale position sensor, to achieve precise acceleration and pressure regulation, suitable for high-precision complex parts production.
Large tonnage coverage:
From 90 tons to 3000 tons (such as HCD880-C model), support larger molds and longer mold opening strokes.
Application areas:
Automotive parts (such as radiators, structural parts), LED lamp housings, aluminum cookware, etc.
Configuration:
Adopt Siemens PLC, American/German hydraulic components (such as Vickers valves), support multi-language operation interface.

Hot chamber die casting machine (HCH series):

Applicable materials:
Low melting point alloys such as zinc and lead (low melting temperature, furnace and machine integrated).
Technical features:
Efficient injection structure:
Gooseneck metal conveying system for fast filling and high productivity.
Tonnage range:
15 tons to 280 tons, suitable for small precision parts (such as door lock cylinders, pipe joints).
Energy-saving design: Optional servo system to reduce energy consumption.
Technological innovation and advantages
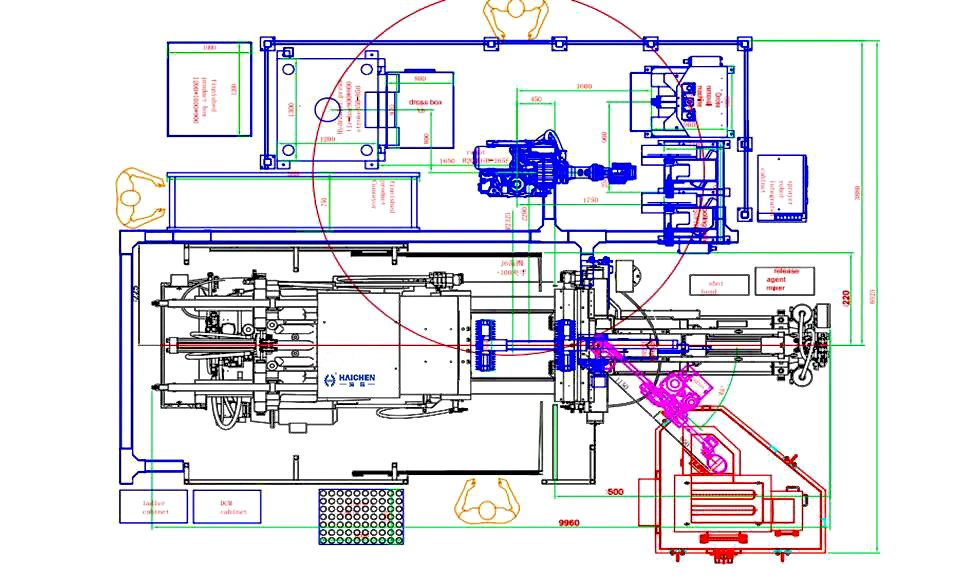
Automation and intelligence: The machine supports automated auxiliary equipment (such as robot picking, automatic spraying), and integrates vacuum casting, extrusion casting and other technologies to improve production efficiency and product quality.
Energy-saving and high efficiency: The cold chamber model adopts a servo hydraulic system to reduce energy consumption; the hot chamber model optimizes the design to reduce maintenance costs.
High-precision control: Real-time injection curve display and digital temperature-controlled furnace ensure the dimensional stability and surface finish of the casting.
Market and application cases
Global market: Mainly covering India, Russia, Mexico, China, etc., especially in the automotive industry, with significant demand growth.
Successful cases:

Automobile radiator: 880-ton cold chamber die-casting machine is used to achieve integrated molding, improve heat dissipation efficiency and lightweight.

Zinc alloy medal: Hot chamber die-casting machine is used to manufacture zinc alloy medals with a diameter of 70mm, and the thickness accuracy reaches 1.3-1.4mm.

After-sales service and support
Warranty policy:
Warranty service is provided after the machine leaves the factory, and the user needs to operate it correctly and maintain it regularly.
Online technical guidance and engineer on-site service are supported during the warranty period.
Spare parts supply:
International brand parts (such as BUSAK seals) are used to facilitate local procurement and maintenance.
Haichen precision die-casting machines are based on high precision, multi-material adaptability and intelligent production as their core competitiveness. The products cover two types: cold chamber and hot chamber, and are widely used in automobiles, home appliances, hardware and other fields.
Its technical advantages are reflected in the four-stage injection control, servo energy-saving system and global service support, which can meet the efficient production needs of complex parts.
Welcome to us at any time, Haichen will provide you with more precision die-casting technical support.

Overall
Precision die casting bridges the gap between mass production and high-performance engineering, delivering parts with near-net-shape accuracy, durability, and cost efficiency.



