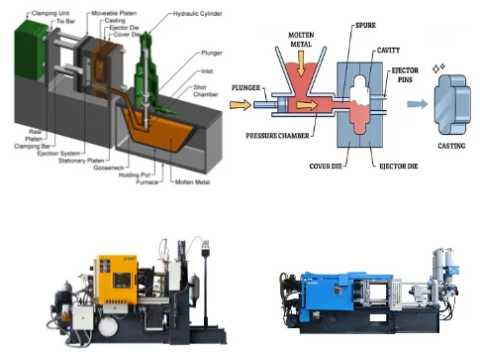
Shot in die casting is the core link of the die casting process, which refers to the process of injecting molten metal into the mold cavity at high speed and high pressure through the injection mechanism of the die casting machine.
In die casting, “shot” refers to the complete injection cycle where molten metal fills the mold cavity under high pressure.
Molten metal is shot into the die under high pressure, typically ranging from 10 to 175 MPa (1,500 to 25,000 psi).
This high-pressure injection ensures rapid filling of the die cavity, avoiding discontinuities even in thin sections.
It encompasses both the physical material injected and the process parameters controlling the injection.
Shot die casting
Shot die casting is a metal casting process that utilizes a pressurized injection of molten metal into a precisely designed die or mold.
The die is made of metal, usually steel or hardened alloy, and features a cavity that mirrors the desired shape of the final product.
Once the molten metal is injected into the die, it solidifies under pressure, resulting in a high-quality casting with precise dimensional accuracy and smooth surface finish.
Haichen can provide customers with cold chamber die casting and hot chamber die casting services.
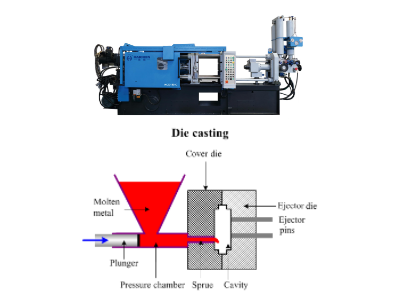
Advantages of Haichen die casting shot
The die-casting machine can produce tens to thousands of parts per hour.
Whether you need large-scale production or small-scale production, Haichen can meet your requirements.
Haichen’s press injection process ensures uniform surface finish, eliminating the need for extensive surface treatment.

Whether it’s complex shapes and fine details of parts, or thin-walled and complex geometries.
Haichen’s die-casting machines can produce castings with strict tolerances and excellent dimensional accuracy, and have received consistent praise from customers.
And the waste generated during the production process is usually recycled, which helps reduce waste and lower production costs.
Definition and core role of shot in die casting
Shot is a critical stage in the die casting process in which the molten metal is filled with a mold, the core of which is to apply a high pressure (usually 10-175 MPa) to the molten metal in the press chamber by the injection punch, so that it enters the mold cavity at an extremely fast speed (16-80 m/s).
According to the definition of GB/T 5611-2017 standard, the process of pushing the molten metal filling cavity in the pressure chamber of the injection punch is “injection”.
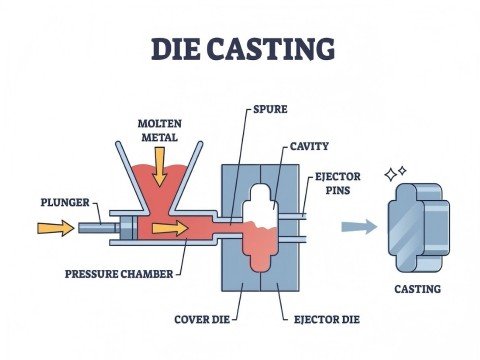
The Anatomy of a Shot
- The Injection Cycle
- Physical Components
The Injection Cycle
A shot represents one complete sequence:
Metal injection → 2. Solidification → 3. Part ejection.
Example: A 500-ton machine achieves 220 shots/hour for automotive brackets.
Physical Components
Net part: Final product (e.g., laptop housing)
Biscuit: Excess metal in the shot sleeve (cold chamber) or gooseneck (hot chamber).
Overflows/Flash: Waste material from vents and mold gaps.
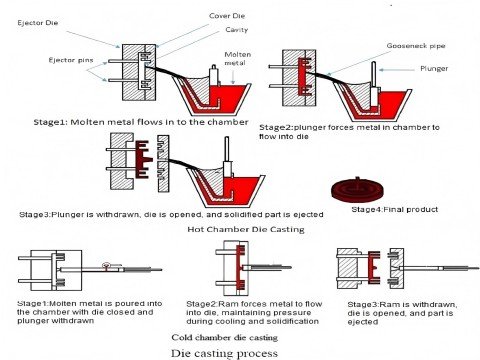
Cold Chamber vs. Hot Chamber: Shot Execution
- Cold Chamber Die Casting
- Hot Chamber Die Casting
Cold Chamber Die Casting
Process: Operators ladle molten metal into a horizontal shot sleeve.
A hydraulic plunger injects metal at >800 bar.
Materials: Aluminum (ADC12), Copper alloys (melting point >600°C).
Shot Characteristics:
Longer injection path → Requires higher pressures.
Biscuit thickness = 1.5× plunger diameter.
Cycle time: 15–45 seconds (e.g., auto engine blocks)
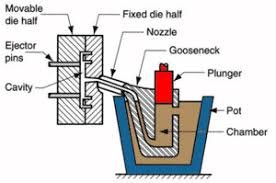
Hot Chamber Die Casting
Process: Metal resides in a gooseneck immersed in molten alloy.
Pneumatic pressure forces metal into molds.
Materials: Zinc, Magnesium alloys (melting point <450°C).
Shot Characteristics:
Shorter flow path → Faster cycles (3–15 seconds).
No separate biscuit – gooseneck holds residual metal.
Example: Zinc door handles at 8-second cycles.

Why shot in die casting control dictates quality
- Defect Prevention
- Process Monitoring Tools
Defect Prevention
Gas porosity: Excessive fast shot speed (>8 m/s for Al) traps air.
Cold shuts: Slow shot speed causes premature solidification.
Shrinkage voids: Inadequate intensification pressure leaves voids.
Process Monitoring Tools
Real-time sensors: Track shot speed/pressure curves. Deviations >5% trigger alarms.
AI systems: Auto-adjust parameters based on thermal drift or alloy viscosity changes.

Case Study: Shot Efficiency Gains
A zinc connector producer achieved:
25% scrap reduction by optimizing switchover point (88% → 93% fill)
18% faster cycles via intensified pressure (900 → 1,100 bar).
Material savings: 7% lighter biscuit design
Haichen: Your trusted partner for die-casting solutions
We offers first-class die-casting machines, providing comprehensive support from mold design to final detail processing.
HAICHEN offers you reliable and cost-effective solutions to meet your needs.
If you are looking for high-quality die-casting machines with both precision and efficiency, we are willing to assist you.
You can contact us at any time to discuss your production requirements and learn how HAICHEN can provide you with the perfect solution.




