The cold die casting chamber, or the Die casting Shot sleeve, is a very crucial part of aluminum die cast. The wear results from deformation of the sleeve due to unequal internal temperatures causing expansion, leading to inconsistent injection speeds and extended downtime as well as premature wear.
Following the right steel and heat treatment specs plus good quality machining processes can reduce deformation and make the sleeve last longer, increasing its resistance to wear. Coatings that can bear the needs of the thermal zone (including nitriding treatment) is a good way out for keeping lubricity, while proper micro-machining of mating surfaces may increase the service life of the sleeve.
The shot sleeve is also called a gooseneck (hot chamber machines) or casting chamber (cold chamber machines). The reservoir and conduit are not accurate descriptions of its function. The sleeve acts as a temporary conduit, holding the metal until it is poured into the mold cavity.

Die casting machine shot sleeve related knowledge
- Key Functions
- Design and Components
- Types of Shot Sleeves
- Interaction with the Plunger
- Common Issues and Solutions
- Maintenance Best Practices
Key Functions

- Molten Metal Transfer:
- Holds molten metal delivered from the furnace (in cold chamber machines) or directly from the molten bath (in hot chamber machines).
- Guides the metal into the mold cavity via the plunger (piston).
- Pressure Generation:
- Works with the plunger to build high pressure (up to 150–200 MPa) to force metal into the mold.
- Controlled Filling:
- Ensures precise flow of molten metal into the mold during the slow shot and fast shot phases.
Design and Components
- Material: Made from heat-resistant steel (e.g., H13 or H11), hardened to withstand high temperatures (up to 700°C) and abrasive molten metal.
- Shape: Cylindrical tube with a nozzle at one end connecting to the mold sprue.
- Internal Coating: Often coated with ceramic or nitrided surfaces to reduce wear and prevent metal adhesion.
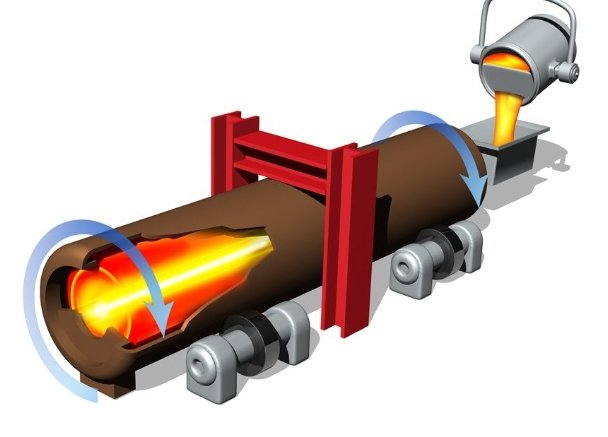
Types of Shot Sleeves
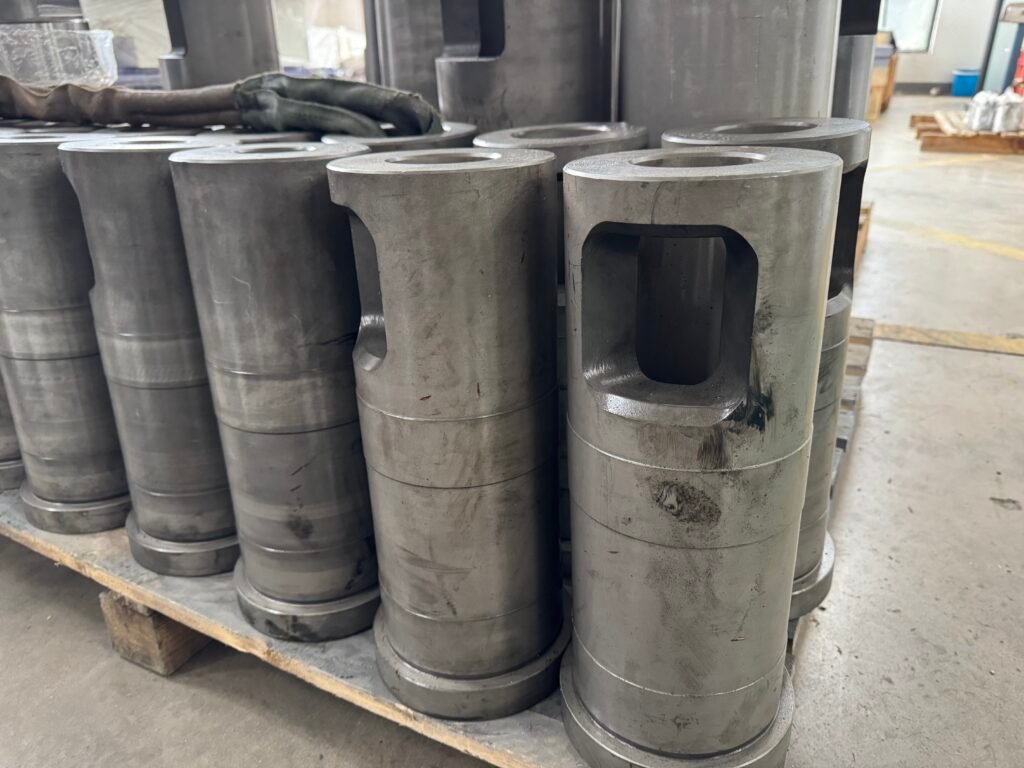

- Cold Chamber Shot Sleeve:
- Used for metals with high melting points (e.g., aluminum, copper, brass).
- Molten metal is manually ladled or automatically poured into the sleeve.
- Example: Aluminum engine blocks, automotive parts.
- Hot Chamber Shot Sleeve (Gooseneck):
- Used for low-melting-point alloys (e.g., zinc, magnesium, lead).
- Submerged in molten metal, allowing continuous operation.
- Example: Zinc die-cast hardware, electronic connectors.
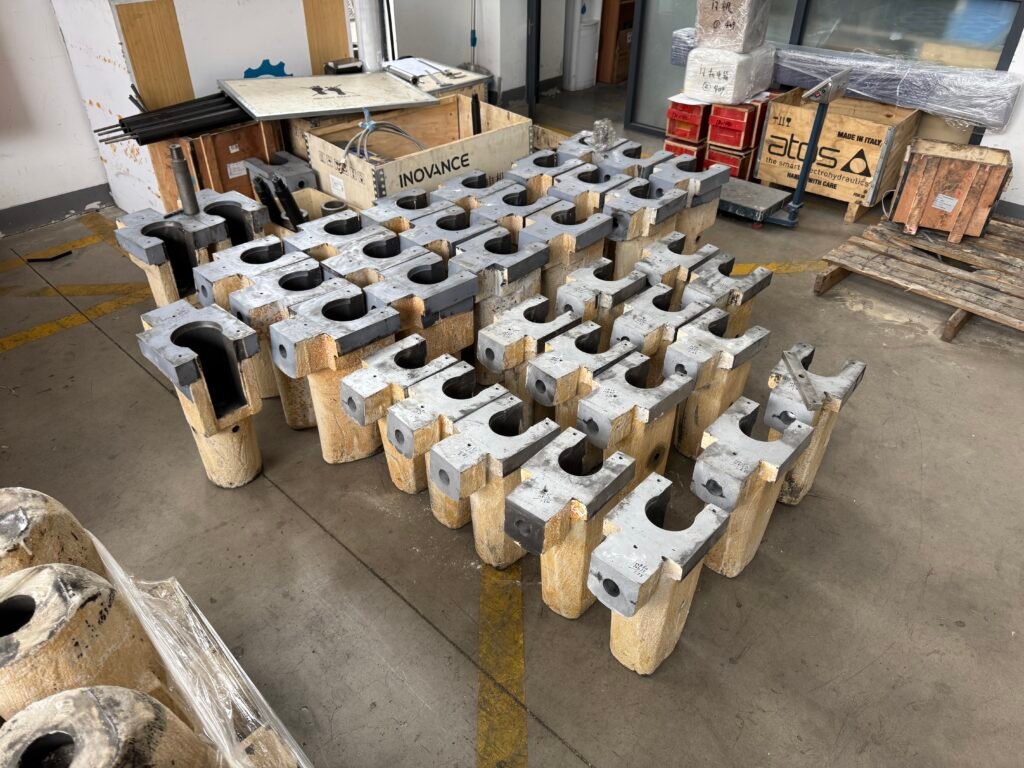

Interaction with the Plunger

- The plunger (piston) moves inside the shot sleeve to push molten metal into the mold.
- Slow Shot Phase: Fills the sleeve to avoid air entrapment.
- Fast Shot Phase: Rapidly injects metal into the mold cavity.
Common Issues and Solutions
| Issue | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Wear and Erosion | Abrasion from molten metal flow. | Use hardened steel sleeves; apply coatings (e.g., TiN). |
| Metal Soldering | Adhesion of molten metal to the sleeve. | Optimize lubrication and cooling. |
| Thermal Fatigue | Repeated heating/cooling cycles. | Use H13 steel with high temper resistance. |
| Misalignment | Improper plunger-sleeve fit. | Regular maintenance and alignment checks. |
Maintenance Best Practices

- Lubrication: Apply die lubricants to reduce friction between the plunger and sleeve.
- Cooling: Use water or oil channels to regulate sleeve temperature.
- Inspection: Check for cracks, warping, or scoring after each production run.
Why the Shot Sleeve Matters
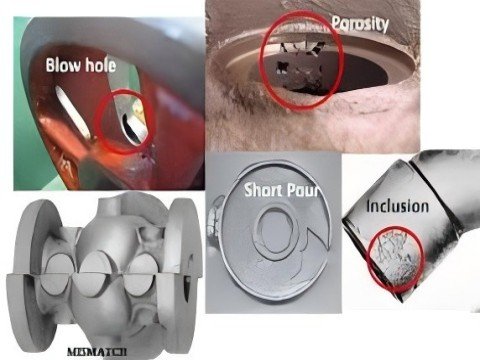
- Quality Control: A worn or misaligned sleeve causes defects like porosity, cold shuts, or incomplete fills.
- Efficiency: Optimized sleeve design reduces cycle time and material waste.
- Tool Life: High-quality sleeves last 50,000–200,000 cycles, depending on alloy and maintenance.
Example Applications
- Aluminum Die Casting: Shot sleeves for automotive parts (e.g., transmission housings) are larger and heavily cooled.
- Zinc Die Casting: Smaller sleeves with integrated goosenecks for high-speed production of consumer goods.
What material is die casting shot sleeve?
The shot sleeve in die casting is a critical component designed to withstand extreme thermal and mechanical stresses. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the material and its properties:

- Material Used for Die Casting Shot Sleeves
- Why H13 Steel?
- Key Considerations
- Example Applications
Material Used for Die Casting Shot Sleeves
- Primary Material:
- H13 Tool Steel
- Composition: Chromium (Cr), molybdenum (Mo), vanadium (V), and silicon (Si).
- Key Properties:
- Thermal Fatigue Resistance: Withstands repeated heating/cooling cycles (up to 600–700°C).
- High Toughness: Resists cracking under mechanical stress.
- Wear Resistance: Minimizes abrasion from molten metal flow.
- Moderate Thermal Conductivity: Balances heat transfer without excessive cooling.
- H13 Tool Steel
- Alternative Materials:
- H11 Tool Steel: Similar to H13 but with slightly lower molybdenum content.
- Specialized Alloys: Some manufacturers use proprietary steels (e.g., Maraging Steel) for high-performance applications.
- Surface Treatments:
- Nitriding: Enhances surface hardness and wear resistance.
- Ceramic Coatings: Reduce molten metal adhesion (e.g., Titanium Nitride (TiN).
Why H13 Steel?

- Thermal Stability: Retains hardness even at high temperatures.
- Durability: Lasts 50,000–200,000 cycles with proper maintenance.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Widely available and optimized for die casting environments.
Key Considerations
- Application-Specific Adjustments: Shot sleeves for aluminum (higher melting point) may require thicker walls or enhanced cooling vs. zinc/magnesium.
- Maintenance: Regular lubrication and inspection prevent premature wear.
Example Applications
- Automotive: Aluminum engine blocks, transmission housings.
- Electronics: Zinc die-cast connectors, heat sinks.
The H13 tool steel is the industry standard for die casting shot sleeves due to its exceptional thermal fatigue resistance, mechanical strength, and durability. Advanced coatings or alternative alloys may be used for specialized cases, but H13 remains the most practical choice for balancing performance and cost.
Haichen high quality die casting shot sleeve
Haichen, a professional manufacturer of die-casting machines, ensures the high quality of its shot sleeves (injection sleeves) through innovative design and advanced engineering. Here’s a detailed breakdown of its core features and applications:
- Core Functions and Importance
- Material and Process Technology
- Quality Control and Certifications
- Maintenance and Lifespan Management
- Applications and Case Studies

Core Functions and Importance
The shot sleeve plays a critical role in transporting molten metal (e.g., aluminum, magnesium alloys) during die casting. Haichen optimizes its design to:
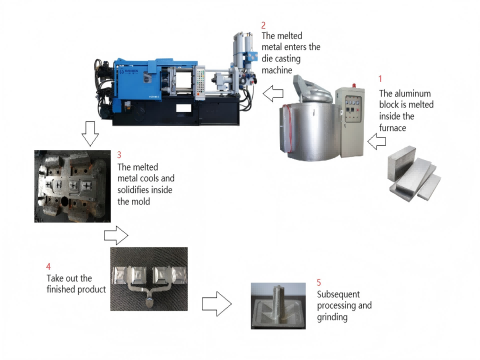
- Minimize turbulence: Adjustable diameter, length, and taper improve metal flow stability.
- Precision temperature control: Integrated water/air cooling systems reduce porosity and enhance casting density.
- Boost efficiency: Streamlined structure shortens filling time and increases production rates.
Material and Process Technology

- High-strength alloys: Resistant to thermal stress and repeated high-pressure impacts (e.g., in HCD-C series cold chamber die-casting machines).
- Structural optimization: Finite element analysis (FEA) ensures durability under extreme pressures.
- Smart control systems: Servo-driven four-stage injection process (slow, first fast, second fast, and intensification stages) ensures precise linear control of metal flow.
Quality Control and Certifications
- Compliance: ISO 9001 and CE certified, adhering to standards like GB/T 21269-2023 (cold chamber die-casting machine specifications).
- Rigorous testing: Key parameters include:
- Dynamic/static platen parallelism error (≤0.12 mm).
- Tie-bar elongation tolerance (≤0.1 mm).
- Surface hardness and wear resistance verification.
Maintenance and Lifespan Management
- Routine checks: Daily inspection of hydraulic seals and lubrication systems.
- Scheduled maintenance: Replace worn parts every 500-700 cycles; monitor for cracks or erosion.
- Global support: Localized spare parts inventory and technical assistance minimize downtime.
Applications and Case Studies
Haichen’s shot sleeves excel in producing:
- Automotive parts: Radiators, structural components with high dimensional accuracy.
- LED housings: Thin-walled zinc alloy castings (1.3–1.4 mm thickness).
- Consumer goods: Aluminum cookware with optimized density via real-time injection curve monitoring.

Haichen’s shot sleeves combine material innovation, precision engineering, and intelligent control to deliver reliability and longevity in high-pressure, high-temperature environments. These advancements solidify their role as a cornerstone of efficient, high-quality die-casting production.
The shot sleeve is a vital link between the molten metal supply and the mold cavity. Its design, material, and maintenance directly impact part quality, production efficiency, and tool longevity. For high-performance applications, Haichen offers advanced sleeves with coatings and cooling systems tailored to specific alloys.
By the end
Haichen’s shot sleeves combine material innovation, precision engineering, and intelligent control to deliver reliability and longevity in high-pressure, high-temperature environments. These advancements solidify their role as a cornerstone of efficient, high-quality die-casting production.

Contact Haichen anytime if you need further technical details! 😊



