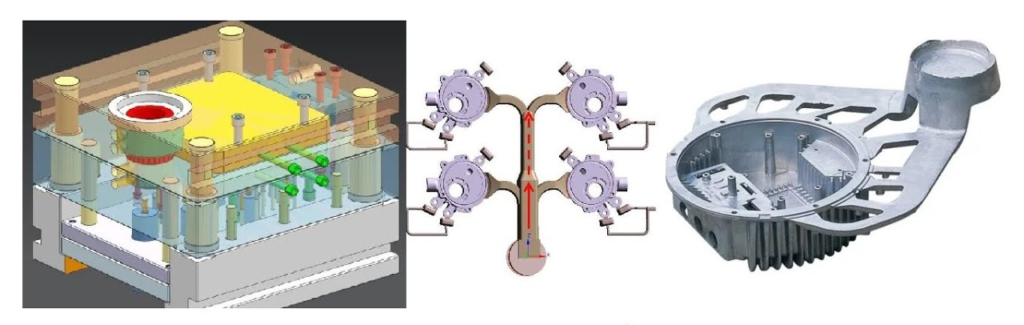
High Pressure Die Casting (HPDc)Process
High-Pressure Die Casting (HPDC) is a casting process in which molten metal is injected into the mould cavity under high pressure and high speed, and the casting is formed by cooling and pressure curing.
The process is widely used to produce metal parts with complex shapes, high precision and high surface finish, especially for high-volume production.
- mould Preparation
- Metal Smelting and Treatment
- Injection
- Cooling and Curing
- mould Removal and Dressing
- Follow-up Treatment
Mould Preparation
First of all, the mould needs to be cleaned and lubricated to ensure that the casting can be released smoothly and the temperature of the mould can be controlled.
The mould is preheated before die casting begins, which is an integral part of the die casting process.
To ensure that the temperature difference between the mould surface and the molten metal is not too large.
The preheating temperature is usually between 150 and 350 degrees Celsius, depending on the type of alloy used.
When preheating, a gradual and uniform method should be adopted, and a constant temperature heating control system should be used to avoid sudden cooling.
Especially for moulds with inserts, which need to be heated slowly to keep the inserts and mould base expanding synchronously.
Metal Melting & Processing
Heat selected metals (such as aluminum, zinc, magnesium, etc.) to their melting point and remove impurities and gases by methods such as nitrogen degassing to improve metal quality.
High Pressure Die Casting Injection
Injection Molten metal is injected into the mould cavity under high pressure. This process is usually divided into three phases: slow filling, fast filling, and pressure enhancement phase.
In the slow filling stage, the molten metal slowly enters the mould inlet to avoid air entrapment.
Subsequently, in the rapid filling phase, the molten metal quickly fills the mould cavity, ensuring that all details are accurately reproduced.
Finally, during the pressure enhancement phase, higher pressure is applied to ensure the integrity and strength of the casting.
Cooling & Curing
While the mould maintains high pressure, the metal cools and solidifies quickly.
The cooling method can be either water-cooled or air-cooled, depending on the size and material properties of the casting.
Demolding& Trimming
When the casting is fully cured, the mould opens and the casting is ejected through the pusher. Subsequently, trimming may be required, such as deburring, cutting excess, etc., to obtain the final product.
Post-processing Castings
Post-processing Castings may also require surface treatments, such as sandblasting, polishing, or coating, to improve their appearance and performance.
There are various surface treatment techniques after high pressure casting, mainly including the following methods:
Shot peening
Spraying abrasives (such as steel shots) at high speed to remove burrs and impurities on the surface of castings, improving surface finish and strength.
This method can effectively improve the surface quality of the casting, making it smoother and smoother.
Grinding and polishing
Grinding and polishing the surface of a casting using mechanical or chemical methods to remove surface defects and improve surface finish.
Sanding usually uses sandpaper or grinding wheels, while polishing may involve the use of abrasives and polishing fluids.
Hot & Cold Spray
These techniques create a protective coating by spraying metal powder or ceramic particles onto the surface of the casting at high or ambient temperatures.
Thermal spraying is suitable for corrosion protection and abrasion resistance in high-temperature environments, while cold spraying is suitable for low-temperature environments.
Electroplating
Electrochemical methods are used to deposit metal layers, such as nickel, chromium, etc.
On the surface of castings to improve surface hardness, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
Moreover, electroplating can significantly improve the appearance and performance of castings.
Laser surface treatment
Laser technology is used to modify the surface of castings, such as laser cutting, laser etching and laser cladding.
These methods can improve the surface hardness, wear resistance, and fatigue resistance of castings.
Chemical coating
A protective film is formed on the surface of the casting through a chemical reaction, such as a chromic acid conversion coating.
This method can effectively prevent the casting from being corroded during use.
Heat treatment
Processes such as annealing, quenching, and tempering are used to improve the mechanical properties of a casting by altering its internal microstructure, such as tensile strength and toughness.
Heat treatment also relieves the stresses generated during the casting process and prevents the formation of cracks.
Pickling and water washing
Used to remove grease and other impurities from the surface of castings.
It is usually pickled with a mixed solution of sulfuric acid, hydrochloric acid and water, followed by water washing to remove residues.
Advantages of Haichen’s High Pressure Die Casting
The advantages of the HPDC process are the ability to efficiently produce parts with complex shapes,high precision, and excellent surface finish.
which are widely used in industries such as automotive, aerospace, electronics, and consumer goods.
In addition, Haichen’s HPDC process has the advantages of fast production speed, low energy consumption and high material utilization.



