Zinc die casting services includes optimize zinc alloy compsition and performace, mold design, surface treatment, production problems solutions, etc.
What is zinc alloy? Zinc alloy is zinc alloy materials made by adding other metals. (Such as aluminum, copper, magnesium, nickel, tin, etc.) to zinc as the base metal through smelting or die casting processes. By adjusting the proportions of different alloying elements, zinc alloys can obtain a variety of performance characteristics. With their low melting point, good castability, moderate mechanical properties, and excellent corrosion resistance, zinc alloys have become a commonly used material for manufacturing lightweight and cost-effective metal parts.
The core application scenarios of zinc alloy die-casting are small precision automotive parts, electronic shielding housings, bathroom hardware and industrial valves and pumps. Its low melting point, thin-wall capability and cost advantages make it irreplaceable in specific fields, but the surface treatment process needs to be selected according to the part size and corrosion resistance requirements.
The performance and production efficiency of zinc alloy die castings can be further improve by using advanced casting technologies.
- Optimization of zinc alloy composition and performance
- Mold design and optimization
- Surface treatment and decorative performance
- Application areas of zinc alloy

Optimization of zinc alloy composition and performance
- Basic Composition and Adjustments
- Special Alloy Types
- Improved Mechanical Properties
- Surface Treatment and Aesthetics
High-fluidity zinc alloy (HF alloy) significantly improves the fluidity of zinc alloy by adding elements such as aluminum and magnesium, enabling it to produce thinner-walled parts while reducing defects such as cold shut and pores.
Adding a small amount of low-melting-point metal elements (such as bismuth, gallium and indium) can improve the mechanical properties and hardness of zinc alloys while achieving lightweight.
For hot die casting process, research has found that by adjusting the composition ratio of zinc-based alloys (such as the ratio of aluminum, magnesium and copper). Its casting performance and mechanical properties can effectively improve.
Basic Composition and Adjustments
- Typical zinc alloys are based on zinc (approximately 86%), with additions of aluminum (4%-7%), copper (7%-10%), and trace amounts of magnesium.
- High-fluidity alloys (HF alloys) are achieved by increasing the aluminum content and reducing the magnesium content. Laboratory tests have shown a 40% increase in fluidity, making them suitable for ultra-thin-wall castings.
- Impurity control is crucial: lead (Pb), cadmium (Cd), and tin (Sn) must be below 0.003%, 0.003%, and 0.001%, respectively. Failure to do so can lead to casting aging, deformation, and decreased mechanical properties.
Special Zinc Alloy Types
- Zamak 5: Contains zinc, aluminum, magnesium, and copper, offering both high strength and precision casting capabilities, with a tensile strength of 331 MPa and a yield strength of 228 MPa.
- ZA Alloy: Contains a higher aluminum content than standard zinc alloys, providing increased hardness and bearing performance.

Improved Mechanical Properties
Room-Temperature Performance: Zinc alloys exhibit excellent compressive strength, ductility, and wear resistance at room temperature, making them suitable for precision and complex parts (e.g., thin-wall thicknesses up to 0.3mm).
Surface Treatment and Aesthetics
- Supports a variety of treatments, including electroplating, spray painting, and chemical polishing, allowing you to simulate metal textures (such as stainless steel and brass) or add textures.
- Highly polished surfaces allow for direct use or minimize machining.

Mold design and optimization
- Comprehensive design optimization
- Digital tool application
- Flow Simulation Analysis
- Materials and Heat Treatment
- Cooling System Optimization
In the design of zinc alloy die-casting molds, it need consider the pouring system, cooling system and ejection structure. To ensure the stability of the mold and the high-quality production of parts.
For large thin-walled zinc alloy parts, it can optimize the temperature distribution and pressure field of the mold. Through numerical simulation and process improvement. Thereby reducing defects and improving production efficiency.
Comprehensive design optimization
The company provides a full-process service from casting design, 3D modeling (using software such as SolidEdge), filling simulation to drawing documentation to ensure that the design meets production requirements and optimizes costs.
Digital tool application
Use CAD/CAM software for precision design and achieve high-precision mold manufacturing through CNC processing.
Flow Simulation Analysis
- Software simulates metal flow, temperature distribution, and pressure changes to predict defects (such as porosity and shrinkage) in advance, optimizing gating systems and cooling channel designs.
- Simulation technology can reduce mold trials, shorten development cycles by over 30%, and extend mold life.
Materials and Heat Treatment
- Mold steels utilize highly wear-resistant materials (hardness HRC 48-52) such as ASSAB 420 and H13, combined with rigorous heat treatment processes, to enhance corrosion resistance and durability.
- Zinc alloy’s low melting point (approximately 380°C) reduces mold wear, extending mold life to 10 times that of aluminum die-casting molds (approximately 1 million cycles or more).
Cooling System Optimization
Sensors monitor mold temperature in real time, adjusting cooling parameters (such as cooling time T15 and mold opening and closing wait time T33/T44) to achieve uniform solidification and minimize thermal stress and deformation.
Surface treatment and decorative performance
- Electroplating
- Conversion Coatings
- Spraying and Painting
- Decorative priority
- Prioritizing protection
Zinc alloy die castings are usually surface treated by electroplating, painting and other methods to improve their corrosion resistance and aesthetics. For example, electroplating nickel and copper coatings can effectively prevent the corrosion of zinc alloys.
Surface-treated zinc alloy die castings may show color changes, such as blue spots, in long-term use. This is related to the diffusion mechanism of the coating and environmental factors. Therefore, it is necessary to select appropriate coating materials and processes to extend their service life.
Electroplating
- The most common types of plating are decorative chrome (bright chrome) or functional hard chrome, which provide a high-gloss appearance, wear resistance, and corrosion resistance.
- Zinc alloys (such as the Zamak series) are widely used in hardware and automotive parts due to their excellent electroplating suitability.
Conversion Coatings
Such as chromate passivation, these coatings form a protective film to prevent corrosion during storage or mild environmental conditions and can serve as a paint base.
Spraying and Painting
Powder coating (epoxy, polyester), wet painting, electrophoretic coating (KTL/CMD), etc., offering a variety of colors and textures (such as imitation gold, stainless steel, and leather).
Decorative priority
Choose electroplating chrome or double-layer zinc plating for high gloss and durability.
For complex parts, consider mechanical plating to ensure uniformity.
Prioritizing protection
For corrosive environments (such as marine and industrial areas), thick coatings (such as powder coating, 50–75 μm) or hard chrome plating are recommended.
Application areas of zinc alloy
- Automotive Industry (Core Industry)
- Electronics, appliances, and communications equipment
- Industrial Equipment and Machinery Parts
Zinc alloy die castings widely use in automobiles, electronic products, household appliances and other fields. Its advantages include high strength, good corrosion resistance and the ability to manufacture complex shapes.
Especially for products with lightweight and high performance requirements, such as smartphone housings and toys, zinc alloy has become the preferred material due to its excellent surface quality and lightweight characteristics.
Automotive Industry (Core Industry)
- Interior Parts: Door handles, locks, interior trim (high surface finish, can be directly electroplated or sprayed)
- Powertrain: Engine components (such as brackets), steering system parts, fuel system components (corrosion resistance supports their application)
- Safety and Functional Parts: Brake system parts, air conditioning components, seatbelt buckles, sunroof structural parts
Electronics, appliances, and communications equipment
- Electromagnetic shielding housings: TV/computer cases, CD/VCD drive housings, router/communication equipment housings (zinc alloy offers superior electromagnetic shielding performance compared to most materials)
- Heat dissipation and structural components: LED lamp housings, power adapter housings (thermal conductivity + thin-wall casting capability)
- Micro-precision parts: Optical pickup brackets, connectors (capable of casting precision parts with wall thicknesses ≤ 0.5mm)
Industrial Equipment and Machinery Parts
- Pump and Valve Systems: Valves, Pump Bodies, Pipe Fittings (Corrosion Resistance + Sealing)
- Transmission Parts: Gears, Bearings, Reducer Housings (Wear Resistance and High Dimensional Stability)
- Tools and Instruments: Power Tool Housings, Instrument Housings (Impact Resistance + Surface Treatment Compatibility)
HAICHEN zinc die casting services offer a full range of solutions. From standard parts to fully customized components, suitable for structural and decorative parts in various industries. Such as auto parts, electronical and home appliances. We have been produced of zinc alloy pipe fitting couplings, zinc alloy die casting medals, zinc-alloy door handles and so on. With zinc alloy low melting point, good flowability, and diverse surface treatment processes give it a significant competitive advantage in lightweighting, high precision, and rapid delivery. Haichen have rich experience and advanced production skills to produce these zinc die casting products.

Zinc die casting services cover multiple links from alloy composition design, mold development to surface treatment and production process optimization. By continuously optimizing these links, the performance and quality of the product can be significantly improved while reducing production costs and environmental impact.
Haichen die casting
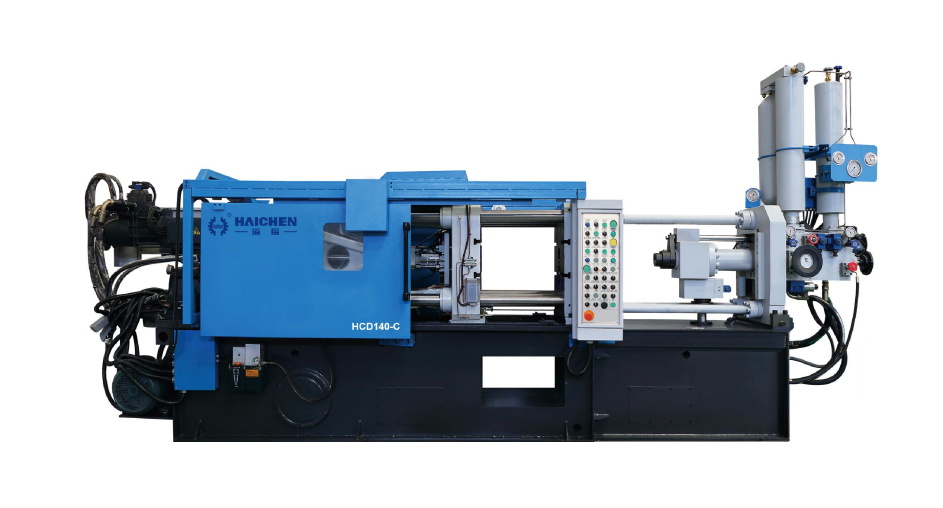
We are Haichen, also produce both high pressure cold chamber die casting machine , hot chamber die casting machine and spare parts. They have durable and highly precise features.


Haichen also produce die casting machine auxiliary equipment. Such as conveyor, vacuum machine, mold temperature controller, industrial robot, sprayer and so on.

We supply cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machine spare parts.
Welcome contact us.



