Cast aluminum is often referred to as “cast aluminum alloy”.
Casting aluminum is a process method that involves pouring molten aluminum or aluminum alloy into a mold, followed by cooling and solidifying, to form aluminum parts of the desired shape.
This is an aluminum alloy produced through a casting process that involves pouring molten aluminum or aluminum alloy into a mold that, after cooling, forms a part with a specific shape.
Cast aluminum alloys often contain alloying elements such as silicon, copper, and magnesium to enhance their strength, corrosion resistance, and fluidity.
Lightweight
Aluminum castings have a low density and are typically much lighter than steel, which makes them useful in applications that require weight reduction, such as the automotive and aerospace sectors.
High strength
Although aluminum itself is a lightweight material, the casting process can create aluminum castings with high strength, which is suitable for structural components.

Corrosion resistance
Air, water, and chemical media do not easily corrode casting aluminum, giving it excellent corrosion resistance in harsh environments
Thermal conductivity
Casting aluminum has high thermal conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require rapid heat dissipation, such as electronics and automotive engine components.
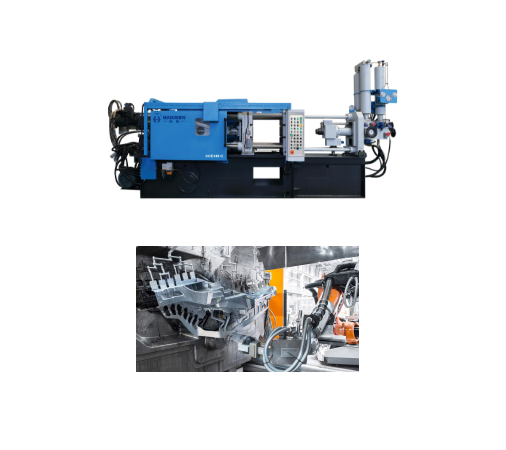

Machinability
Aluminum castings achieve a high surface finish and precision, meet usage requirements without excessive machining.
And exhibit excellent plasticity and ductility, enabling diverse modeling designs.
Cost-effective
Aluminium castings are relatively inexpensive to manufacture, suitable for high-volume production, and recyclable to further reduce costs.
Diversity
A variety of casting processes, such as sand casting, die casting, and low-pressure casting, can manufacture aluminum castings suitable for parts of different shapes and sizes.

Wide application
Aucually,various industries widely use aluminum castings in automotive, aerospace, consumer electronics, construction, and rail transit
And other fields to meet the individual needs of different industries for performance, structure, size and appearance.
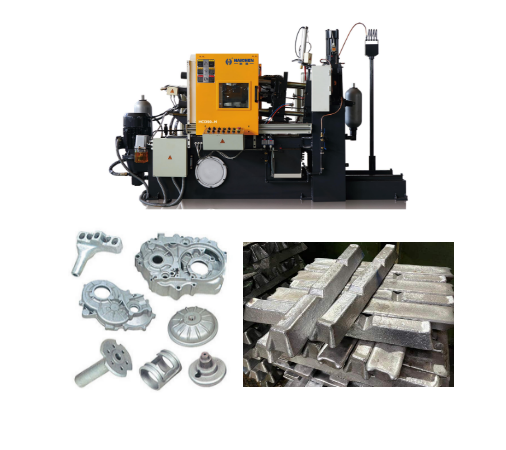

The production process of casting aluminum
- Raw material preparation
- Melting
- Core making
- Casting
- Cooling and demoulding
- Cutting
- Wet grinding
- Heat treatment
- Post-processing
- Inspection
Raw material preparation
First, select high-purity aluminum ingots or aluminum blocks, and carry out visual inspection and chemical composition analysis to ensure that technical standards are met.
Melting
Secondly, Workers heat the aluminum ingot to the melting point (usually 650°C to 750°C) in a furnace.
Technicians add the appropriate amount of alloying elements and additives, such as copper, zinc, etc., to adjust the composition and temperature.
The control system needs to maintain the temperature and composition during the melting process to prevent local overheating and uneven composition.
Core making
Then,in the core making process, the coated sand is heated to about 260 °C and injected into the mold to form a finished sand core.
Casting
Molten aluminum is poured into a pre-prepared mold and cast through a gating system such as a pouring cup, sprue.
The pouring speed and temperature need to be controlled during the casting process to ensure the quality of the casting.
Cooling and demoulding
After the casting is cooled and solidified in the mold, the demoulding operation is carried out.
After demolding, there may be oxide scale and burrs on the surface of the casting, which needs to be cleaned.
Cutting
Use a sawing machine or other cutting tools to remove the risers and excess parts on the blank casting to form a complete casting.
Wet grinding
Wet grinding is performed on the surface of the casting to remove burrs and oxide scales and improve the surface finish.
Heat treatment
Water quenching and tempering of castings to eliminate internal stress, adjust metal properties, and improve the mechanical properties of castings.
Post-processing
Including shot blasting, machining, surface treatment such as spraying, anodizing, electrophoretic coating, etc.
And quality inspection to ensure that the appearance and performance of the casting meet the requirements.
Inspection
Conduct physical examination and quality inspection of finished products, including size, appearance.
Mechanical properties, corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity and other tests to ensure that they can be put on the market.
The entire aluminum casting production process involves multiple links, each of which requires strict control of parameters and quality standards to ensure the quality and performance of the final product.

Advantages of cast aluminium
- Lightweight and durable
- High strength and corrosion resistance
- Good thermal and electrical conductivity
- High production efficiency
- Excellent economic effect
- Customizability and design flexibility
Lightweight and durable
Cast aluminium has a low density of only 2.7 g/cm³, which is much lighter than steel.
Which makes cast aluminium components particularly suitable for automotive, aerospace and other fields while maintaining strength while reducing weight.
High strength and corrosion resistance
Cast aluminum has high strength and hardness, and has good corrosion resistance in the atmosphere and seawater.
And is suitable for radar bases, aircraft engine casings, propellers and other components.
Good thermal and electrical conductivity
Cast aluminum has good thermal and electrical conductivity, making it suitable for applications that require heat dissipation or electrical connections.
High production efficiency
The production efficiency of die-cast aluminum parts is high, the machine productivity is high.
Then,the die-casting aluminum mold has a long life, and it is easy to realize mechanization and automation.
Excellent economic effect
The size of the aluminum casting is accurate, the surface is smooth.
Which reduces the processing equipment and man-hours, and improves the metal utilization rate.
Customizability and design flexibility
Cast aluminum can be easily molded into complex shapes and sizes to meet specific design needs, making it suitable for innovative solutions.



