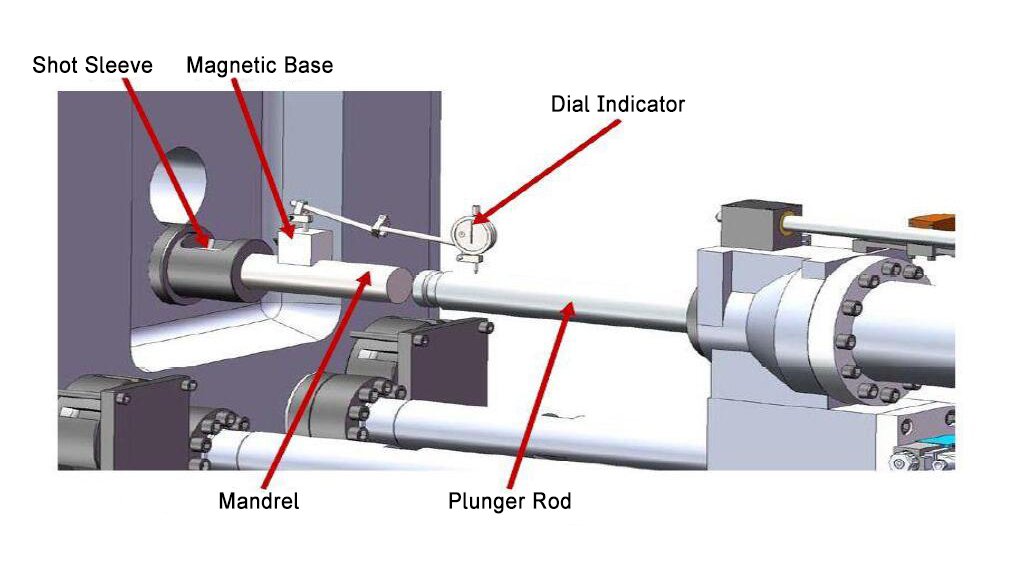
The plunger rod is a critical component in die casting, responsible for driving molten metal into the mold cavity. Its design, material selection, and operational parameters directly influence casting quality.
The plunger rod constitutes a vital component of the die casting injection end assembly, responsible for forcing molten metal into the mould cavity. Rational design and machining precision are paramount for trouble-free production of the plunger rod, particularly concerning lubrication between its tip and sleeve.
Two critical characteristics of the plunger rod are cooling and lubrication. Maintaining temperature control in the high-heat zone is vital for both functionality and service life. Haichen meticulously positions the plunger lubrication lines. Our plunger rods incorporate cooling lines of maximum diameter without compromising overall structural integrity.
The specific structure and operation of the injection rod of the die casting machine
Below is a detailed analysis synthesized from multiple sources:
- Function & Structure
- Material Selection
- Key Parameters & Technology
- Sealing & Durability
- Process Optimization
- Applications
Function & Structure

- Primary Role: Hydraulically driven, the plunger rod moves within the shot sleeve, injecting molten metal under high pressure into the mold cavity. Precise control of pressure, speed, and position is essential to ensure complete cavity filling and minimize defects.
- Tip Design: The front end of the plunger rod is connected to a plunger tip (e.g., hemispherical shape), which laterally displaces molten metal to reduce flow resistance and promote porosity closure. Self-aligning tips accommodate shot sleeve misalignment, ensuring sealing integrity and uniform metal flow.
Material Selection
- Plunger Rod Body: Common materials include H13 steel or 45# steel, heat-treated and CNC-machined for enhanced wear resistance and high-temperature strength, suitable for aluminum, zinc, and other alloys.
- Plunger Tip: Requires advanced materials:
- Copper Alloys (e.g., beryllium copper): Excellent thermal conductivity and fatigue resistance for high-temperature applications.
- Ceramic or Cu-Ti Alloys: Superior thermal stability and wear resistance for precision casting.
- Ductile Iron: Cost-effective durability for aluminum die casting machines.
Key Parameters & Technology
- Pressure Range: Typical die casting pressures range from 5–35 MPa (hot chamber) to 500 MPa (cold chamber). For example, Greenlee die casting machines achieve plunger pressures up to 17,000 psi (~117 MPa) via hydraulic intensification.
- Speed Control: Plunger speed impacts cavity filling patterns and porosity. Excessive speed increases porosity; optimization balances efficiency and quality.
- Cooling Systems: Built-in water channels or coolant circulation (e.g., water) in the plunger rod/tip dissipate heat, preventing thermal deformation and extending lifespan.
Sealing & Durability
- Sealing Design: O-rings (e.g., high-temperature chloroprene) or self-aligning structures between the plunger tip and shot sleeve prevent metal leakage and maintain pressure.
- Wear Management: High-strength, corrosion-resistant plunger rings minimize friction in aluminum, magnesium, and other alloys.

Process Optimization
- Vacuum Assist: Reduces gas porosity by creating localized vacuum zones, lowering plunger thrust requirements and extending mold life.
- Simulation & Monitoring: Real-time thermal imaging and sensors track plunger temperature and motion. For example, high-temperature molybdenum blocks simulate molten metal thermal shock in testing.

Applications
- Aluminum Die Casting: Requires high-temperature-resistant tips to reduce friction and ensure smooth aluminum flow.
- Complex Castings: Automotive transmission pump covers use plunger cores and fixed cores to create pre-machined grooves, minimizing post-processing.
How to connect the plunger rod of die casting machine?
To connect the plunger rod of a die-casting machine, follow these steps, incorporating technical details from relevant evidence:
- Mechanical Connection of Plunger Tip to Plunger Rod
- Cooling System Integration
- Connection to Injection Cylinder and Hydraulic System
- Material and Maintenance Considerations
Mechanical Connection of Plunger Tip to Plunger Rod
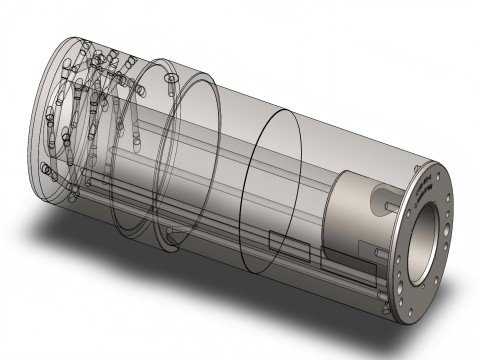
- Threaded Interface Installation: The plunger rod features a threaded socket at its front end. Attach the plunger tip (with external or internal threads, as specified) by screwing it into the socket. Use tools (e.g., wrenches) to tighten securely. Evidence highlights the use of a threaded tubular fitting (e.g., fitting 37) to ensure a robust connection.
- Self-Aligning Design: A spherical joint (spherical formation) between the plunger tip and rod allows automatic alignment within the sleeve, minimizing wear or leakage caused by misalignment.
Cooling System Integration
- Coolant Tube Installation: Insert the internal coolant tube of the plunger rod through the axial bore (bore 47) of the plunger tip. Ensure the tube extends to the front of the tip for effective heat dissipation. Coolant flows forward through the tube and returns via the annular space (space 49) to complete the circulation loop.
- Sealing and Heat Management: High-temperature seals (e.g., chloroprene O-rings) prevent molten metal leakage between the plunger tip and sleeve. Coolant is directed to the front chamber (chamber 81) of the tip for localized cooling of critical areas.
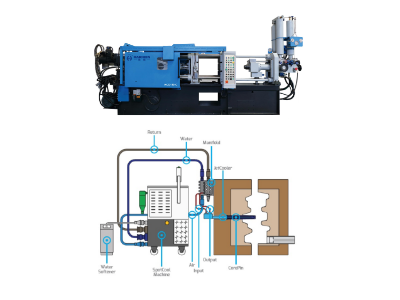
Connection to Injection Cylinder and Hydraulic System
- Hydraulic Drive: The rear end of the plunger rod connects to the shot cylinder’s drive system. A connecting rod (e.g., connecting rod 60) links the plunger rod to a dual-cycle hydraulic cylinder (hydraulic cylinder 58), enabling reciprocating motion for metal injection.
- Control System Integration: Integrate the plunger rod with monitoring systems (e.g., Visi-Trak) and servo valves to regulate position, speed, and acceleration in real time, ensuring precise control during injection.
Material and Maintenance Considerations

- Material Selection: Use high-strength, heat-resistant materials (e.g., H13 steel or copper-titanium alloys) for the plunger rod and tip to withstand high temperatures and pressures.
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check threaded connections, seal integrity, and coolant flow due to prolonged exposure to molten metal. Address wear or blockages promptly to prevent thermal damage or leaks.
Summary of Steps
- Install the Plunger Tip: Secure the tip to the rod’s front end via the threaded interface, ensuring self-alignment functionality.
- Integrate Cooling System: Route the coolant tube through the tip’s bore and test circulation efficiency.
- Connect Hydraulic Drive: Attach the rod’s rear end to the shot cylinder’s hydraulic system.
- Sealing and Monitoring: Install seals, link to control systems, and perform pressure tests and calibration.

Note: Details may vary between hot-chamber and cold-chamber die-casting machines, but the core principles remain consistent. Always refer to the specific equipment manual for model-specific guidance.
Overall

The plunger rod is not merely a mechanical force transmitter; its material selection, cooling design, sealing technology, and motion control must be meticulously coordinated. High thermal conductivity in tip materials (e.g., copper alloys), high-pressure capabilities (e.g., 20,000–30,000 psi penetration pressure), and innovations like vacuum assist ensure dense, low-porosity, and high-surface-quality castings. Future trends may include smarter monitoring systems (e.g., thermal vision) and novel alloys to enhance efficiency and sustainability.



