Die casting is one of the most flexible and innovative manufacturing techniques for fabricating metal parts.
Also die casting processes in the manufacturing industry due to its efficiency, precision, and flexibility, particularly suitable for high-volume production of complex metal parts.
Die Casting is a metal casting process that involves injecting molten metal into a mold at high pressure and rapidly cooling it to produce high-precision, complex-shaped parts.
Benefits of die casting, with its high efficiency, high precision and material adaptability has become a core manufacturing technology in the fields of automobiles, electronics, and home appliances.
Definition and core principles of Die Casting
Die casting uses a manufacturing process where machines inject molten metal into reusable steel molds crafted from hardened tool steel.
The process utilizes fast filling and high pressures to achieve precise molding of complex shapes.
The core steps include mold preparation, injection molding, cooling, demoulding, and trimming.
Based on the melting points of metals, die casting processes fall into two categories:
Hot chamber die casting for zinc and magnesium alloys, and cold chamber die casting for aluminum and copper alloys.
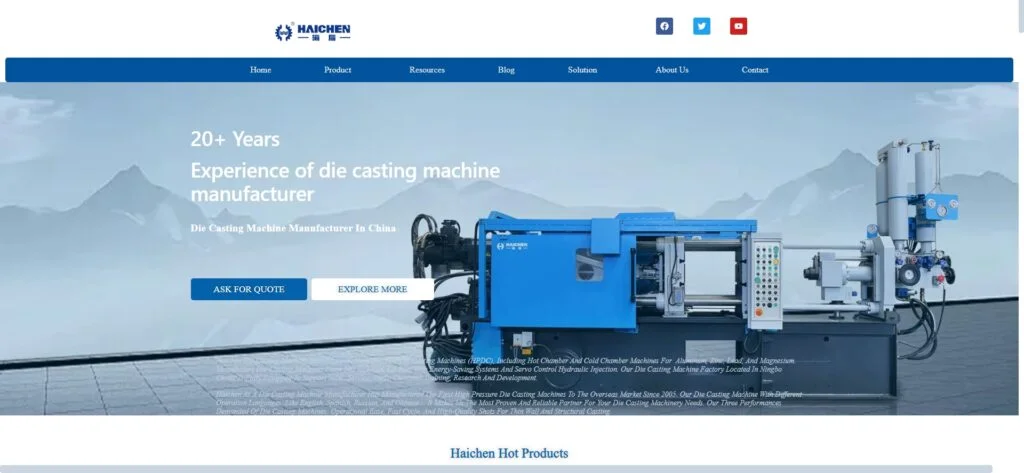
Types of Die Casting
Die casting processes operate under different conditions per process specifications and final part requirements.
Among the many specialist processes in die casting, two are worth elaborating on: the hot chamber die casting and cold chamber die casting processes.
Haichen will assist you in learning about these two techniques so that you can better understand them.
Hot Chamber Die Casting
The hot chamber in the hot chamber die casting process refers to an internal furnace within the casting machine.
A feeding system called the “gooseneck” connects the furnace to the die cavity.
Since the casting machine melts the metal internally, this process delivers fast cycle times of around 20 minutes, qualifying it for mass production.
The hot chamber, however, cannot reach very high temperatures.
Therefore, the process is most suitable for low melting point metals such as lead alloys, zinc alloys and magnesium alloys.
As the metal melts, it is forced into the die through the gooseneck by a plunger.
The plunger withdraws when the metal in the die solidifies. The mould opens and the casting is removed.
Then, the mould closes once again, the plunger transfers the hot metal into the die cavity, and repeats the process.
The hot chamber die casting process is popular for its speed, accuracy and consistency.
Additionally, it offers a longer die life and improved corrosion resistance.
For items like door handles and medals, Haichen recommends using a hot chamber die-casting machine. For more details, you can refer to our case studies.

Cold Chamber Die Casting
The cold chamber die casting process is similar to the hot chamber process, except that the metal is not melted in the casting machine.
The metal is melted in an external high-temperature furnace and transferred to the cold chamber die casting machine via a ladle.
In the cold chamber machine, a hydraulic piston forces the metal into the metal die for casting.
This process is suitable for metals with higher melting points such as aluminium and their alloys.
In the case of Haichen, you can find examples of the production of road studs or heating systems.

Haichen‘s die casting benefits
- Efficiency – Once the die casting mold is made, it can be used repeatedly. This allows you to quickly produce hundreds, if not millions, of parts with exactly the same specifications.
- Repeatability – yes, mass production is important – but what’s more important? It’s consistency. Haichen‘s die casting process is favored for its high precision and repeatable results, which is crucial for many metal parts.
- Cost-effective – With its high speed, precision, and low waste, the die casting process becomes a cost-effective method for mass-producing metal parts.
- Flexibility – Haichen can be tailored to your specific needs and can be designed to be as simple as possible or as complex as possible. It is this design flexibility that makes the die casting process widely used in numerous industries and suitable for a wide variety of parts.
- Surface Finish Options – While not always required, surface finishing options in the die casting process mean you can further customize and optimize the appearance of the final product. It can include adding decorative elements, enhancing chemical resistance, and more, and is the final step in ensuring that the finished part meets specifications exactly.
Benefits of die casting
- High precision and complex geometries
- Productivity & Economies of Scale
- Optimization of material properties
- Cost-effective and environmentally friendly
High precision and complex geometries
Die casting produces precision parts with very tight tolerances (± 0.1 mm) and reproduces details.
Such as textures and logos without the need for secondary operations.
For example, die casting can directly mold the delicate heat dissipation holes in the enclosure of electronic devices.
Productivity & Economies of Scale
Single cycle times are as short as 1 second, making them suitable for high-volume production.
The mold life is up to more than 100,000 times, which significantly reduces the cost per piece.
Compared with sand casting, die-casting does not need to change molds frequently, and the efficiency is increased by 5-10 times.
Haichen’s die casting machines are durable and efficient, if you are interested, you can check out our official website.

Optimization of material properties
- Thin-walled construction:High-pressure injection molding enables wall thicknesses as low as 0.5 mm, therefore, it is suitable for lightweight designs (e.g., aerospace components).
- Mechanical strength:Rapid cooling to form a fine-grained structure, improving part fatigue resistance and surface hardness.
Cost-effective and environmentally friendly
The material utilization rate exceeds 95%, and the furnace can recycle the waste, further enhancing sustainability.
Then,die casting offers significant advantages, such as reduced machining requirements and energy consumption, as it minimizes material waste and allows for complex part integration in a single process .
For example, integrated components like threaded sleeves and sensors can be cast directly, simplifying assembly and reducing production costs.

Die Casting Common Products & Application Cases
- Automotive Industry
- Consumer electronics
- Heat dissipation components
- Household appliances
Automotive Industry
- Engine components:Aluminum cylinder heads, such as the Ford EcoBoost engine, combine light weight and high strength by cold chamber die-casting, with a wall thickness uniformity error of <1%.
- Transmission housing:Magnesium alloy die-cast housings (such as the Tesla Model 3) weigh up to 40% less than traditional steel parts while maintaining rigidity.
- Structural parts:Then,suspension bracket and battery tray are made of vacuum die-casting technology to reduce porosity to less than 0.5%.

Consumer electronics
Apple uses aluminum die-casting to create the MacBook body.
The manufacturing process achieves the integrated Unibody design through anodizing, with a surface roughness of Ra≤1.6μm.
Heat dissipation components
The GPU heat dissipation fins are die-cast by zinc alloy, and the thermal conductivity is increased by 30%.
Household appliances
- Compressor bracket:The aluminum alloy bracket for refrigerator can carry 500kg static load, and the production cycle time is up to 120 pieces/hour.
- Motor housing:Actually,the motor housing of the washing machine is die-cast from zinc alloy, and the corrosion resistance has passed the salt spray test for more than 1,000 hours.
- Aerospace turbine blades:Magnesium alloy die-cast blades have a tensile strength of 320MPa after T6 heat treatment, which is 20% lighter than traditional forgings.
- Cabin structural parts:Then,the seat bracket is made of vacuum-assisted die-casting, and the porosity is controlled within 0.2% to meet aviation standards.

Typical application fields and products of die castings
- Automotive industry
- Electronics and home appliances
- Industrial & Energy Equipment
- Aerospace & Medical Aviation
- Medical
- Cases in emerging fields
Automotive industry
- Power system:Engine block, cylinder head, crankcase, oil pan, clutch housing.
- Such as CVT transmission housing to solve shrinkage defects through high-pressure spot cooling technology).
- Haichen has experience in the design and production of gearbox die-casting molds in this regard.

- Structural parts:Body reinforcing beams, suspension brackets, battery pack shells (the integrated die-casting technology of new energy vehicles can reduce the number of parts by 30%).
- Other parts:Alloy wheels, brake calipers, steering knuckles.
Electronics and home appliances
Consumer electronics include metal shells for mobile phones and notebooks, such as MacBook Unibody, as well as heat sinks and camera mounts.
Air conditioner compressor housing, washing machine drum bracket, refrigerator door hinge, which is made of zinc alloy die-casting and exhibits strong corrosion resistance.

Industrial & Energy Equipment
- Hydraulic system:Then,Pump body, valve block copper alloy die-casting parts that can withstand high pressure.
- Energy equipment:Wind turbine gearbox housings, nuclear power plant cooling pipe joints.
Aerospace & Medical Aviation
Aircraft seat frames, non-load-bearing door accessories (magnesium alloy weight reduction by 30%).
Medical
Surgical instrument handles, X-ray machine stents (no pores on the surface, easy to sterilize).
Cases in emerging fields
- Super-large die-casting:The rear floor of the Tesla Model Y is integrally molded by a 6000T die-casting machine, reducing 79 welding points.
- Material innovation:Heat-free aluminum alloys (such as AlSi10MnMg) are used in structural parts of new energy vehicles to avoid high-temperature deformation.



