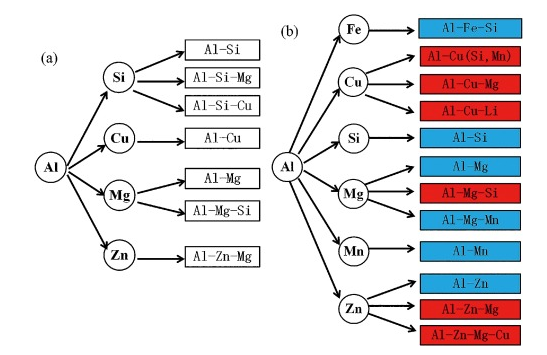
Common Cast Aluminum Alloys:
- Al-Si series
- Al-Cu series
- Al-Mg series
- Al-Zn series
- Al-Fe-RE alloys
Cast aluminum alloys occupies an important position in the industry because of its excellent casting properties, mechanical properties and adaptability.
According to the alloying elements and performance requirements, cast aluminum alloys can be divided into five categories.
The alloy offers high fracture toughness and stress corrosion resistance. High strength after heat treatment is achieved at the expense of lower ductility.
The material is ideal for structural applications and offers suitability in various metalworking processes including forming, machining and cold working.
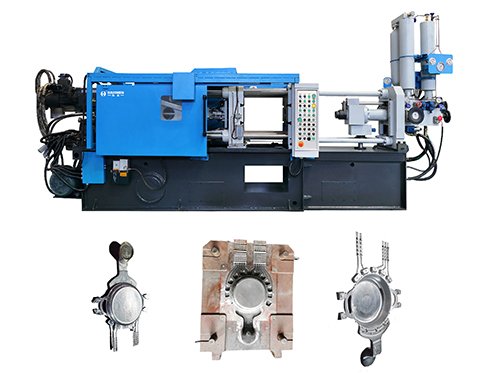
Haichen’s cold chamber die-casting machines have received widespread praise from customers for their performance in manufacturing aluminum castings, such as aluminum screws, aluminum pots, aluminum radiators, and so on.
Aluminum Alloys
Aluminum alloys, the most widely utilized metal structural materials, after iron and steel, have the potential for application and development in the aviation, aerospace, automobile, naval, weapons and power electronics fields due to their low density, high specific strength, easy processing, and good corrosion resistance as well as their excellent electric and thermal conductivity.
Based on their composition, microstructure and process characteristics, aluminum alloys can be categorized into cast aluminum alloys and wrought aluminum alloys.
In general, the alloying element content of cast aluminum alloys is 10%–12%, while that of wrought aluminum alloys is 1%–2% .
According to whether the alloy responds to heat treatment by precipitation hardening, aluminum alloys can be further divided into heat treatable and non-heat treatable aluminum alloys.
Al-Si cast aluminum alloy
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical properties
- Applications
- Advantages and disadvantages
Chemical composition
Silicon (Si) content: 4%~13% (generally near eutectic composition).
Other elements: Copper (Cu) and magnesium (Mg) are often added to enhance mechanical properties.
Such as the EU brand AlSi7Mg containing Si 6.5~7.5% and Mg 0.25~0.45%.
Typical grades: ADC12, A380, A356, ZL102, etc.

Mechanical properties
Tensile strength (UTS): 145~384 MPa (higher value can be reached after heat treatment.
Such as 384 MPa for Al-7.01Si-0.62Mg alloy UTS in T6 state).
Elongation (A): 1.6%~11.3%. Hardness: 194.8~542 MPa.
Applications
Automotive industry: large thin-walled complex parts such as shock absorbing towers, subframes, hydraulic pump housings, etc.
Aerospace: engine blocks, aircraft structural parts.
General industry: instrument housings, pistons, motor housings.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: good fluidity, low hot cracking tendency, strong corrosion resistance, suitable for precision casting.
Disadvantages: The unmodified Al-Si alloy has low tensile strength and needs to be strengthened by heat treatment or adding elements.

Al-Cu cast aluminum alloy
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical properties
- Fields of application
- Advantages and disadvantages
Chemical composition
Copper (Cu) content: 4.5%~5.3% (the best strengthening effect).
Other elements: manganese (Mn),titanium (Ti) are added to improve high temperature strength and casting performance.
Mechanical properties
Tensile strength (UTS): 240~415 MPa (for example, Al-0.42Si-0.58Mg alloy is 240 MPa after T6 treatment).
High temperature performance: It still maintains high strength at 200~300°C.
Fields of application
High-temperature environment: engine parts, aviation high-temperature parts.
High-load structural parts: sand castings such as transmission boxes, suspension system parts.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: high strength, excellent heat treatment strengthening effect.
Disadvantages: poor corrosion resistance, poor casting performance (easy to hot cracking).

Al-Mg cast aluminum alloy
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical properties
- Fields of application
- Advantages and disadvantages
Chemical composition
Magnesium (Mg) content: about 12% (minimum density and highest strength).
Other elements: Iron (Fe) content (<0.2%) is strictly controlled to avoid brittle phases.
Mechanical properties
Tensile strength (UTS): 214~415 MPa (such as ZL301 alloy).
Elongation (A): 5%~14.8%.
Corrosion resistance: Excellent performance in the atmosphere and seawater.
Fields of application
Shipbuilding industry: propellers, marine pump bodies.
Military industry: radar base, aircraft landing gear.
Corrosion-resistant parts: chemical equipment, sea vessel accessories.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: excellent corrosion resistance, good comprehensive mechanical properties at room temperature.
Disadvantages: poor casting performance (easy oxidation in melting), mechanical properties are greatly affected by wall thickness.

Al-Zn cast aluminum alloy
- Chemical composition
- Mechanical properties
- Fields of application
- Advantages and disadvantages
Chemical composition
Zinc (Zn) content: the main element, often added with silicon (Si) and magnesium (Mg) to form a strengthening phase.
Typical formulation: Al-Zn-Mg-Si, such as Al-8.33Si-0.36Mg-0.27Zn alloy.
Mechanical properties
Tensile strength (UTS): 164~214 MPa (lower in sand casting).
Heat treatment effect: The strength can be significantly improved after deterioration heat treatment.
Fields of application
Models & Tools: Pattern Plates, Equipment Brackets.
Medical devices: low-cost structural parts.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages: low price, can be used directly without heat treatment.
Disadvantages: high susceptibility to hot cracking and poor performance at high temperatures.

Special cast aluminium alloy
- Al-Fe-RE alloy
- Rare earth reinforced aluminum alloy
- Heat-free aluminium alloy
Al-Fe-RE alloy
Specifically, the chemical composition includes iron (Fe) and rare earth (RE) elements such as Ce (0.4~0.5%) and La (0.15~0.25%).
Crucially, these elements deliver excellent high-temperature stability, enabling operation up to 400°C.
This performance makes the material ideally suited for complex high-temperature environments.
Consequently, key applications encompass engine valves and aerospace high-temperature components.

Rare earth reinforced aluminum alloy
Typical grade: ZL401 (including Y, Ce, Zr, etc.).
Mechanism of action: Rare earth refines grains, reduces gas inclusions, and improves fluidity and mechanical properties.
Application: New energy vehicle battery shell, large die-casting.
Heat-free aluminium alloy
Features: Avoid heat treatment deformation through component formula optimization.
Such as adding Sr, Sb, and are suitable for integrated die casting.
Applications: Tesla body structure, electric vehicle chassis.

Cast Aluminum Alloys
Fundamentally, aluminum is a lightweight material known for its corrosion resistance and ease of machining.
When strengthened through additional alloying and heat treat conditioning, aluminum becomes a material that provides strength similar to mild, low carbon alloy steel, thereby making it ideal for a range of aluminum casting applications.

Consequently, it is because of these physical and mechanical property improvements that aluminum alloy castings are being more commonly used in various environmental conditions throughout many industries.
Specifically, the fluidity of aluminum alloys not only provides the component designer flexibility to use thin-walled sections when needed but also enables complex part geometries.

To further optimize designs, support webbing can be incorporated to maximize strength and provide rigidity in critical areas.
Additionally, aluminum’s low melting point and rapid heat transfer collectively result in shorter casting cycles and decreased production time.
Common cast aluminum manufacturing products
Stepping into everyday life, we often come across cast aluminum parts:
- Kitchen Utensils
- Automotive Components
- Sporting Goods
- Building Materials
- Medical Equipment
Kitchen Utensils
Cast aluminum is used in kitchen utensils because of its excellent thermal conductivity and durability, ensuring even heat distribution for more uniform and efficient cooking.
Examples include frying pans, skillets, and baking sheets.
If you need any of the above products or are interested in the production of aluminum pots, please feel free to contact Haichen for further information.

Automotive Components
In the automotive industry, cast aluminum parts are widely used in the manufacturing of engine components and wheels due to their strength and lightweight properties, enhancing vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Haichen has developed products including cylinder heads, pistons, intake manifolds, as well as wheels, brackets and housings, etc.

Sporting Goods
Cast aluminum parts are commonly used in manufacturing sporting equipment like bicycle frames, golf club heads, and fishing reel spools.
The lightweight and durable nature of cast aluminum make it an ideal material for sporting equipment.
Building Materials
Cast aluminum is commonly used in making door and window frames, decorative moldings, and fences, due to its corrosion resistance and durability, perfect for outdoor use.
Medical Equipment
Cast aluminum parts are widely used in medical equipment because of their strength and heat resistance. They’re ideal for making pump components, surgical tools, and hospital bed gearboxes.
Each example showcases the versatility and practicality of cast aluminum in everyday life.




