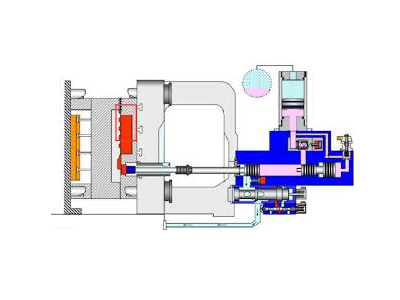
Die casting machine injection unit components mainly include injection cylinder, injection screw, press oil cylinder, gate, piston and so on.
All these components work together to ensure that the metal can fill the mold with high precision and quality during the die casting process, thereby producing castings that meet the requirements. In addition, modern die casting machines may also equippes with intelligent monitoring systems to optimize the injection process and improve production efficiency.
The injection unit of the die casting machine is a vital part of the die casting process. Its main components include:
- Injection Cylinder
- Injection Screw
- Pressure Oil Cylinder
- Gate
- Piston
- Connection Mechanism

Injection Cylinder
- Core Functions of the Injection Cylinder
- Injection Cylinder Rod
- Plunger/Punch
- Shot Sleeve
- Accumulator
- Mounting Frame
The injection cylinder is the core component of the injection unit. And it is responsible for injecting the molten metal into the mold cavity. It usually drives hydraulically or electrically to achieve precise injection action.
Core Functions of the Injection Cylinder
- Plunger/Punch: The injection cylinder is hydraulically driven, pushing the injection rod and plunger forward, injecting molten metal into the mold cavity at high speed.
- Pressure Transmission: In a cold chamber die-casting machine, the injection cylinder converts hydraulic energy into mechanical force, enabling the plunger to apply high pressure to the molten metal, ensuring that the metal fills the mold.
- Multi-Stage Control: The injection process is typically divided into slow filling, high-speed injection, and pressurization stages. The injection cylinder requires an accumulator to precisely regulate pressure.
Injection Cylinder Rod
This precision component connects the injection cylinder and plunger, requiring strict alignment to prevent wear and tear. It has a high-quality surface finish and is sealed with a packing gland to prevent leakage of high-pressure hydraulic oil.
Plunger/Punch
This component directly contacts the molten metal and is responsible for pushing the metal into the shot sleeve or gooseneck, ultimately injecting it into the mold. It must be resistant to high temperatures and wear.
Shot Sleeve
In cold-chamber die-casting machines, it serves as a channel for molten metal, connecting the injection cylinder and the mold. The shot sleeve design must be insulated to prevent premature solidification of the metal.
Accumulator
Supplies instantaneous high-pressure oil to the injection cylinder, ensuring injection speed and pressure requirements during the boost phase.
Mounting Frame
The injection cylinder is typically mounted on a C-frame or A-frame to ensure precise alignment with the shot sleeve and mold, reducing wear.
Injection plunger
- Core Functions
- Structural Design
The injection plunger uses to push the molten metal into the mold cavity. In some designs, the injection plunger works in conjunction with the injection cylinder to fill the mold by advancing the screw.
Core Functions
The injection plunger is responsible for applying high pressure to the molten metal, forcing it into the mold cavity. Its speed and pressure accuracy directly impact casting quality and filling efficiency:
- In a hot chamber die casting machine, the plunger presses down on the molten metal, injecting it into the mold through the gooseneck and nozzle.
- In a cold chamber die casting machine, the plunger pushes the molten metal into the mold from within the shot sleeve.
Structural Design
A plunger is typically made of a high-strength material (such as high-quality steel) that is resistant to high temperatures and wear. It includes the following key components:
- Plunger Tip: This directly contacts the molten metal and may be designed as a disposable structure (such as a “disposable piston head”), ejected along with the casting after casting. Some plunger tips incorporate precision features such as lubrication chambers and scraper rings to reduce friction and metal residue.
- Plunger Rod: This connects the drive unit to the plunger tip.
- Description: Its tapered surface (inner/outer cone) mates tightly with the base to ensure a tight seal.
- Piston Ring: This is mounted on the outside of the plunger tip. Its diameter matches the barrel’s inner diameter and provides both sealing and guidance.
- Connectors, such as bolts and caps, secure the plunger tip to the rod.
Pressure Oil Cylinder
- Core Functions
- Cylinder and Piston
- Hydraulic System
- Sealing and Protection
The pressure oil cylinder uses to increase the pressure during the injection process to ensure that the metal can fully fill the mold.
Core Functions
- Providing injection force: Hydraulic oil acts on the piston in the injection cylinder, pushing the injection plunger to inject molten metal into the mold cavity at high speed and high pressure.
- Enabling multi-stage control: The hydraulic system regulates oil pressure and flow, dividing the injection process into slow and fast shot stages, ensuring smooth filling of the molten metal and preventing air entrapment.
Cylinder and Piston
- The cylinder is secured to the fixed platen via a C-frame, housing a precision-machined piston rod.
- The front end of the piston rod is connected to the plunger rod and plunger tip via a coupling, pushing the molten metal within the cold chamber.
Hydraulic System
- Dual-end oil supply design: Separate head-side and rod-side oil circuits. Head-side oil pressure drives the piston forward (injection), while rod-side oil pressure controls the return stroke.
- Accumulator Support: The accumulator stores high-pressure oil and releases energy instantly during rapid injection, meeting high-speed injection requirements.
- Boosting Mechanism: Some models utilize a “series injection cylinder and boosting cylinder” configuration (as described above), with the boosting cylinder amplifying the oil pressure to increase injection force.
Sealing and Protection
- The piston rod passes through the packing gland, sealing the high-pressure oil.
- Precise alignment is required to prevent wear and leakage.
HAICHEN Injection Unit Technology
Boosting Productivity with Stability
HAICHEN works hard on the design and making of die casting machine injection unit components for high reliability and performance. Here is a real case.
The Customer’s Problem: a maker of large aluminum parts had unstable product quality. Their parts often had surface flaws or internal holes.
HAICHEN’s Component Solution
- The root cause was the old die casting machine injection unit components. Their injection speed and intensifier response were not good enough. HAICHEN upgraded the injection cylinder and control system on their machine.
- Teamwork After the Upgrade: The new injection cylinder gave more steady power. The upgraded control system managed the shift from slow shot to fast shot to intensification more exactly. This made the metal fill pattern smoother and intensification faster.
- The Results Achieved: After the upgrade, the internal quality of the customer’s castings got much better. The good part rate went up by about 15%. Also, the injection unit components ran more smoothly and needed less maintenance.
Gate
- Definition and Location of the Gate
- Components of the Gating System
Definition and Location of the Gate
The gate is the final passage for molten metal into the mold cavity. It is located at the junction of the injection unit and the mold system.
It is a core component of the gating system, connecting the runner and the mold cavity.
Components of the Gating System
The gate is part of the gating system, which includes:
- Sprue (biscuit): Receives molten metal from the injection unit.
- Branch runner: Connects the sprue to the gate.
- Gate: Controls the flow of molten metal into the mold cavity.
- Overflow wells: Contains excess molten metal and vents gases.
- Venting channel: Works with the gating system to vent gases from the mold cavity.
Piston
- The basic function and location
- Materials and Cooling
- Connection Method
The piston usually installes in the injection cylinder and driven by hydraulic or electric means to push the molten metal into the mold.
The basic function and location
The piston is a key component of the die-casting machine’s injection unit. Located within the injection cylinder or shot sleeve.
It generates thrust through hydraulic or mechanical drive, forcing molten metal from the furnace or injection chamber into the mold cavity.
Materials and Cooling
Pistons are often made of heat-resistant alloys, with emphasis on lubrication and cooling channel design to prevent overheating and seizure. For example, lubrication chambers and air nozzles are used to reduce metal adhesion.
Connection Method
The piston is typically fixed to the piston rod, describing a floating piston connection mechanism: the injection piston is connected to the booster piston rod via threads and a lock nut, and a cotter pin is used to prevent loosening, ensuring stability under high loads.

Connection Mechanism
- Basic Function
- Piston/push rod thread locking structure
It is used to fix and connect the various components of the injection unit, such as the injection cylinder, nozzle, etc.
For example, a C-shaped frame is used in some designs to enhance the connection rigidity.
Basic Function
The connection mechanism of the injection unit of the die-casting machine is a key structure to ensure the coordinated work of various components of the injection system. Its design directly affects the injection accuracy and stability.
Piston/push rod thread locking structure
- The ejector rod and hammer are rigidly connected via threads, ensuring synchronized movement.
- The injection piston and booster piston rod utilize a floating piston connection: The booster rod is threaded at the front and secured with a connecting nut and cotter pin to prevent loosening.
Haichen die casting machine
Haichen is one Chinese die casting machine manufacturer for more than 10years. We produce both high pressure cold chamber die casting machine and hot chamber die casting machine.They have durable and highly precise features.
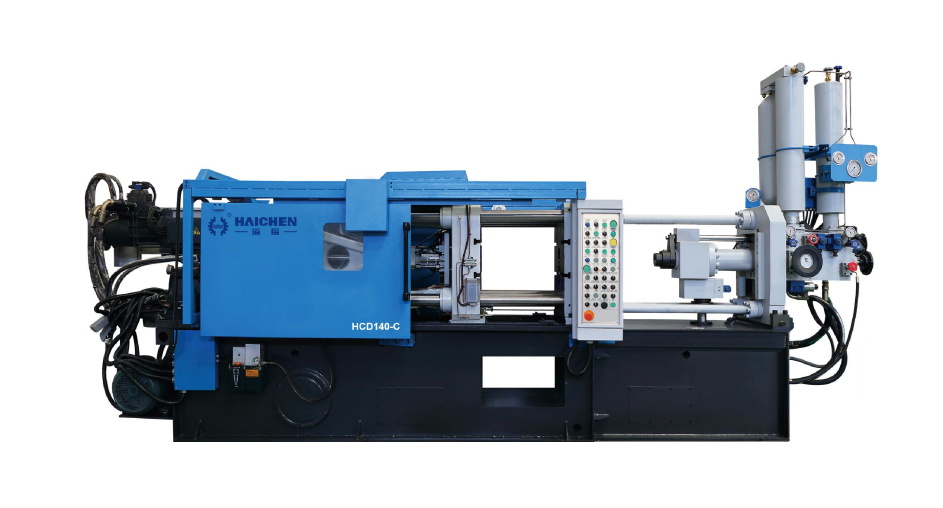


Haichen also produce die casting machine auxiliary equipment. Such as conveyor, vacuum machine, mold temperature controller, industrial robot, sprayer and so on.

We supply cold chamber and hot chamber die casting machine spare parts.
When you have any demand, feel free to contact us.



