The heating bush in die casting is primarily used for localized temperature control in molds. Its material selection and performance design must balance high-temperature stability, thermal conductivity efficiency, and durability.
In die casting, temperature controllers (oil temperature controllers or pressurised water controllers) are employed to heat and cool the mould.
This serves to heat the mould (see mould preheating) and maintain it at operating temperature, the latter encompassing both heating and cooling of the die casting mould (in many instances, this is also termed the heating/cooling unit of the temperature controller).
Analysis of the characteristics of heating bush die casting
- Material Selection
- Performance Characteristics
- Contradictions and Considerations
Material Selection

- AISI H-13 Hot-Work Tool Steel:
- Widely used for die-casting mold components (e.g., sprue bushes). After heat treatment, H-13 steel exhibits excellent thermal fatigue resistance, anti-softening capability, and dimensional stability.
- For components subjected to cyclic heating (e.g., heating bushes), high-temperature quenching (e.g., 1050°C) enhances thermal stability and reduces cracking risks.
- Advanced materials (e.g., those with 50% higher thermal conductivity than H-13) are occasionally explored for temperature control optimization, but H-13 remains the mainstream choice due to cost and process limitations.
- Other Alloy Materials:
- Nickel-chromium-molybdenum alloys: Used in high-volume molds to improve high-temperature hardness.
- Copper or aluminum: High thermal conductivity materials are typically reserved for cooling systems rather than heating components, as heating bushes prioritize heat resistance over rapid heat dissipation.
Performance Characteristics

- Thermal Stability and Fatigue Resistance:
- Heat-treated H-13 steel maintains structural integrity under high temperatures, minimizing deformation or cracking caused by thermal cycling.
- Quenching temperature optimization is critical: high-temperature quenching (e.g., 1050°C) prioritizes strength, while lower temperatures (e.g., 980°C) enhance toughness.
- Heating Methods and Design:
- Oil heating systems: Integrated into mold channels for differential temperature control, enabling precise local heating.
- Synergy with cooling systems: Heating bushes must coordinate with cooling systems (e.g., water cooling or cascade cooling) to ensure uniform temperature distribution, optimizing mold filling speed and casting quality.
- Manufacturing Process Impacts:
- Residual stress in thick-walled bushes: Uneven stress distribution during casting may compromise performance. Simulation tools (e.g., MAGMA software) are used to optimize processes and reduce defects.
- 3D printing technology: Enables complex internal cooling channels, indirectly improving heating system efficiency.
Contradictions and Considerations
- Cooling vs. Heating Balance: While H-13 is often used for cooling components, heating bushes face higher thermal loads. Heat treatment adjustments are essential to tailor material properties for heating applications.
- Material Substitution Limits: High-thermal-conductivity materials (e.g., copper) are ideal but restricted by cost and manufacturing challenges. H-13 remains the cost-effective standard.
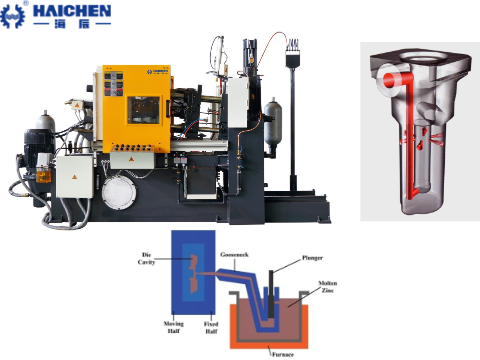
Haichen die casting machine heating bush
Haichen’s die casting machine heating bush is mainly used in its hot chamber die casting machine to maintain the molten state of low melting point metals such as zinc alloy and ensure the stability of the injection process.
The following is a detailed analysis:
- Function and Design of the Heating Bush
- Application Scenarios
- Technical Advantages and Maintenance
- Integration with Other Components
- Market Validation and Case Studies
Function and Design of the Heating Bush

- Furnace Temperature Control: In Haichen’s hot chamber die casting machines, the heating bush works with an integrated furnace to maintain molten metal (e.g., zinc alloy, melting point ~419°C) at precise temperatures via digital control systems. Stable temperature ensures consistent metal flow during injection, preventing defects like cold shuts.
- Material Compatibility: Critical components like nozzles and gooseneck tubes are made of high-temperature-resistant steel (e.g., H13 tool steel), ensuring durability under continuous thermal stress. The heating bush is designed to complement these materials for long-term reliability.
Application Scenarios

- Low-Melting-Point Alloys: Optimized for zinc, lead, and magnesium alloys. For example, zinc alloy parts (e.g., door handles) require rapid injection cycles (1–2 seconds), where the heating bush prevents premature solidification.
- Machine Tonnage Range: Haichen’s hot chamber machines span 15–280 tons of clamping force. Smaller machines (e.g., 50-ton) use compact heating bushes for precision parts, while larger models (e.g., 280-ton) accommodate bulkier components with higher thermal capacity.
Technical Advantages and Maintenance
- Hydraulic and Control Systems: High-speed injection (up to 4m/s) is enabled by servo-driven hydraulics (e.g., Vickers pumps). The heating bush’s stable temperature control ensures smooth metal flow during these high-pressure cycles (10–70 MPa).
- Maintenance Protocols: Key components (nozzles, goosenecks) have a 2-month warranty. Regular checks of lubrication systems and temperature sensors are recommended to maintain heating efficiency and prevent downtime.
Integration with Other Components

- Gooseneck and Nozzle Synergy: The heating bush tightly couples with the gooseneck to maintain a continuous molten metal path. Any temperature drop in this zone risks clogging or uneven filling.
- Automation Compatibility: Machines feature auto-lubrication and spray systems, reducing manual intervention. The heating bush’s reliability is critical for uninterrupted 24/7 production cycles.
Market Validation and Case Studies
- Long-Term Durability: Customer reports confirm Haichen machines operating reliably for 15+ years in zinc alloy production (e.g., automotive hardware), validating the heating bush’s robust design.
- Global Adaptability: Multilingual interfaces (English, Spanish) and localized maintenance guides simplify operation across international markets.
Haichen’s heating bush is engineered for precision and durability in hot chamber die casting. By integrating advanced temperature control, wear-resistant materials, and high-speed hydraulics, it ensures efficient production of low-melting-point alloys. Configurations adapt to machine tonnage (15–280 tons), while user-friendly maintenance supports long-term operational stability. This design philosophy aligns with Haichen’s focus on reliability, efficiency, and global market needs.

All in all
The core material for heating bushes is AISI H-13 steel, optimized via heat treatment (e.g., high-temperature quenching) to enhance thermal resistance. Advanced temperature control systems (e.g., oil heating or 3D-printed channels) enable precise thermal management. Performance requirements include stability under cyclic thermal loads and synergy with overall mold cooling designs to ensure casting quality and production efficiency.

Welcome to contact us at any time to learn more about hot chamber die casting!



