Metallic Lightweight Materials Market continues to grow, driven by both environmental policies and technological innovations.
With the Asia-Pacific region becoming the growth engine, while high-end applications such as aerospace titanium alloys are still dominated by Europe and the United States.
In the future, material performance optimization, cost control and recycling technology will be the key to competition.
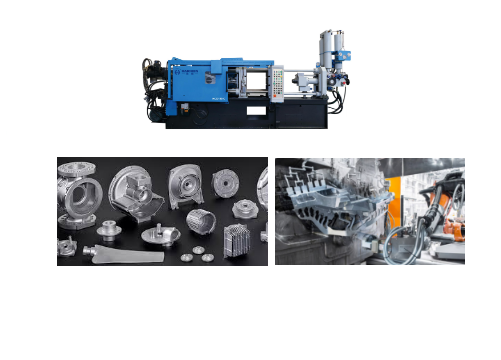
Die casting, which is closely related to lightweight metal materials, is a process in which molten metal is injected into a mold through high pressure to form it, and is often used to produce components made of lightweight metal materials.
For example, lightweight metals such as zinc, magnesium, and aluminum are common materials for die casting processes due to their low density and high specific strength.
For example, magnesium alloys are widely used in the aerospace and automotive industries due to their light weight and good die-casting properties, and Haichen has also designed die-casting parts such as gearboxes for customers.
Metallic Lightweight Materials Market size and growth forecast
The global lightweight materials market size is valued at USD 137.09 billion in 2023, with metal alloys (aluminum, magnesium, titanium, high-strength steel, and others) dominating.
Based on a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.15%, the market size is expected to reach approximately USD 151.5 billion by 2025.
Another forecast shows that the market size could jump to $225.3 billion in 2024, driven by energy efficiency and composite applications.
The differences between different data sources stem from dynamic changes in statistical caliber and growth drivers.
With the growing preference for lightweight materials in various industrial applications, the demand for such materials has also surged.
This also increases the demand for die casting machines to a certain extent, for example, Haichen has received inquiries from overseas manufacturers about die casting machines for more than a year.

Core drivers
- Energy conservation and emission reduction demand
- Technological advancements
- Policy support
- Consumption upgrading
Energy conservation and emission reduction demand
Global carbon emission policies are becoming stricter, and automobiles, aerospace and other fields can reduce energy consumption through lightweight.
Such as aluminum alloy can reduce the weight of car bodies by 15%-60%.
Technological advancements
Additive manufacturing (such as magnesium alloy 3D printing) and nano-modification technologies have improved material properties and production efficiency.
Policy support
Countries are promoting green manufacturing regulations, such as the EU carbon emission standards and China’s “dual carbon” goals.
Consumption upgrading
The demand for cruising range of new energy vehicles promotes the application of aluminum alloy in battery packs and body structures.

Application field distribution
- Automotive industry (40%-50%)
- Aerospace (20%-25%)
- Buildings & Energy (15%-20%)
- Regional Market Structure
Automotive industry (40%-50%)
Aluminum alloy
It accounts for 55% of the aluminum used in automobiles, and is used for wheels, body frames, etc., with significant weight reduction effects.
Magnesium alloys
Although they currently account for only 0.3% of automotive materials, they have a weight reduction potential of 25%-75%, mainly used in bracket parts.
High-strength steel
Still accounts for 62% of automotive materials due to low cost and high safety.

Aerospace (20%-25%)
Aluminum alloy accounts for 60%-80% of civil aircraft, and aluminum alloy for C919 large aircraft accounts for 65%.
The proportion of titanium alloys and composite materials (such as carbon fiber) has increased, and composite materials account for 50% of the Boeing 787.
Buildings & Energy (15%-20%)
The proportion of aluminum used in buildings has been declining from 24% year by year, shifting to photovoltaic brackets and smart grids.
The demand for lightweight materials in the wind energy field is growing the fastest, with a compound growth rate of more than 8%.
Regional Market Structure
Asia-Pacific (45%-50%)
China and India are expected to increase their share further in 2031 driven by demand and driven by investment in new energy vehicles and renewable energy.
North America (25%-30%)
The automotive and aerospace industries are mature, with leading processing technologies for high-strength steel and aluminum.
Europe (20%-25%)
Strict environmental regulations, composite research and development and circular economy models are prominent.

Major Manufacturers and Competitive Landscape
- Leading companies
- Technical cooperation
- Technical cooperation
Leading companies
Alcoa, ArcelorMittal, and Yunhai Metal (the world’s largest magnesium alloy producer) dominate.
With the top three manufacturers having a combined market share of more than 50%.
Technical cooperation
The company integrates the industrial chain through mergers and acquisitions.
Such as Baosteel’s stake in Yunhai Metal and lays out magnesium alloy die-casting and recycling technologies.

Metallic Lightweight Materials Market Technology R&D Trends
- Lightweight titanium alloy
- Additive manufacturing of magnesium alloys
- Green manufacturing
- Composite and intelligent
Lightweight titanium alloy
After the pore structure is optimized, the density is only 1.53g/cm³, and the tensile strength is 613MPa, which is suitable for high-temperature environments.
Additive manufacturing of magnesium alloys
Complex parts are manufactured by SLM (Selective Laser Melting) technology, but the process stability needs to be improved.
Green manufacturing
Fluorine-free anodizing, efficient recycling technology to reduce environmental impact.
Composite and intelligent
Aluminum/carbon fiber hybrid materials and self-healing metal coatings have become research hotspots.

Metallic Lightweight Materials Market Challenges and Risks
- Cost and processing difficulty
- Material competition
- Regional policy fluctuations
Cost and processing difficulty
Magnesium alloy is flammable, and titanium alloy is expensive to process, which limits large-scale application.
Lightweight metal materials such as aluminum, magnesium, zincare the core materials of the die casting process, but their price fluctuations such as aluminum, zinc, and other metals directly affect production costs and profit margins. Cost control has always been a challenge that Haichen continues to overcome.
Material competition
Composites (such as carbon fiber) will replace metals in the aerospace sector, accounting for more than 30% by 2025.
The die casting process requires high-precision molds and advanced equipment, the initial investment cost is high, and the rapid technological updates such as high-pressure die casting, automation technology are also a challenge for Haichen.
Regional policy fluctuations
Trade barriers and unstable raw material supply affect the layout of the industrial chain.