The key methods for quick die change (QDC) systems in die casting involve a combination of methodologies, mechanical innovations, automation, and process optimization.
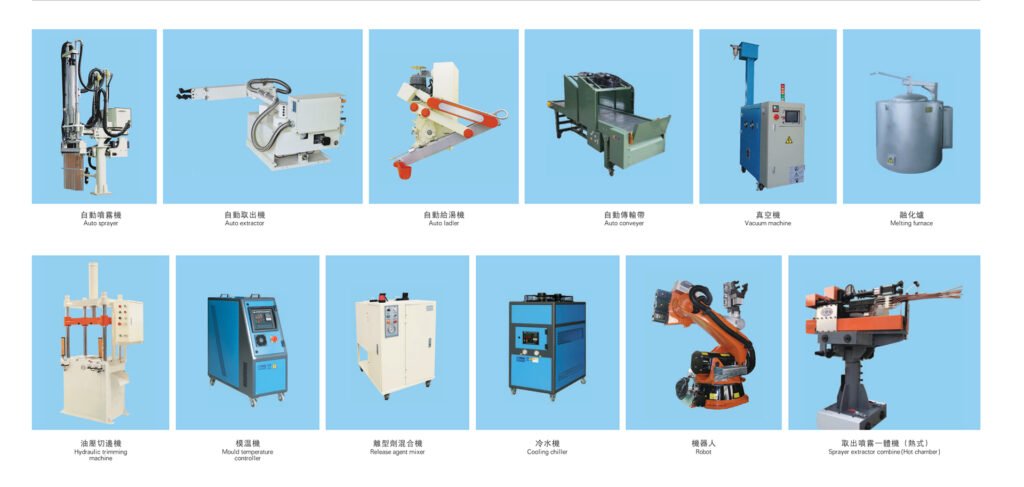
Technical details of die casting rapid mold change system
- SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) Methodology
- Mechanical Innovations
- Automation and Auxiliary Equipment
- Cooling and Parameter Optimization
- Software and Simulation Support
- Specialized Services and Rapid Tooling
SMED (Single-Minute Exchange of Die) Methodology

Mechanical Innovations
- Quick Clamping Fixtures and Hydraulic/Pneumatic Locking:
- Replace traditional bolting with hydraulic/pneumatic systems for instant clamping. For example, “one-touch” hydraulic locking systems eliminate manual tightening.
- Quick-release clamps or toggle mechanisms enable rapid die fixation.
- Guide Pillar Extraction Systems:
- Retractable guide pillars on one side simplify die removal/installation, especially for large dies, avoiding disassembly of cylinders or platens.

Automation and Auxiliary Equipment
- Rolling Bolsters and Die Carts:
- Rolling bolsters with integrated rollers allow seamless die positioning. Programmable die carts automate die transportation and alignment.
- Swing Arms and T-Slot Rollers:
- Swing-out arms assist in die handling, while T-slot roller systems ensure precise die alignment via standardized bolster interfaces.

Cooling and Parameter Optimization
- Integrated Cooling Systems:
- Optimized cooling parameters (e.g., water temperature control at 13°C/18°C, cooling time of 0.8–2 seconds) reduce thermal stabilization delays post-changeover.
- Standardized Injection Parameters:
- Pre-set injection speed (4–5 m/s), melt temperature, and pressure profiles ensure consistency across die changes.
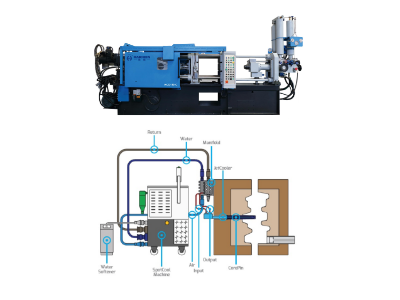
Software and Simulation Support
- Die Design Software:
- Tools like CAST-DESIGNER enable parametric die design, machine selection (cold/hot chamber), and interference/simulation checks to reduce trial runs.
- Real-Time Monitoring:
- Data-driven adjustments based on hydraulic pressure, shot rod position, and cycle time statistics maintain process stability.
Specialized Services and Rapid Tooling
- SMED Solution Providers:
- Companies like EAS Change Systems offer customized QDC solutions to minimize non-productive changeover time.
- Rapid Tooling Technologies:
- Laser sintering (SLS), high-speed machining, and H-13 steel prototyping accelerate die preparation for short-run production.
Application Scenarios
- High-Mix Low-Volume Production: Relies on quick clamps, standardized interfaces, and modular dies.
- Large Dies/High-Melting Alloys: Cold chamber machines combined with hydraulic locking and rolling bolsters.
- Precision Castings: SMED process refinement and parameter standardization (e.g., controlled cooling) ensure dimensional accuracy.
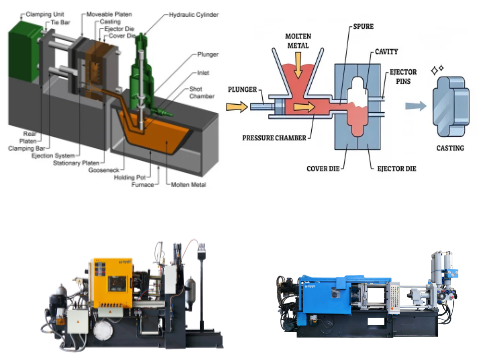
Haichen Quick die change Die Casting Machine
Technical Overview
While direct descriptions of Haichen’s QDC technology are limited in public sources, key features of its die-casting machines suggest advanced capabilities for rapid mold changeovers. Here’s a synthesized analysis:
- Rapid Mold Opening/Closing System
- Automated Auxiliary Configurations
- Parameter Memory and Optimization
- Modular Design Philosophy
Rapid Mold Opening/Closing System
Machines like Haichen Metal’s HDC series (potentially related to Haichen) utilize a closed-loop energy storage system for fast mold movement. This system optimizes hydraulic efficiency and energy recovery, enabling high-speed mold opening and closing. Such performance reduces cycle times and indirectly supports quicker mold changes by minimizing downtime between cycles.At the same time, this process greatly improves the quality of die casting parts.
Automated Auxiliary Configurations
Haichen’s machines integrate automation tools such as:
- Automatic part extraction (e.g., lift-out during mold opening).
- Auto-spraying of release agents (reducing manual intervention).
- Simultaneous core-pulling functions (synchronized with mold movements).
- These features streamline workflows during mold changes, ensuring minimal human involvement and faster transitions between production runs.

Parameter Memory and Optimization
The HDC series (and likely Haichen’s systems) include AI-assisted parameter calculation and quality parameter memory functions.
Benefits for QDC:
- Pre-stored mold-specific parameters (injection pressure, speed, cooling profiles) allow instant recall during mold swaps.
- Reduces trial-and-error adjustments, cutting setup time post-changeover.
Modular Design Philosophy
Though not explicitly stated, Haichen’s emphasis on integrated solutions (from mold design to machine configuration) implies modular components.
Examples may include:
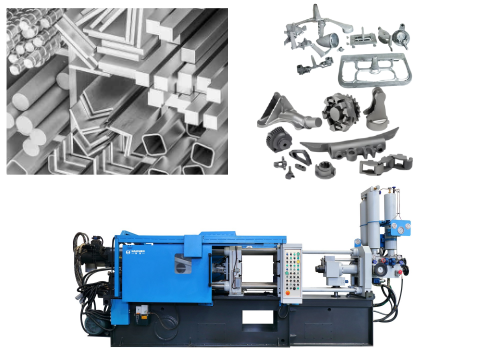
- Standardized mold interfaces.
- Quick-clamping mechanisms (e.g., hydraulic or magnetic locking).
- Integrated thermal management to stabilize molds faster.
Haichen’s die-casting machines may facilitate quick mold changes by high-speed hydraulics, automation, parameter tuning, and modular engineering. Precise QDC metrics (e.g., time per changeover) are not available but these characteristics match those found in other efficient mold switching within the industry

More to tell
Quick die change systems integrate the SMED principle with mechanical automation (hydraulic clamps), process optimization (cooling/parameters), and digital tools for simulation/monitoring to achieve >90% reduction in changeover time. It takes such a multi-disciplinary approach to drive toward the maximization of OEE-Overall Equipment Effectiveness in today’s die casting operations.At the same time, this process greatly improves the quality of die casting parts.
Feel free to contact Haichen for more die casting technical support.



