Zinc Casting Alloys offer many significant advantages such as high strength, stable low melting point and more.
Zinc alloys allow for thinner sections, design flexibility, tighter dimensional tolerances, high impact strength, long die life, and lower pressure and temperature requirements, reducing die maintenance.

This makes it a very popular material choice in modern manufacturing.
Detailed explanation of the characteristics of zinc alloy die casting
Below are the key benefits of zinc casting alloys:

- Zinc casting alloy high strength and toughness
- Good dimensional stability and precision
- Excellent corrosion resistance of zinc casting alloys
- Low melting point and high productivity
- Cost Effectiveness
- Diverse Surface Finishing Capabilities
- Zinc casting alloy lightweight design
- Environmentally friendly and recyclable
Zinc casting alloy high strength and toughness

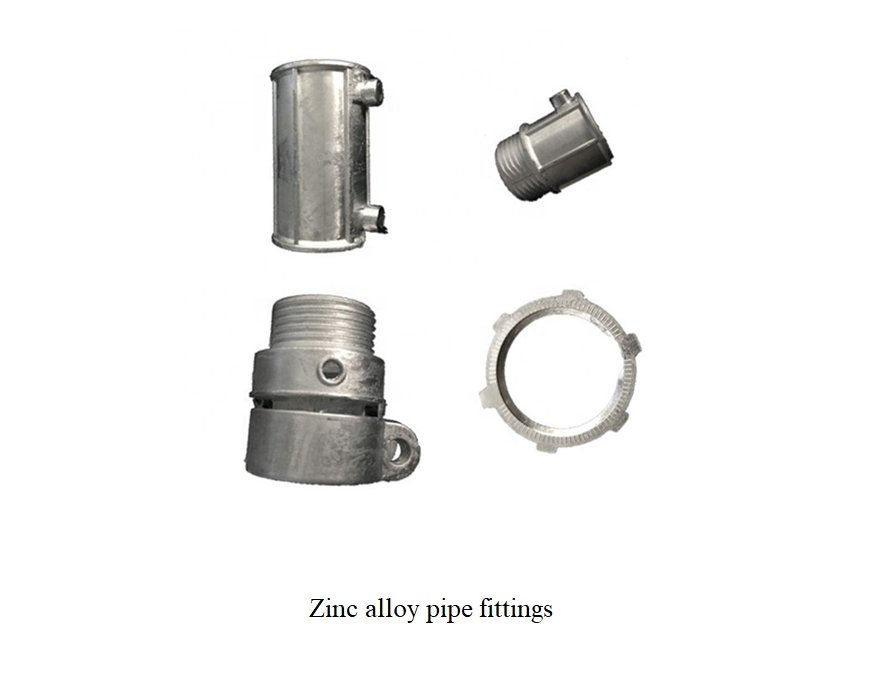
Zinc casting alloys are known for their excellent strength and toughness.This is particularly evident in Haichen’s mature pipe-fittings production system.
This makes them ideal for applications that require them to withstand high loads.
Compared to other casting materials, such as aluminium or magnesium alloys, zinc alloys offer significant advantages in terms of mechanical properties.
Good dimensional stability and precision
Zinc alloys have excellent dimensional accuracy and stability, enabling the production of very complex and detailed parts.
This high level of precision makes zinc alloys particularly suitable for industrial applications requiring precision machining.
Excellent corrosion resistance of zinc casting alloys

Zinc alloys have excellent corrosion resistance.
This extends their service life and reduces maintenance costs.
This property allows zinc alloys to perform well in many environments.
Low melting point and high productivity
The low melting point of zinc alloys makes them easier to handle during the casting process, which reduces energy consumption and production costs.
In addition, due to its good fluidity, zinc alloys can solidify quickly, increasing productivity.
Cost Effectiveness
The raw material cost of zinc alloy is low and due to its good casting properties and long life moulds.
It makes the overall production cost low.
These characteristics make zinc alloy a cost-effective material choice.
Diverse Surface Finishing Capabilities
Zinc alloy castings can be decorated and protected by a variety of surface treatment methods (e.g. electroplating, powder coating, etc.).
Thus meeting different aesthetic and functional needs.
Zinc casting alloy lightweight design
Due to the relatively low density of zinc alloy.
Designers can utilise its excellent ductility and strength to design lighter components.
This reduces product weight and improves energy efficiency.
Environmentally friendly and recyclable
Zinc alloy is a fully recyclable material, which not only reduces waste of resources, but also lowers the impact on the environment.
Zinc casting alloys are known for their excellent mechanical properties, dimensional accuracy, corrosion resistance, low cost and environmental friendly properties.
They are widely using in modern manufacturing industries.

These advantages make zinc alloys the material of choice for many industrial applications.
High strength advantages of Zinc casting alloys
Zinc alloys exhibit significant high-strength advantages in the casting process.
This is mainly due to their unique chemical composition and microstructure.
Zinc alloys are able to significantly improve their mechanical properties, including strength and hardness, through the addition of elements such as aluminium, copper and magnesium.
- Zinc Casting Alloys High strength and tensile strength
- Good toughness and impact resistance
- Excellent fatigue strength and creep resistance
- Microstructure optimisation
- Comprehensive performance advantages
Zinc Casting Alloys High strength and tensile strength
The yield and tensile strengths of zinc alloys are typically higher than those of many other casting alloys.
For example, the yield strength of some zinc alloys (e.g., ZA-27) is approximately 2.5 times that of ordinary aluminium 380 alloy.
The Brinell hardness is also about 50% higher than aluminium.
In addition, the yield strength of zinc alloys can even reach 57,000 psi (about 394 MPa).
And some special grades of zinc alloys can reach a Brinell hardness of 120 HB, which is about 50% higher than aluminium.
Good toughness and impact resistance
Zinc alloys not only have high strength, but also show excellent toughness.
For example, ZA-12 alloy has an elongation of up to 4-7%, showing good plasticity and toughness.
In addition, zinc alloys excel in impact testing, with impact strengths up to 213 ft-lb/in (approximately 292 J/m).

Excellent fatigue strength and creep resistance
Zinc alloys also excel in fatigue strength, especially under high stress cycling conditions.
For example, ZA-27 alloy outperforms many other cast alloys in fatigue testing.
In addition, some zinc alloys have good creep resistance, allowing them to remain stable under long-term loading.
Microstructure optimisation
The microstructure of zinc alloys has a significant impact on their mechanical properties.
By adding elements such as aluminium and copper, a dendritic or eutectic microstructure can be formed.
This improves the mechanical properties of the alloy.
For example, ZA-8 alloy not only improves its strength by adding aluminium and copper, but also maintains good machinability.
Comprehensive performance advantages
Zinc alloys not only excel in strength, but also have a variety of other advantages.
Such as good dimensional stability, excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
This makes it a versatile material for a wide range of industrial applications.
Zinc alloys occupy an important position in the foundry field due to their high strength, good toughness and excellent mechanical properties.

These properties make zinc alloys ideal for the manufacture of complex parts, especially in applications where high strength and durability are required.
Corrosion resistance advantages of Zinc casting alloys
Zinc alloys offer significant advantages in terms of corrosion resistance, such as low degradation rates and environmental adaptability.

This is reflected in six main areas:
- Excellent corrosion resistance
- Low degradation rate
- Comparison with other materials
- Versatility of surface treatments
- Environmental adaptability
- Combination of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance
Excellent corrosion resistance
Zinc alloys have excellent corrosion resistance, especially in atmospheric environments.
Zinc alloys can be further enhanced by surface treatment (e.g. electroplating, spraying, etc.) to enhance their corrosion resistance.
For example, zinc alloys can be passivated with trivalent chromium passivation to significantly improve their corrosion resistance, even more so than conventional hexavalent chromium passivation.
In addition, zinc alloys maintain good corrosion resistance in certain harsh environments, such as salt spray and humid environments.
Low degradation rate
The relatively slow degradation rate of zinc alloys makes them advantageous for long-term corrosion-resistant applications.
For example, in the biomedical field, zinc alloys are considered ideal due to their slow degradation rate and adequate corrosion resistance.
Comparison with other materials
Zinc alloys are comparable to stainless steel in some cases, and at a lower cost.
Zinc alloys perform better than magnesium alloys in high temperature and salt spray environments and do not require special surface treatments.
Versatility of surface treatments
Zinc alloys can be treated with a variety of surface treatments to improve their corrosion resistance, including electroplating, spraying, and anodising.
These treatments not only improve the corrosion resistance of zinc alloys, but also enhance their aesthetic and engineering properties.

Environmental adaptability
Zinc alloys have also shown good corrosion resistance in different environmental conditions, such as chloride and ammonia environments.
For example, zinc-based coatings are self-healing in these environments and effectively resist corrosion.
Combination of mechanical properties and corrosion resistance
Zinc alloys not only have good corrosion resistance, but also high strength, high hardness and excellent mechanical properties.
These properties make zinc alloys very suitable for applications requiring high strength and durability.
Zinc alloys exhibit excellent corrosion resistance, low degradation rates, a wide variety of surface treatments and good mechanical properties in a wide range of industrial applications.
In particular, zinc alloys offer significant advantages in environments where die-cast parts are subjected to long-term corrosion resistance and high strength.
Economic advantages of die-casting zinc alloys
Die casting zinc alloy with low cost, low energy consumption and high utilisation rate in the economy has significant advantages.

Let’s list seven aspects:
- Advantages of zinc die casting in Low-cost materials
- Low melting point and low energy consumption
- Zinc Casting Alloys High production efficiency
- Reduce the assembly process
- Zinc Casting Alloys Low mould costs
- High material utilisation
- Environmental protection and sustainability
Advantages of zinc die casting in Low-cost materials
The raw material price of zinc alloy is relatively low, compared with other metals, zinc alloy is more cost-effective.
This makes zinc alloys more economically advantageous for mass production.
Low melting point and low energy consumption
Zinc alloys have a low melting point, which means low energy consumption during the melting process, thus reducing production costs.
At the same time, zinc alloys have good fluidity, which reduces mould wear and prolongs mould life.
Further reducing the cost of maintenance and replacement of moulds.
Zinc Casting Alloys High production efficiency
Zinc alloy die casting process can achieve rapid cooling and high efficiency production, shorten the production cycle, improve the production efficiency.
This high efficiency not only reduces production time, but also reduces the manufacturing cost per unit of product.
Reduce the assembly process
Zinc alloy die castings can usually be formed in one go without additional assembly processes.
This production advantages of zinc die casting is obvious.
This not only saves on labour costs, but also reduces the number of parts, which in turn reduces overall production costs.

Zinc Casting Alloys Low mould costs
Zinc alloy moulds are relatively inexpensive to manufacture and have a longer mould life, reducing the frequency of mould replacement.
This reduces long-term production costs.
High material utilisation
Zinc alloy die castings are dimensionally accurate and have a high surface finish.
Usually don’t need further machining or only a small amount of processing, thus improving the material utilisation rate.
Environmental protection and sustainability
Zinc alloy die casting process in line with the development trend of green manufacturing, zinc alloy can be recycled and reused, reducing environmental pollution.
In addition, the life cycle assessment of the zinc alloy die casting process shows that it has a low environmental impact and meets the requirements of sustainable development.
Die casting zinc alloy because of its low cost, high efficiency, low energy consumption, long mould life and environmental protection characteristics.
They offer significant advantages in terms of economics and are particularly suitable for mass production and for manufacturing areas that require high precision and low cost.




