Chillers in die-casting mainly have these functions:
- Controlling the mold temperature
- Improve product quality
- Improve production efficiency
- Extend the life of the mold
- Defect reduction
- Improves casting hardness and strength
The chiller is the core of the die-casting temperature control system, ensuring the stability of the mold and the consistency of the product.
When selecting the type, it is necessary to take into account the material properties, mold structure and production capacity requirements.
And establish a preventive maintenance system to ensure the long-term efficient operation of the equipment.

Chillers used in casting
- water chillers
- air-cooled chillers
water chillers
Efficient heat dissipation and temperature stability
Remove the heat of the molten metal absorbed by the mold during the high-pressure injection process (usually above 400℃).
And maintain the working temperature of the mold within a reasonable range.
For example, for aluminum alloy die-casting molds, it needs to be controlled at 180-250℃).
The water temperature is regulated through the PID control system (with an accuracy of ±0.5℃) to avoid defects.
Such as shrinkage cavities and hot cracks in the castings caused by local overheating of the mold.
Improve product quality and consistency
Stabilizing the mold temperature can ensure uniform fluidity and solidification rate of the molten metal.
Reduce defects such as pores and cold shuts, and improve the density and surface finish of the castings.
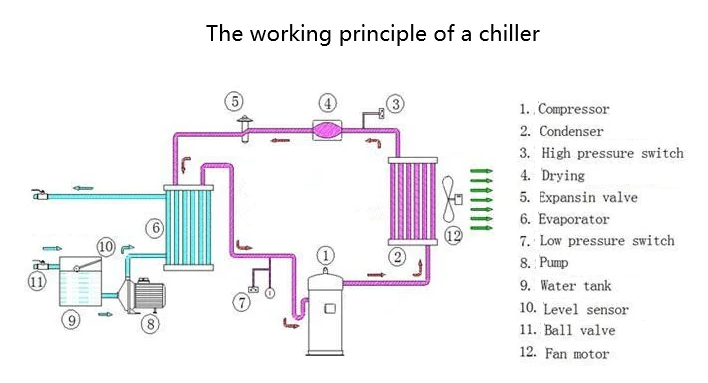
Extend the service life of the equipment
Reducing the thermal stress of the mold, slowing down thermal fatigue cracks and corrosion.
The service life of the mold can be increased by more than 30%.
Energy Conservation and Environmental Protection
Closed-cycle systems reduce water consumption, and high-efficiency compressor designs.
Such as scroll type/screw type lower energy consumption, which is in line with the trend of green manufacturing.

Air-cooled chillers
Supplementary cooling of complex-structured molds
Air-cooled machines are designed for areas such as deep cavities and small cores that cannot be covered by water cooling.
And they provide targeted heat dissipation through compressed air or blowers.
Auxiliary process optimization
The airflow blowing ensures that the mold release agent adheres evenly, avoiding surface defects of the casting caused by local accumulation.
This is to reduce the accumulation of gas in the cavity and lower the porosity of the casting.
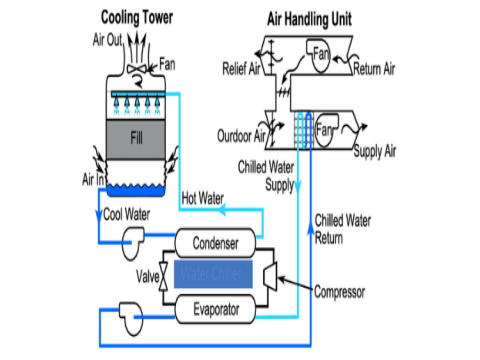
Rapid cooling in the post-processing stage
After the casting is demolded, the air-cooled conveyor can reduce the temperature from 400℃ to 20℃ within 300 seconds, significantly shortening the production cycle.
For example, the simulation data shows that the effect is optimal when the fan deflection Angle is 20° and the distance is 300mm).

Controlling the mold temperature
The chillers ensures thermal balance by adjusting the temperature of the mold.
Thereby improving the quality and production efficiency of die castings.
Improve product quality
A reasonable cooling system can effectively control the solidification process of castings and reduce the occurrence of defects.
Such as porosity and inclusions, and surface defects such as thermal cracks and porosity.
so as to improve the quality and reliability of products.
For example, in aluminum alloy die casting, the use of water cooling technology can significantly improve the compactness of the die casting, reduce the air leakage rate, and reduce the scrap rate.
Improve production efficiency
The optimized cooling system can speed up the cooling rate of castings, shorten the production cycle, and improve production efficiency and productivity.
For example, a mold that is not water-cooled can only produce 50-60 castings per hour.
While a mold that is water-cooled can produce 100-120 pieces per hour, which is a doubling increase in productivity.
Extend the life of the mold
For example, the mold core jet cooler with fine hole cooling developed abroad can effectively improve the core life and die casting quality even at high temperatures.
Chillers affect die casting
- Cooling rate
- Selection of cooling medium
Cooling rate
Cooling rate is one of the key factors affecting the hardness and strength of castings.
Rapid cooling allows for grain refinement, increasing the continuity of grain boundaries and thus increasing the hardness of the material.
However, too fast cooling can also lead to increased internal stresses and even cracks.
Therefore, controlling the proper cooling rate is essential to achieve the desired hardness and strength.
Selection of cooling medium
Different cooling media such as water, oil, brine, etc., have a significant impact on the cooling rate and final quality of molten aluminum castings due to their different thermal conductivity.
Choosing the right cooling medium can effectively prevent the concentration of thermal stress caused by uneven cooling and reduce the risk of cracking in castings.
Haichen‘s Chiller
In actual production, the production efficiency and product quality of die castings can be significantly improved by applying a cooler.
For example, Haichen can offer dozens of different models of coolers for foundries to choose from.
The application of chiller not only improves the performance of die castings.
But also provides an important reference for research and practice in related fields.




